MODULE CODE: AHAN7024 TITLE: Heavenly Discourses DATED
... To become familiar with the cultural context of modern developments in modern astronomy. LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of this module successful students should be able to: demonstrate a systematic understanding of the origins of zodiacs and constellations and the mapping of the sky in a variety ...
... To become familiar with the cultural context of modern developments in modern astronomy. LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of this module successful students should be able to: demonstrate a systematic understanding of the origins of zodiacs and constellations and the mapping of the sky in a variety ...
Star Formation
... This H-R diagram shows the evolution of stars somewhat more and somewhat less massive than the Sun The shape of the paths is similar, but they wind up in different places on the Main Sequence ...
... This H-R diagram shows the evolution of stars somewhat more and somewhat less massive than the Sun The shape of the paths is similar, but they wind up in different places on the Main Sequence ...
Document
... systems are born – with wavelengths of a millimeter or less. “Astronomers can use it to study the chemical and physical conditions of these clouds. Often such regions are dark and obscured in visible light, but they shine brightly in the millimeter and submillimeter part of the spectrum.” ALMA began ...
... systems are born – with wavelengths of a millimeter or less. “Astronomers can use it to study the chemical and physical conditions of these clouds. Often such regions are dark and obscured in visible light, but they shine brightly in the millimeter and submillimeter part of the spectrum.” ALMA began ...
No Slide Title
... The participants in NUVA have realized with great concern that no firm plans exist to maintain an Ultraviolet observing capability for astrophysics for the future. This is despite the fact that the range of important astrophysical issues in astrophysics which require observations in the Ultraviolet ...
... The participants in NUVA have realized with great concern that no firm plans exist to maintain an Ultraviolet observing capability for astrophysics for the future. This is despite the fact that the range of important astrophysical issues in astrophysics which require observations in the Ultraviolet ...
5a: So, what was wrong with Ptolemy`s model to a contemporary
... for Newton’s amazing synthesis, which produced Newton’s 3 laws of motion and of universal gravitation: a. He developed the concept of inertia: 1) Aristotle had asserted that all bodies tended toward their most natural state – a state of rest. 2) Galileo said that a body in uniform motion (i.e. at a ...
... for Newton’s amazing synthesis, which produced Newton’s 3 laws of motion and of universal gravitation: a. He developed the concept of inertia: 1) Aristotle had asserted that all bodies tended toward their most natural state – a state of rest. 2) Galileo said that a body in uniform motion (i.e. at a ...
Brahe, Kepler
... orbits would run along spheres (rather than circles), with the planetary orbits being along the equators. In three dimensions, the five spaces between concentric spheres two spheres could just be the five regular solids! The outer sphere passes through the vertices of the regular solid, and the inne ...
... orbits would run along spheres (rather than circles), with the planetary orbits being along the equators. In three dimensions, the five spaces between concentric spheres two spheres could just be the five regular solids! The outer sphere passes through the vertices of the regular solid, and the inne ...
New Almagest - University of Notre Dame
... circular motion about the center of the universe, in which its weight is not a factor.12 Then there is pro-geocentrism argument number 53 (one of only two among the 126 that involve religious questions), which says that if Earth is not the center of the universe, then Hell is not at the lowest place ...
... circular motion about the center of the universe, in which its weight is not a factor.12 Then there is pro-geocentrism argument number 53 (one of only two among the 126 that involve religious questions), which says that if Earth is not the center of the universe, then Hell is not at the lowest place ...
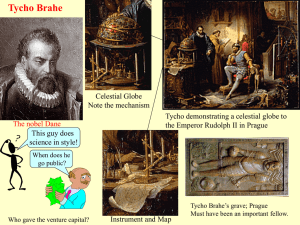
Tycho Brahe
... the Alfonsine Tables were off by a month in predicting the event and the Copernican Tables missed it by a week. He decided it would be his job to create the most accurate tables possible. He began constructing his own instruments; some of his own design, including a radie (a pair of calipers) made o ...
... the Alfonsine Tables were off by a month in predicting the event and the Copernican Tables missed it by a week. He decided it would be his job to create the most accurate tables possible. He began constructing his own instruments; some of his own design, including a radie (a pair of calipers) made o ...
What, and Why, is the International Astronomical Union?
