We’ll treat the charge and current in Maxwell’s Equations in Matter
... (4) ∇ × B = μ0J + μ0ε0 ∂E/∂t where ρ(x,t) and J(x,t) satisfy the continuity equation, ∇·J = −∂ρ/∂t (conservation of charge) Now consider the effects of macroscopic matter; i.e., matter with many atoms (6 x 1023 per mole). ...
... (4) ∇ × B = μ0J + μ0ε0 ∂E/∂t where ρ(x,t) and J(x,t) satisfy the continuity equation, ∇·J = −∂ρ/∂t (conservation of charge) Now consider the effects of macroscopic matter; i.e., matter with many atoms (6 x 1023 per mole). ...
physics_100_chapt_16
... B-field lines never end E-fields are produced by changing B fields B-fields are produced by electric currents ...
... B-field lines never end E-fields are produced by changing B fields B-fields are produced by electric currents ...
Phys2102 Spring 2002
... and Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later. ...
... and Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later. ...
Notes
... phenomena known at the time in a compact set of four equations. Though expressed in the language of vector calculus, we will give the essence of the equations below. Maxwell found his equations predicted that electromagnetic waves would propagate through space at the speed of light. This led to the ...
... phenomena known at the time in a compact set of four equations. Though expressed in the language of vector calculus, we will give the essence of the equations below. Maxwell found his equations predicted that electromagnetic waves would propagate through space at the speed of light. This led to the ...
Homework on FTC [pdf]
... (2) Let F be a vector field in the plane. Prove that the circulation density of F at (x, y) is equal to the value of (∇ × F) · k at (x, y). (Use a similar argument to the one we used in class to show that the flux density of F is equal to ∇ · F.) (3) Prove that the flux form of Green’s Theorem impli ...
... (2) Let F be a vector field in the plane. Prove that the circulation density of F at (x, y) is equal to the value of (∇ × F) · k at (x, y). (Use a similar argument to the one we used in class to show that the flux density of F is equal to ∇ · F.) (3) Prove that the flux form of Green’s Theorem impli ...
Course Outline - Madeeha Owais
... The definition of the magnetic field, the magnetic force on free charges and currents, Inductance Steady magnetic field ...
... The definition of the magnetic field, the magnetic force on free charges and currents, Inductance Steady magnetic field ...
Discussion Session 14 1 Conceptual Questions
... 4. Why is Maxwell’s modification of Ampere’s law essential to the existence of electromagnetic waves? 5. The presence of magnetic monopoles would require a modification of Gauss’s law for magnetism. Which other Maxwell equation would need modification? 6. When light travels across a given region, wh ...
... 4. Why is Maxwell’s modification of Ampere’s law essential to the existence of electromagnetic waves? 5. The presence of magnetic monopoles would require a modification of Gauss’s law for magnetism. Which other Maxwell equation would need modification? 6. When light travels across a given region, wh ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. What is motional e.m.f.? 6. Write down any two Maxwell’s equations and give significance. 7. Write second order Wave equations for E and B 8. What is Brewster’s angle? 9. What is an acceleration field? 10. Is charge Lorentz invariant? Justify? PART-B Answer any four questions 4 X 7.5 = 30 11. Der ...
... 5. What is motional e.m.f.? 6. Write down any two Maxwell’s equations and give significance. 7. Write second order Wave equations for E and B 8. What is Brewster’s angle? 9. What is an acceleration field? 10. Is charge Lorentz invariant? Justify? PART-B Answer any four questions 4 X 7.5 = 30 11. Der ...
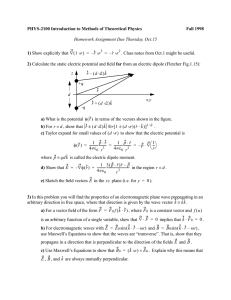
PHYS-2100 Introduction to Methods of Theoretical Physics Fall 1998 1) 2)
... 3) In this problem you will find the properties of an electromagnetic plane wave propagating in an arbitrary direction in free space, where that direction is given by the wave vector k ≡ kk̂ . a) For a vector field of the form F = F 0 f ( k ⋅ r ) , where F 0 is a constant vector and f ( u ) is an ar ...
... 3) In this problem you will find the properties of an electromagnetic plane wave propagating in an arbitrary direction in free space, where that direction is given by the wave vector k ≡ kk̂ . a) For a vector field of the form F = F 0 f ( k ⋅ r ) , where F 0 is a constant vector and f ( u ) is an ar ...





![Homework on FTC [pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008882242_1-853c705082430dffcc7cf83bfec09e1a-300x300.png)