MT2
... Gauss’s Law & Electric Potential (1 Mark each, Total = 4 marks) Q1. An advantage of evaluating surface integrals related to Gauss’s law for charge distributions is: A) the electric field is a constant on any surface B) the electric field is of constant magnitude on certain surfaces C) the charge is ...
... Gauss’s Law & Electric Potential (1 Mark each, Total = 4 marks) Q1. An advantage of evaluating surface integrals related to Gauss’s law for charge distributions is: A) the electric field is a constant on any surface B) the electric field is of constant magnitude on certain surfaces C) the charge is ...
Nothing would demonstrate your love of, and dedication to physics
... Be sure you can do the clicker quizzes, especially the circuit we did in class. I'm going to change the numbers and give you the same problem.Also, go over the worksheets (posted) that we did in 168, the problems class. Be sure you can answer questions correctly about how circuits behave if a light ...
... Be sure you can do the clicker quizzes, especially the circuit we did in class. I'm going to change the numbers and give you the same problem.Also, go over the worksheets (posted) that we did in 168, the problems class. Be sure you can answer questions correctly about how circuits behave if a light ...
Light III
... magnetic fields changing in space and time, i.e., they are electromagnetic waves. • A light wave is a 3-dimensional transverse wave. • Light waves do not need a medium to travel, i.e., they can travel in a vacuum. Wave types ...
... magnetic fields changing in space and time, i.e., they are electromagnetic waves. • A light wave is a 3-dimensional transverse wave. • Light waves do not need a medium to travel, i.e., they can travel in a vacuum. Wave types ...
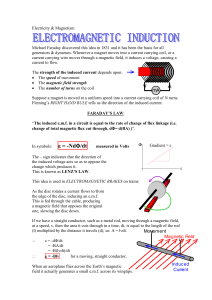
EM_INDUCTION
... “The induced e.m.f. in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage (i.e. change of total magnetic flux cut through, d= d(BA) )”. ...
... “The induced e.m.f. in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage (i.e. change of total magnetic flux cut through, d= d(BA) )”. ...
Tutorial Problem Sheet
... GP 2.5 Two molecules each have a dipole moment p pointing along their line of centres with the same sense. How does the force between the molecules vary with their separation r? What is the potential energy due to the dipole-dipole interaction when r = 3.1 .10-10 m. p water = 6.2 . 10-30 Cm. [ans: 1 ...
... GP 2.5 Two molecules each have a dipole moment p pointing along their line of centres with the same sense. How does the force between the molecules vary with their separation r? What is the potential energy due to the dipole-dipole interaction when r = 3.1 .10-10 m. p water = 6.2 . 10-30 Cm. [ans: 1 ...
Electric Potential - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... A circular loop of wire of radius r is in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. The magnetic field varies with time according to B(t) = a + bt, where a and b are constants. a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop at t = 0. b) Calcul ...
... A circular loop of wire of radius r is in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. The magnetic field varies with time according to B(t) = a + bt, where a and b are constants. a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop at t = 0. b) Calcul ...
PHYS 136: Introduction to Physics for Physical Science and Mathematics Majors II
... magnetism, 3) circuits and circuit elements 4) geometrical optics 5) interference and diffraction Sample Text “Fundamentals of Physics, 6th Ed.”, Halliday, Resnick, and Walker; Wiley. Minimum Material Covered Temperature, heat, and the equation of state Thermodynamics and the zeroth, first, second, ...
... magnetism, 3) circuits and circuit elements 4) geometrical optics 5) interference and diffraction Sample Text “Fundamentals of Physics, 6th Ed.”, Halliday, Resnick, and Walker; Wiley. Minimum Material Covered Temperature, heat, and the equation of state Thermodynamics and the zeroth, first, second, ...
A Drop of the Hard Stuff: How Maxwell Created His
... Now suppose the ‘voltmeter’ side is opened up so that we just see an electric field, E, across a gap. The electric field in the gap is approximately given by: ...
... Now suppose the ‘voltmeter’ side is opened up so that we just see an electric field, E, across a gap. The electric field in the gap is approximately given by: ...
Today: Oscilloscope and Faraday’s Law
... Last week we put a voltage on a coil of wire. The resulting current in the coil made it act like a magnet. In other words a current can produce an magnetic field – evidence that electricity and magnetism are connected. Q. Can a magnetic field produce a current? A. Yes… but it is not as easy. A const ...
... Last week we put a voltage on a coil of wire. The resulting current in the coil made it act like a magnet. In other words a current can produce an magnetic field – evidence that electricity and magnetism are connected. Q. Can a magnetic field produce a current? A. Yes… but it is not as easy. A const ...
Aim: What is an Electric Field? Do Now: What does the word field
... A region in space in which an electrostatic force acts on a charge Exists around every charged object Mapped by drawing field lines (indicate the direction of the electrostatic force an a + test charge placed in a field.) It is a vector quantity ...
... A region in space in which an electrostatic force acts on a charge Exists around every charged object Mapped by drawing field lines (indicate the direction of the electrostatic force an a + test charge placed in a field.) It is a vector quantity ...