... to cover the sky. Most of them were eventually taken, but, 35 years after the project began, only four of the 20 zones had been completely measured, printed, and distributed (those of Greenwich, Oxford, Perth, and the zone Hyderabad had originally agreed to do, they took on another later). The Carte ...
... to cover the sky. Most of them were eventually taken, but, 35 years after the project began, only four of the 20 zones had been completely measured, printed, and distributed (those of Greenwich, Oxford, Perth, and the zone Hyderabad had originally agreed to do, they took on another later). The Carte ...
The Sky This Month
... • Red supergiant, one of the largest stars we know about! • 4200 x Sun’s diameter. ...
... • Red supergiant, one of the largest stars we know about! • 4200 x Sun’s diameter. ...
Astronomy
... 4c. Big Dipper: diagram 4d. Milky Way '5a. Planet location and visibility by month - Solar System with planet links - Details on the planets 5b. Monthly planner for upcoming moon and planet events Constellation Chart for any date, time, and location Click Select from map to enter your location then ...
... 4c. Big Dipper: diagram 4d. Milky Way '5a. Planet location and visibility by month - Solar System with planet links - Details on the planets 5b. Monthly planner for upcoming moon and planet events Constellation Chart for any date, time, and location Click Select from map to enter your location then ...
The Sky Viewed from Earth - Beck-Shop
... firmament, nothing was easier for pre-technical peoples than to pick out patterns – persisting, recurring patterns – in the stars. Looking up at the sky on an August night in the northern hemisphere, we can see the summer patterns: Lyra, Cygnus the swan, and Aquila the eagle. In December, those patte ...
... firmament, nothing was easier for pre-technical peoples than to pick out patterns – persisting, recurring patterns – in the stars. Looking up at the sky on an August night in the northern hemisphere, we can see the summer patterns: Lyra, Cygnus the swan, and Aquila the eagle. In December, those patte ...
Copernican Revolution
... Copernican Revolution - Summary Geocentric Vs. Heliocentric Five people, contributions, significance Copernicus Brahe Kepler Galileo Newton ...
... Copernican Revolution - Summary Geocentric Vs. Heliocentric Five people, contributions, significance Copernicus Brahe Kepler Galileo Newton ...
Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 5b: So, what was
... for Newton’s amazing synthesis, which produced Newton’s 3 laws of motion and of universal gravitation: a. He developed the concept of inertia: 1) Aristotle had asserted that all bodies tended toward their most natural state – a state of rest. 2) Galileo said that a body in uniform motion (i.e. at a ...
... for Newton’s amazing synthesis, which produced Newton’s 3 laws of motion and of universal gravitation: a. He developed the concept of inertia: 1) Aristotle had asserted that all bodies tended toward their most natural state – a state of rest. 2) Galileo said that a body in uniform motion (i.e. at a ...
81 - Armenian Astronomical Society
... The IAU fully supports the involvement of the general public in the naming of astronomical objects, whether directly or through an independent organised vote, in the naming of planetary satellites, newly discovered exoplanets, and their host stars. This follows a well-established tradition for namin ...
... The IAU fully supports the involvement of the general public in the naming of astronomical objects, whether directly or through an independent organised vote, in the naming of planetary satellites, newly discovered exoplanets, and their host stars. This follows a well-established tradition for namin ...
Sky & Astronomy - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... • Galileo’s astronomical observations confirmed the Copernican heliocentric model of the universe – This eventually put him in conflict with the authorities of the 17th century Church, who still upheld the geocentric ideas of Aristotle and Ptolemy – For Galileo himself, there was no contradiction be ...
... • Galileo’s astronomical observations confirmed the Copernican heliocentric model of the universe – This eventually put him in conflict with the authorities of the 17th century Church, who still upheld the geocentric ideas of Aristotle and Ptolemy – For Galileo himself, there was no contradiction be ...
Refracting vs Reflecting Telescopes
... mirror area A = π (D/2)2 These properties are much more important than magnification which is produced by placing another lens - the eyepiece - at the mirror focus. Astronomers do not look through telescopes with their eyes - a light gathering detector (for instance a camera) records the image which ...
... mirror area A = π (D/2)2 These properties are much more important than magnification which is produced by placing another lens - the eyepiece - at the mirror focus. Astronomers do not look through telescopes with their eyes - a light gathering detector (for instance a camera) records the image which ...
