Lecture-15
... magnetic field lines are perpendicular to the magnetic force on a moving charge. 2. Electric field lines begin on positive charges and end on negative charges; magnetic field lines neither begin nor end. ...
... magnetic field lines are perpendicular to the magnetic force on a moving charge. 2. Electric field lines begin on positive charges and end on negative charges; magnetic field lines neither begin nor end. ...
955
... 1. Figure OQ31.1 is a graph of the magnetic flux through a certain coil of wire as a function of time during an interval while the radius of the coil is increased, the coil is rotated through 1.5 revolutions, and the external source of the magnetic field is turned off, in that order. Rank the emf in ...
... 1. Figure OQ31.1 is a graph of the magnetic flux through a certain coil of wire as a function of time during an interval while the radius of the coil is increased, the coil is rotated through 1.5 revolutions, and the external source of the magnetic field is turned off, in that order. Rank the emf in ...
EM Guided Notes KEY
... When you approach the door knob, the electrons make the leap from you to the door knob and a miniature lightning bolt forms. Just like water flowing downhill, free electrons move from a position of high potential energy to a position of low potential energy. When the charges are accelerated (speedin ...
... When you approach the door knob, the electrons make the leap from you to the door knob and a miniature lightning bolt forms. Just like water flowing downhill, free electrons move from a position of high potential energy to a position of low potential energy. When the charges are accelerated (speedin ...
Course Review
... A given charge configuration above an infinite grounded perfectly conducting plane may be replaced by the charge configuration itself, its image, and an equipotential surface in place of the conducting plane. The method can be used to determine the fields only in the region where the image charges a ...
... A given charge configuration above an infinite grounded perfectly conducting plane may be replaced by the charge configuration itself, its image, and an equipotential surface in place of the conducting plane. The method can be used to determine the fields only in the region where the image charges a ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD THEORY
... Using Biot-Savart, find the magnetic field at a distance z along the z-axis for the current loop of radius R with current I shown below. ...
... Using Biot-Savart, find the magnetic field at a distance z along the z-axis for the current loop of radius R with current I shown below. ...
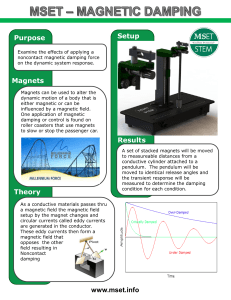
Purpose Magnets Theory Results www.mset.info Setup
... One application of magnetic damping or control is found on roller coasters that use magnets to slow or stop the passenger car. ...
... One application of magnetic damping or control is found on roller coasters that use magnets to slow or stop the passenger car. ...
Picturing Electric Forces
... Group Question – Predict the net electric force a test charge will experience when placed next to a charge dipole. Draw three vectors for each point – one for each charge and one for the net force. In the next diagram sketch your prediction for the electric field around the dipole. ...
... Group Question – Predict the net electric force a test charge will experience when placed next to a charge dipole. Draw three vectors for each point – one for each charge and one for the net force. In the next diagram sketch your prediction for the electric field around the dipole. ...
Review
... The key to equations is ________________________. Some literal equations (formulas) have several variables. In order to solve for a certain variable, you must consider the ______________________of the variable you are solving for and “________________” what is around it. When the entire equation is ...
... The key to equations is ________________________. Some literal equations (formulas) have several variables. In order to solve for a certain variable, you must consider the ______________________of the variable you are solving for and “________________” what is around it. When the entire equation is ...
4.3.1
... • The needle of a compass is a small MAGNET • The north pole of a compass needle – … is marked with a small “N” or a prominent color – … points toward magnetic SOUTH poles. ...
... • The needle of a compass is a small MAGNET • The north pole of a compass needle – … is marked with a small “N” or a prominent color – … points toward magnetic SOUTH poles. ...
Physics 231 Course Review, Part 1
... electric field at that point The “density” of electric field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field at that point The direction of the electric field line give the direction of the force on a charge particle at that point. It does not necessarily represent the direction of moti ...
... electric field at that point The “density” of electric field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field at that point The direction of the electric field line give the direction of the force on a charge particle at that point. It does not necessarily represent the direction of moti ...
3-1 Study Guide and Intervention Solving Systems of Equations
... same variables. You can solve a system of linear equations by using a table or by graphing the equations on the same coordinate plane. If the lines intersect, the solution is that intersection point. The following chart summarizes the possibilities for graphs of two linear equations in two variables ...
... same variables. You can solve a system of linear equations by using a table or by graphing the equations on the same coordinate plane. If the lines intersect, the solution is that intersection point. The following chart summarizes the possibilities for graphs of two linear equations in two variables ...
5 Math Review
... Because two equations impose two conditions on the variables at the same time, they are called a system of simultaneous equations. • When you are solving a system of equations, you are looking for the values that are solutions for all of the system’s equations. • Methods of Solving: ...
... Because two equations impose two conditions on the variables at the same time, they are called a system of simultaneous equations. • When you are solving a system of equations, you are looking for the values that are solutions for all of the system’s equations. • Methods of Solving: ...