Chapter 29: Magnetic Fields By Tori Cook This chapter examines
... 3. [Hard] A metal rod having a mass per unit length λ carries a current I. The rod hangs from two vertical wires in a uniform vertical magnetic field. The wires make an angle θ with the vertical when in equilibrium. Determine the magnitude of the electric field. ...
... 3. [Hard] A metal rod having a mass per unit length λ carries a current I. The rod hangs from two vertical wires in a uniform vertical magnetic field. The wires make an angle θ with the vertical when in equilibrium. Determine the magnitude of the electric field. ...
Solutions to Period 16 Exercises
... d) An electromagnet is used to spin an electromagnet. e) An electric motor can be made from all of the above designs. Since you need at least one changing magnetic field, two permanent magnets do not work. E.2 = c 16-Ex 1&2 ...
... d) An electromagnet is used to spin an electromagnet. e) An electric motor can be made from all of the above designs. Since you need at least one changing magnetic field, two permanent magnets do not work. E.2 = c 16-Ex 1&2 ...
Electric Fields - the SASPhysics.com
... • An electric field is a region where a charged body experiences an electrostatic force • Like gravitational fields, we can represent electric fields by field lines – Lines show the direction of the force experienced by a positive test charge – Lines never cross – The more lines, the stronger the fi ...
... • An electric field is a region where a charged body experiences an electrostatic force • Like gravitational fields, we can represent electric fields by field lines – Lines show the direction of the force experienced by a positive test charge – Lines never cross – The more lines, the stronger the fi ...
Unit 6 Magnetism
... • Some motors use a commutator to do this, others use household alternating current ...
... • Some motors use a commutator to do this, others use household alternating current ...
Final - Kuniv.edu.kw
... A positive charge is distributed uniformly within a non-conducting spherical object. If the magnitude of the electric field and the electric potential (with respect to infinity) at the center of the object are denoted by E and V, respectively, then a) E ≠ 0 and V = 0 b) E ≠ 0 and V > 0 c) E = 0 and ...
... A positive charge is distributed uniformly within a non-conducting spherical object. If the magnitude of the electric field and the electric potential (with respect to infinity) at the center of the object are denoted by E and V, respectively, then a) E ≠ 0 and V = 0 b) E ≠ 0 and V > 0 c) E = 0 and ...
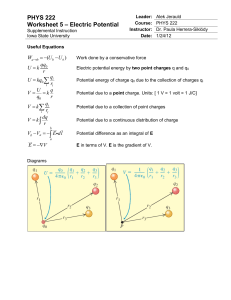
PHYS 222 Worksheet 5 Electric Potential
... E field points towards the direction of lower potential, thus potential at point a is lower that at point b. (b) Calculate the value of E xb ...
... E field points towards the direction of lower potential, thus potential at point a is lower that at point b. (b) Calculate the value of E xb ...
Weekly Lesson Plan - Edward M. Kennedy Academy for Health
... Students will receive “skeleton notes” to help assist them with the note taking process. Students will receive written, multi-step directions for classroom/homework assignments. Students will receive a graphic organizer with probing questions to help them with the textbook reading and homework. Stud ...
... Students will receive “skeleton notes” to help assist them with the note taking process. Students will receive written, multi-step directions for classroom/homework assignments. Students will receive a graphic organizer with probing questions to help them with the textbook reading and homework. Stud ...
Chapter 22
... Space around charge filled with lines of force or electric field lines Direction of E-field lines or direction of the tangent to a curved field line gives the direction of E at that point. Number of E-field lines per unit area , measured in a planeto the lines, is proportional to the magnitud ...
... Space around charge filled with lines of force or electric field lines Direction of E-field lines or direction of the tangent to a curved field line gives the direction of E at that point. Number of E-field lines per unit area , measured in a planeto the lines, is proportional to the magnitud ...
Physics
... – In order to show this we always draw the field lines as Arrows pointed in the direction a positive charge would move in the field ______________________________________________________. – Again there is an important difference between gravitational fields and electric fields due to the fact that… ...
... – In order to show this we always draw the field lines as Arrows pointed in the direction a positive charge would move in the field ______________________________________________________. – Again there is an important difference between gravitational fields and electric fields due to the fact that… ...
cp19
... 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y plane: (a) (5,0,0) (b) (1,0,0) (c) (3,1,0) ...
... 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y plane: (a) (5,0,0) (b) (1,0,0) (c) (3,1,0) ...