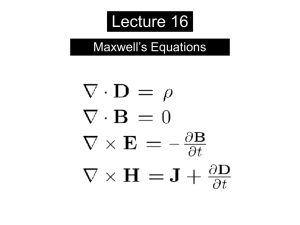chapter 23 electric field
... Electrical conductors are materials in which some of the electrons are free electrons that are not bound to atoms and can move relatively freely through the material; electrical insulators are materials in which all electrons are bound to atoms and cannot move freely through the material .When mater ...
... Electrical conductors are materials in which some of the electrons are free electrons that are not bound to atoms and can move relatively freely through the material; electrical insulators are materials in which all electrons are bound to atoms and cannot move freely through the material .When mater ...
Behavior of a Collection of Magnets
... the computer simulator model to observe what happens when a magnet was moved near other magnets that were free to rotate. The observations with the test tube and simulator might have suggested the following model for the inside of a nail: that it behaves as if it contains a large number of entities, ...
... the computer simulator model to observe what happens when a magnet was moved near other magnets that were free to rotate. The observations with the test tube and simulator might have suggested the following model for the inside of a nail: that it behaves as if it contains a large number of entities, ...
Ch 8 Magnetism and Its Uses: Section 1 Magnetism
... Ch 8 Magnetism and Its Uses: Section 3 Producing Electric Current A. From mechanical to electrical energy 1. Electromagnetic induction—the production of an electric current by moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field or moving a magnet through a wire loop 2. Generator—a device that produces e ...
... Ch 8 Magnetism and Its Uses: Section 3 Producing Electric Current A. From mechanical to electrical energy 1. Electromagnetic induction—the production of an electric current by moving a loop of wire through a magnetic field or moving a magnet through a wire loop 2. Generator—a device that produces e ...
Circular Polarization and Nonreciprocal Propagation in Magnetic Media
... shows that a linearly polarized plane wave propagating in free space consists of two equal but counter-rotating components of circular polarization. In magnetized media, these circular modes can be arranged to produce the nonreciprocal propagation effects that are the basic properties of isolator an ...
... shows that a linearly polarized plane wave propagating in free space consists of two equal but counter-rotating components of circular polarization. In magnetized media, these circular modes can be arranged to produce the nonreciprocal propagation effects that are the basic properties of isolator an ...
Book 1
... 1. Two different lines cannot intersect each other. (Because if they do, there would be two directions for the electric field at the point of intersection.) 2. The lines are not closed. They either come out of positive charges, terminate at negative charges, or extend to infinity. 3. Regions where t ...
... 1. Two different lines cannot intersect each other. (Because if they do, there would be two directions for the electric field at the point of intersection.) 2. The lines are not closed. They either come out of positive charges, terminate at negative charges, or extend to infinity. 3. Regions where t ...
Lecture Notes 16: Magnetic Vector Potential, A; B = Curl A, Magnetostatic Boundary Conditions
... i.e. A′ ( r ) = A ( r ) + A ( r ) = A ( r ) + Ao , which leaves the magnetic field B ( r ) unchanged. In general there are many instances involving more complicated physics situations, where B ( r ) ≠ constant vector field, where indeed B ( r ) = ∇ × A′ ( r ) and ∇i A′ ( r ) = 0 are simultaneously s ...
... i.e. A′ ( r ) = A ( r ) + A ( r ) = A ( r ) + Ao , which leaves the magnetic field B ( r ) unchanged. In general there are many instances involving more complicated physics situations, where B ( r ) ≠ constant vector field, where indeed B ( r ) = ∇ × A′ ( r ) and ∇i A′ ( r ) = 0 are simultaneously s ...
PiezoelectricEnergyHarvesting-app1.pdf
... In general, poled piezoceramics (such as PZT-5A and PZT-5H) are transversely isotropic materials. To be in agreement with the IEEE Standard on Piezoelectricity [1], the plane of isotropy is defined here as the 12-plane (or the xy-plane). The piezoelectric material therefore exhibits symmetry about t ...
... In general, poled piezoceramics (such as PZT-5A and PZT-5H) are transversely isotropic materials. To be in agreement with the IEEE Standard on Piezoelectricity [1], the plane of isotropy is defined here as the 12-plane (or the xy-plane). The piezoelectric material therefore exhibits symmetry about t ...
Evidence for reversible control of magnetization in magnetic field
... is enhanced in materials where ferromagnetism is carriermediated4 , because in such materials the control of carrier polarization provides an alternative means for manipulating the orientation of magnetic domains. In some crystalline conductors, the charge current couples to the spins by means of in ...
... is enhanced in materials where ferromagnetism is carriermediated4 , because in such materials the control of carrier polarization provides an alternative means for manipulating the orientation of magnetic domains. In some crystalline conductors, the charge current couples to the spins by means of in ...
Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential
... Conceptual Example 7 Where is the Potential Zero? Two point charges are fixed in place. The positive charge is +2q and the negative charge is –q. On the line that passes through the charges, how many places are there at which the total potential is zero? ...
... Conceptual Example 7 Where is the Potential Zero? Two point charges are fixed in place. The positive charge is +2q and the negative charge is –q. On the line that passes through the charges, how many places are there at which the total potential is zero? ...
MRAM Technical Guide
... to familiarize the reader with examples of these sources and the resultant magnetic field profiles. The first example is a straight wire carrying 200 Amps, such as a starter cable for an engine with a cross-section of 1.5 centimeters. As is shown in Table 1, the field’s magnitude decays rapidly with ...
... to familiarize the reader with examples of these sources and the resultant magnetic field profiles. The first example is a straight wire carrying 200 Amps, such as a starter cable for an engine with a cross-section of 1.5 centimeters. As is shown in Table 1, the field’s magnitude decays rapidly with ...
11 - HCC Learning Web
... insulator. Because of the electrical attraction between the charged balloon and the neutral wall, the balloon sticks to the wall. Imagine now that we have two infinitely large, flat sheets of insulating material. One is charged, and the other is neutral. If these sheets are brought into contact, doe ...
... insulator. Because of the electrical attraction between the charged balloon and the neutral wall, the balloon sticks to the wall. Imagine now that we have two infinitely large, flat sheets of insulating material. One is charged, and the other is neutral. If these sheets are brought into contact, doe ...