Quantum Theory of Light, PY4T02 Problem Set 2 Paul Eastham
... 2. (a) Consider the single-mode electric field operator Ex = E0 sin(kz)(a + a† ). Calculate the expectation value and variance of the electric field when this mode is in a number state |ni. (b) What is the characteristic scale of the electric field fluctuations for a mode of volume 1µm3 at a wavelen ...
... 2. (a) Consider the single-mode electric field operator Ex = E0 sin(kz)(a + a† ). Calculate the expectation value and variance of the electric field when this mode is in a number state |ni. (b) What is the characteristic scale of the electric field fluctuations for a mode of volume 1µm3 at a wavelen ...
Unit 3_electricity and magnetism_97
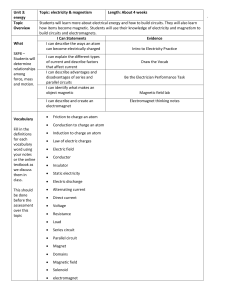
... Students will learn more about electrical energy and how to build circuits. They will also learn how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electr ...
... Students will learn more about electrical energy and how to build circuits. They will also learn how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electr ...
Document
... This set is due by Sunday 27th of Jumada-II, 1435 (27th of April 2014) at 10.00 p.m. ...
... This set is due by Sunday 27th of Jumada-II, 1435 (27th of April 2014) at 10.00 p.m. ...
Math 11 - BigEngine
... When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) ...
... When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 8. Why choke coil is preferred to a resistor in a circuit? 9. Define magnetic susceptibility and magnetic permeability. 10. Define Poynting vector. PART – B Answer any FOUR questions. ...
... 8. Why choke coil is preferred to a resistor in a circuit? 9. Define magnetic susceptibility and magnetic permeability. 10. Define Poynting vector. PART – B Answer any FOUR questions. ...
Lecture 12
... 1) Charges cause electric fields. 2) Currents cause magnetic fields. 3) Changing electric fields cause magnetic fields. 4) Changing magnetic fields cause electric fields. E = Electric field 00 = 1/c2 B = Magnetic field = Charge density J = Current Density = Derivative in space /t = Derivativ ...
... 1) Charges cause electric fields. 2) Currents cause magnetic fields. 3) Changing electric fields cause magnetic fields. 4) Changing magnetic fields cause electric fields. E = Electric field 00 = 1/c2 B = Magnetic field = Charge density J = Current Density = Derivative in space /t = Derivativ ...
The Earth`s magnetic field
... 3) Changing electric fields cause magnetic fields. 4) Changing magnetic fields cause electric fields. E = Electric field 00 = 1/c2 B = Magnetic field = Charge density J = Current Density = Derivative in space /t = Derivative in time (“changing”) ...
... 3) Changing electric fields cause magnetic fields. 4) Changing magnetic fields cause electric fields. E = Electric field 00 = 1/c2 B = Magnetic field = Charge density J = Current Density = Derivative in space /t = Derivative in time (“changing”) ...