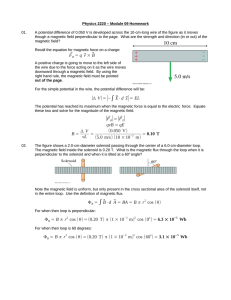
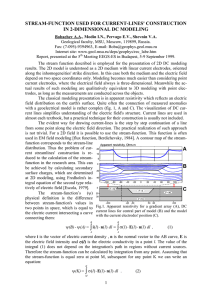
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... magnitude dE cosθ. We can replace cosθ by using the right triangle in the Figure (right) to write ...
... magnitude dE cosθ. We can replace cosθ by using the right triangle in the Figure (right) to write ...
Experiment 14: Electric Fields and Potentials
... state of potential energy, or towards a lower equipotential. Thus, electric field lines are always perpendicular to equipotential lines. Electric field can also be measured by how quickly voltage is changing at that point, in volts/meter. A stronger electric field indicates electric potential is var ...
... state of potential energy, or towards a lower equipotential. Thus, electric field lines are always perpendicular to equipotential lines. Electric field can also be measured by how quickly voltage is changing at that point, in volts/meter. A stronger electric field indicates electric potential is var ...
Static Electricity and Electric Fields
... This makes one side of the paper negative and one side positive. A charge has been induced on the paper and the negative side of the paper is attracted to the positive rod. ...
... This makes one side of the paper negative and one side positive. A charge has been induced on the paper and the negative side of the paper is attracted to the positive rod. ...
PPT
... • A long solenoid has a circular cross-section of radius R. • The current through the solenoid is increasing at a steady rate di/dt. • Compute the variation of the electric field as a function of the distance r from the axis of the ...
... • A long solenoid has a circular cross-section of radius R. • The current through the solenoid is increasing at a steady rate di/dt. • Compute the variation of the electric field as a function of the distance r from the axis of the ...
Magnetism Review and tid-bits
... a magnetic field Permanent magnets are formed of metallic alloys or metals such as iron, nickel, or cobalt. Every spinning electron is a tiny magnet. Electrons spin about their axis like a top spins around its axis. Thus, the electron is a moving charge. Moving charges create a magnetic field. A pai ...
... a magnetic field Permanent magnets are formed of metallic alloys or metals such as iron, nickel, or cobalt. Every spinning electron is a tiny magnet. Electrons spin about their axis like a top spins around its axis. Thus, the electron is a moving charge. Moving charges create a magnetic field. A pai ...
Theory of electromagnetic fields
... electric current density (J~ ·~n is the charge crossing unit area perpendicular to unit vector ~n per unit time). ~ and are generally referred to as the “homogeneous” Equations (2) and (4) are independent of ρ and J, ~ and are generally referred to equations; the other two equations, (1) and (3) are ...
... electric current density (J~ ·~n is the charge crossing unit area perpendicular to unit vector ~n per unit time). ~ and are generally referred to as the “homogeneous” Equations (2) and (4) are independent of ρ and J, ~ and are generally referred to equations; the other two equations, (1) and (3) are ...