Chapter 20: Magnetic field and forces What will we learn in this
... FYI: the definition of the ampere The forces that two straight parallel conductors exert on each other form the basis for the official SI definition of the ampere: Definition of 1 ampere: One ampere is that unvarying current which, if present in each of two parallel conductors of infinite length and ...
... FYI: the definition of the ampere The forces that two straight parallel conductors exert on each other form the basis for the official SI definition of the ampere: Definition of 1 ampere: One ampere is that unvarying current which, if present in each of two parallel conductors of infinite length and ...
Document
... • So, assuming the sinusoidal variation and neglecting the ejwt term in all the expressions, ...
... • So, assuming the sinusoidal variation and neglecting the ejwt term in all the expressions, ...
Electromagnetism - HSphysics
... clever device for reversing the current direction through an armature every half turn. The commutator is made from two round pieces of copper (held apart and do not touch each other), one on each side of the spindle. A piece of carbon (graphite) is lightly pushed against the copper to conduct the el ...
... clever device for reversing the current direction through an armature every half turn. The commutator is made from two round pieces of copper (held apart and do not touch each other), one on each side of the spindle. A piece of carbon (graphite) is lightly pushed against the copper to conduct the el ...
KEY - Rose
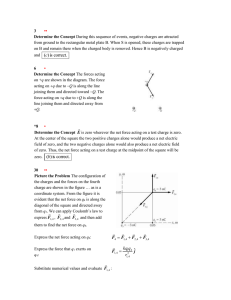
... EVALUATE: The excess charge on the conductor is still 5.00 C, as it originally was. The introduction of the 0.500 C inside the cavity merely induced equal but opposite charges (for a net of zero) on the surfaces of the conductor. 22.30. IDENTIFY: The net electric field is the vector sum of the f ...
... EVALUATE: The excess charge on the conductor is still 5.00 C, as it originally was. The introduction of the 0.500 C inside the cavity merely induced equal but opposite charges (for a net of zero) on the surfaces of the conductor. 22.30. IDENTIFY: The net electric field is the vector sum of the f ...
dielectric_micro
... Net electric dipole moment = (induced dipoles + permanent dipoles + ionic dipoles) electronic orientation “ionic bond” ...
... Net electric dipole moment = (induced dipoles + permanent dipoles + ionic dipoles) electronic orientation “ionic bond” ...
Part 1
... at a point in an electric field Path integral (line integral)—An integral performed over a path such as the path a charge q follows as it moves from one point to another Volt—The unit of electric potential. 1V = 1 J/C Electron volt (eV)—the energy that an electron (or proton) gains or loses by movin ...
... at a point in an electric field Path integral (line integral)—An integral performed over a path such as the path a charge q follows as it moves from one point to another Volt—The unit of electric potential. 1V = 1 J/C Electron volt (eV)—the energy that an electron (or proton) gains or loses by movin ...