ECE 571 ()
... 5. Specific Course Information a. Course Description Analysis of time-varying electromagnetic fields. Maxwell’s equations, waves in ideal and lossy matter. Impedance concept, duality, equivalence principle, energy flow, reciprocity theorem. Transmission lines, wave-guides, resonators, surface waves, ...
... 5. Specific Course Information a. Course Description Analysis of time-varying electromagnetic fields. Maxwell’s equations, waves in ideal and lossy matter. Impedance concept, duality, equivalence principle, energy flow, reciprocity theorem. Transmission lines, wave-guides, resonators, surface waves, ...
cond-mat/0601319 PDF
... is the vector function included in the domain of definition of operator L̂ . In this derivation, no DME are used. Another derivation is based on use of DME: the power flow density of MS waves formally corresponds to the Poynting vector obtained for the curl electric field and the potential (quasimag ...
... is the vector function included in the domain of definition of operator L̂ . In this derivation, no DME are used. Another derivation is based on use of DME: the power flow density of MS waves formally corresponds to the Poynting vector obtained for the curl electric field and the potential (quasimag ...
Magnetism Concepts
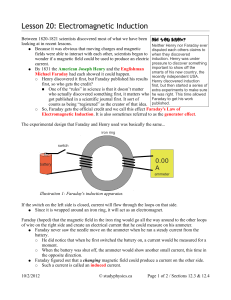
... ____The electromotive force is a force that makes charges flow from a point of higher potential to lower potential. ____Hans Christian Oersted discovered that a changing magnetic field produces an electric current. ____A current is generated when a wire is moved parallel to a magnetic field. ____Len ...
... ____The electromotive force is a force that makes charges flow from a point of higher potential to lower potential. ____Hans Christian Oersted discovered that a changing magnetic field produces an electric current. ____A current is generated when a wire is moved parallel to a magnetic field. ____Len ...
E=- V/ x= -400 volts/8 cm =-400 V/0.08 m=
... charges(lies on the intersection of the bisectors of all three 60o angles), ‘c’ is just as far below the line connecting the bottom two charges as ‘b’ is above this line, and at the same x-coordinate. Calculate the electric field at each of the three points (magnitude and both the x- and y-component ...
... charges(lies on the intersection of the bisectors of all three 60o angles), ‘c’ is just as far below the line connecting the bottom two charges as ‘b’ is above this line, and at the same x-coordinate. Calculate the electric field at each of the three points (magnitude and both the x- and y-component ...
ELECTRIC PHENOMENA
... “field of force”: exists in a region of space when an appropriate object (called the “test object” or “probe”) placed at any point in the region experiences a force. force depends on a property of the test object (e.g. charge,..), the “test charge”; “field strength” = (force experienced by test obje ...
... “field of force”: exists in a region of space when an appropriate object (called the “test object” or “probe”) placed at any point in the region experiences a force. force depends on a property of the test object (e.g. charge,..), the “test charge”; “field strength” = (force experienced by test obje ...
Electric Fields and Electric Potential
... The direction is the direction of the force vector on a positive charge. The arrows therefore always point away from positive charges and toward negative charges. ...
... The direction is the direction of the force vector on a positive charge. The arrows therefore always point away from positive charges and toward negative charges. ...
electrostatics1
... •Number of lines leaving/entering charge amount of charge •Tangent of line = direction of E •Local density of field lines local magnitude of E • Field at two white dots differs by a factor of 4 since r differs by a factor of 2 •Local density of field lines also differs by a factor of 4 (in 3D) ...
... •Number of lines leaving/entering charge amount of charge •Tangent of line = direction of E •Local density of field lines local magnitude of E • Field at two white dots differs by a factor of 4 since r differs by a factor of 2 •Local density of field lines also differs by a factor of 4 (in 3D) ...
Part 3
... The size and direction of the magnetic force can be expressed with one vector equation using the cross product. ...
... The size and direction of the magnetic force can be expressed with one vector equation using the cross product. ...
CC GPS Coordinate Algebra
... There are situations when the units in an answer tell us if the answer is wrong. For example, if the question called for weight and the answer is given in cubic feet, we know the answer cannot be correct. ...
... There are situations when the units in an answer tell us if the answer is wrong. For example, if the question called for weight and the answer is given in cubic feet, we know the answer cannot be correct. ...