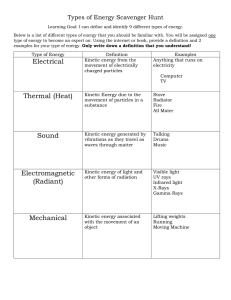
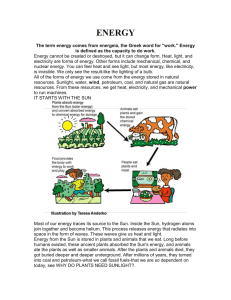
ENERGY
... ENERGY The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can ...
... ENERGY The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can ...
ENERGY STORAGE Part II
... Safe fast charge and discharge Low energy density High power density *Cost US$ 12.8 / Wh (Initial) Efficiency 95% ...
... Safe fast charge and discharge Low energy density High power density *Cost US$ 12.8 / Wh (Initial) Efficiency 95% ...
ENERGY and Energy Transformations
... (Chemical) • Waste (Chemical) MACHINE • Sound (Sound) • Heat (Thermal) ...
... (Chemical) • Waste (Chemical) MACHINE • Sound (Sound) • Heat (Thermal) ...
Chemical Energy
... 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoes a chemical reaction. 3. Electromagnetic Energy – Energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic wa ...
... 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoes a chemical reaction. 3. Electromagnetic Energy – Energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic wa ...
PEKE - Science
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
What is Energy?
... Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position – gravitational potential energy. ...
... Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position – gravitational potential energy. ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes (9/28-29/2016)
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
... • The ability to cause matter to move • The ability to cause matter to change • Measured in joules & calories ...
Energy Forms - Greenwood County School District 52
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
Week 3 CCA Review
... 2. Nonmetals are located primarily to the right of the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Nonmetals are usually dull, brittle, not malleable or ductile, and poor conductors. 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. They are found on the sta ...
... 2. Nonmetals are located primarily to the right of the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Nonmetals are usually dull, brittle, not malleable or ductile, and poor conductors. 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. They are found on the sta ...
Physics Chapter 5 Vocabulary Section 1 Energy: the ability to do
... Friction: a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. ...
... Friction: a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. ...
ECE 364 - Power Electronics
... Energy storage requirements in singlephase grid-connected applications lead to large (electrolytic) capacitors and limit life. Successful designs that minimize energy storage and deliver extreme life at temperature are presented here. ...
... Energy storage requirements in singlephase grid-connected applications lead to large (electrolytic) capacitors and limit life. Successful designs that minimize energy storage and deliver extreme life at temperature are presented here. ...
RK30 Energy Storage System
... bromide battery modules (ZBM). The ZBM is a Generation 2.5, 5kW/10kWh battery that is reliable and robust having been used in remote sites in the Australian outback for more than three years. The batteries are designed to handle both 100 percent discharge and partial discharge without significant de ...
... bromide battery modules (ZBM). The ZBM is a Generation 2.5, 5kW/10kWh battery that is reliable and robust having been used in remote sites in the Australian outback for more than three years. The batteries are designed to handle both 100 percent discharge and partial discharge without significant de ...
A wearable system of micromachined piezoelectric cantilevers
... other tasks. It is desirable to scavenge or harvest Energy from human movement, while the user is performing His/her everyday activities. Some of the earliest work to harvest energy from human gait Dates back almost 250 years and include the self-winding Watch and closely related modern electromecha ...
... other tasks. It is desirable to scavenge or harvest Energy from human movement, while the user is performing His/her everyday activities. Some of the earliest work to harvest energy from human gait Dates back almost 250 years and include the self-winding Watch and closely related modern electromecha ...
Forms of Energy
... Cam – C = Chemical Newton – N = Nuclear Got – G = Gravitational -----------------------------Really – R = Radiant Excited – E = Electrical Making – M = Mechanical Stinky – S = Sound Tacos – T = Thermal ...
... Cam – C = Chemical Newton – N = Nuclear Got – G = Gravitational -----------------------------Really – R = Radiant Excited – E = Electrical Making – M = Mechanical Stinky – S = Sound Tacos – T = Thermal ...
SOL PS 6
... charged particles. • Transfers energy without a medium. • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of the particles. • Depends on the number of particles as well as the temperature . ...
... charged particles. • Transfers energy without a medium. • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of the particles. • Depends on the number of particles as well as the temperature . ...
Energy storage

Energy storage is accomplished by devices or physical media that store energy to perform useful processes at a later time. A device that stores energy is sometimes called an accumulator.Many forms of energy produce useful work, heating or cooling to meet societal needs. These energy forms include chemical energy, gravitational potential energy, electrical potential, electricity, temperature differences, latent heat, and kinetic energy. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store (electricity, kinetic energy, etc.) to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide only short-term energy storage, and others can be very long-term such as power to gas using hydrogen or methane and the storage of heat or cold between opposing seasons in deep aquifers or bedrock. A wind-up clock stores potential energy (in this case mechanical, in the spring tension), a rechargeable battery stores readily convertible chemical energy to operate a mobile phone, and a hydroelectric dam stores energy in a reservoir as gravitational potential energy. Ice storage tanks store ice (thermal energy in the form of latent heat) at night to meet peak demand for cooling. Fossil fuels such as coal and gasoline store ancient energy derived from sunlight by organisms that later died, became buried and over time were then converted into these fuels. Even food (which is made by the same process as fossil fuels) is a form of energy stored in chemical form.