magnetic field - Rosehill
... end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter h ...
... end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter h ...
Lorenz or Coulomb
... As a conclusion, we have shown that the Lorenz equation applies in both Lorentzcovariant relativity as well as Galilean covariant electric limit of Lévy-Leblond and Le Bellac whereas the Coulomb gauge equation applies only within the Galilean covariant magnetic limit. We have explicitly broken gauge ...
... As a conclusion, we have shown that the Lorenz equation applies in both Lorentzcovariant relativity as well as Galilean covariant electric limit of Lévy-Leblond and Le Bellac whereas the Coulomb gauge equation applies only within the Galilean covariant magnetic limit. We have explicitly broken gauge ...
Magnetism
... magnetic field? – Iron Triad - Iron, Cobalt, and Nickel – What is a magnetic field? • The region around the magnet where magnetic force act – This sounds very similar to an electric field!!!!!! ...
... magnetic field? – Iron Triad - Iron, Cobalt, and Nickel – What is a magnetic field? • The region around the magnet where magnetic force act – This sounds very similar to an electric field!!!!!! ...
Document
... variation of the electric field versus r. P2-3 A coaxial line has an inner conductor of a radius “a” and outer conductor of a radius “b”. The inner conductor is charged by +ρℓ while the outer is charged by -ρℓ. Find electric field as function of ρ, and then find the potential difference between oute ...
... variation of the electric field versus r. P2-3 A coaxial line has an inner conductor of a radius “a” and outer conductor of a radius “b”. The inner conductor is charged by +ρℓ while the outer is charged by -ρℓ. Find electric field as function of ρ, and then find the potential difference between oute ...
4 Minute Drill - MrStapleton.com
... Explain the effect of an electric field on free charges in a conductor. Explain why no electric field may exist inside a conductor. Show how a uniform electric field may be created. Explain what happens to an electric field applied to an irregular conductor (with pointier and smoother parts). • Desc ...
... Explain the effect of an electric field on free charges in a conductor. Explain why no electric field may exist inside a conductor. Show how a uniform electric field may be created. Explain what happens to an electric field applied to an irregular conductor (with pointier and smoother parts). • Desc ...
NASC 1110
... If an electric current produces a magnetic field, then a magnet should be able to generate an electric current. A current is produced in a wire when there is relative motion between the wire and a magnetic field. Such a current is called an induced current (emf). The effect is called electromagnetic ...
... If an electric current produces a magnetic field, then a magnet should be able to generate an electric current. A current is produced in a wire when there is relative motion between the wire and a magnetic field. Such a current is called an induced current (emf). The effect is called electromagnetic ...
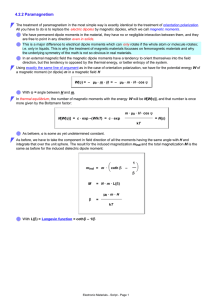
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
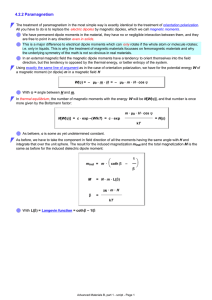
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...
... We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or negligible interaction between them, and they are free to point in any direction even in solids. This is a major difference to electrical dipole moments which can only rotate if the whole atom or molecule rotates; i.e. only in liquids ...