Take our Astronomy Test
... 2. What did Eratosthenes do? 3. What is a geocentric model? 4. What are the contributions of Ptolemy? 5. What was the contribution of Copernicus? 6. What is a heliocentric model? 7. How does the heliocentric model explain retrograde motion? 8. What were the contributions of Galileo? 9. What were the ...
... 2. What did Eratosthenes do? 3. What is a geocentric model? 4. What are the contributions of Ptolemy? 5. What was the contribution of Copernicus? 6. What is a heliocentric model? 7. How does the heliocentric model explain retrograde motion? 8. What were the contributions of Galileo? 9. What were the ...
Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 1. Source of word
... forward again would seem to demand constant attention from a god, who should more properly have better things to be attending to. Ptolemy’s epicycles derived the back and forth motion of the planets from circles turning on circles. • This motion might seem possible for a god to set going and then ha ...
... forward again would seem to demand constant attention from a god, who should more properly have better things to be attending to. Ptolemy’s epicycles derived the back and forth motion of the planets from circles turning on circles. • This motion might seem possible for a god to set going and then ha ...
August - San Diego Astronomy Association
... On Friday, June 8th at Mission Trails Recreational Park, members of the San Diego Astronomy Association gathered to pay respect to long-time member Mike Dietz. Approximately twenty people attended the event. Speakers included Terry Stewart, Bill Griffith, Dennis Amman, Bob Wexel, and Alice Harvey. T ...
... On Friday, June 8th at Mission Trails Recreational Park, members of the San Diego Astronomy Association gathered to pay respect to long-time member Mike Dietz. Approximately twenty people attended the event. Speakers included Terry Stewart, Bill Griffith, Dennis Amman, Bob Wexel, and Alice Harvey. T ...
Astronomy
... (b) Identify at least one red star, ____________________________________________________________________________ one blue star, __________________________________________________________________________________________ and one yellow star (other than the Sun). _______________________________________ ...
... (b) Identify at least one red star, ____________________________________________________________________________ one blue star, __________________________________________________________________________________________ and one yellow star (other than the Sun). _______________________________________ ...
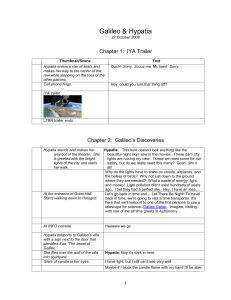
LTBN_Script - Let There Be Night
... things. Light pollution…I wonder what that is… Hypatia: Didn’t you invent the telescope? After all, you did brag about it in your book Starry Messenger. Galileo: (Belly laugh) Aahhh, I have to confess, I didn’t really invent the telescope. A Dutch lens maker named Hans Lippershey and others actually ...
... things. Light pollution…I wonder what that is… Hypatia: Didn’t you invent the telescope? After all, you did brag about it in your book Starry Messenger. Galileo: (Belly laugh) Aahhh, I have to confess, I didn’t really invent the telescope. A Dutch lens maker named Hans Lippershey and others actually ...
powerpoint - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... 50 LY across •H II region (red) high-energy UV hits interstellar gas •dark dust filaments – extinction due to debris from supernovae •blue reflection nebula February 14, 2006 ...
... 50 LY across •H II region (red) high-energy UV hits interstellar gas •dark dust filaments – extinction due to debris from supernovae •blue reflection nebula February 14, 2006 ...
powerpoint - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... The dust tail forms when solar photons collide with the dust in the coma. Ejected dust particles form a long, curved tail that lies slightly farther our from the Sun than the nucleus' orbit. The dust tail has a yellow-white color from reflected sunlight. Both of the tails will stretch for millions ...
... The dust tail forms when solar photons collide with the dust in the coma. Ejected dust particles form a long, curved tail that lies slightly farther our from the Sun than the nucleus' orbit. The dust tail has a yellow-white color from reflected sunlight. Both of the tails will stretch for millions ...
Patronage in astronomy

Patronage in astronomy is an approach which one can use to examine the history of astronomy from a cultural standpoint. Rather than simply focusing on the findings and discoveries of individual astronomers, this approach emphasizes the importance of patronage in shaping the field of astronomy.