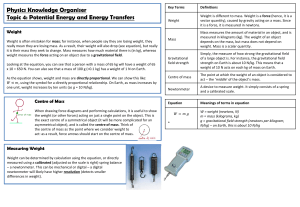
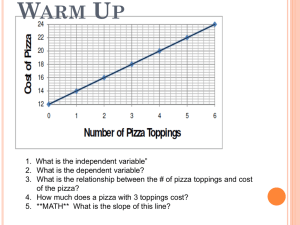
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy in a system remains constant. So, when people say they are “using” energy, what they really mean to say is that they are “converting” energy from one form to another form. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it is transformed from ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy in a system remains constant. So, when people say they are “using” energy, what they really mean to say is that they are “converting” energy from one form to another form. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it is transformed from ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy in a system remains constant. So, when people say they are “using” energy, what they really mean to say is that they are “converting” energy from one form to another form. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it is transformed from ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy in a system remains constant. So, when people say they are “using” energy, what they really mean to say is that they are “converting” energy from one form to another form. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it is transformed from ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy in a system remains constant. So, when people say they are “using” energy, what they really mean to say is that they are “converting” energy from one form to another form. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it is transformed from ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy in a system remains constant. So, when people say they are “using” energy, what they really mean to say is that they are “converting” energy from one form to another form. Energy is never created or destroyed, but it is transformed from ...
4 Potential energy and elasticity
... The extension of an elastic object, like a spring, is directly proportional to the force applied to it, provided the limit of proportionality of the spring is not exceeded. This also works with the compression of an object – you can use the equations below too, ‘e’ just means the amount of compressi ...
... The extension of an elastic object, like a spring, is directly proportional to the force applied to it, provided the limit of proportionality of the spring is not exceeded. This also works with the compression of an object – you can use the equations below too, ‘e’ just means the amount of compressi ...
Energy - Tapp Middle School
... In addition to using energy to do work, objects gain energy because work is being done on them. ...
... In addition to using energy to do work, objects gain energy because work is being done on them. ...
Electricity Storage Technologies for Short Term Power System
... turbines and local power plants in addition to the conventional central plants. As a result of restructuring the electricity supply in Denmark wind turbines are now producing about 20 % of the electricity demand on average and Danish authorities are planning for 50 % in 2025. One consequence of the ...
... turbines and local power plants in addition to the conventional central plants. As a result of restructuring the electricity supply in Denmark wind turbines are now producing about 20 % of the electricity demand on average and Danish authorities are planning for 50 % in 2025. One consequence of the ...
Notes - PowerPoint
... This quantity, H, is called the enthalpy of reaction, or the heat of reaction. Enthalpy is an extensive property. H for a reaction in the forward direction is equal in size, but opposite in sign, to H for the reverse reaction. H for a reaction depends on the state of the products and the state o ...
... This quantity, H, is called the enthalpy of reaction, or the heat of reaction. Enthalpy is an extensive property. H for a reaction in the forward direction is equal in size, but opposite in sign, to H for the reverse reaction. H for a reaction depends on the state of the products and the state o ...
Section 4 Work and Energy
... 12.0 m/s while chasing the mouse. How much work was done on the cat to produce this change in speed? – Answer: 1.32 x 102 J or 132 J ...
... 12.0 m/s while chasing the mouse. How much work was done on the cat to produce this change in speed? – Answer: 1.32 x 102 J or 132 J ...
Energy - Science
... Most renewable energy resources originate either directly or indirectly from the sun. • The sun and Earth are constantly releasing large ...
... Most renewable energy resources originate either directly or indirectly from the sun. • The sun and Earth are constantly releasing large ...
Chemical Energy
... • These bulbs will both be bright because they have their own separate current. ...
... • These bulbs will both be bright because they have their own separate current. ...
Forms of Energy Sources
... Energy travels throughout the universe at the speed of light in the form of electromagnetic radiation. What that radiation is called depends on its energy level. At the really high-energy end of the spectrum, you’ve got gamma rays. You’re probably familiar with a close cousin to these: X-rays. They’ ...
... Energy travels throughout the universe at the speed of light in the form of electromagnetic radiation. What that radiation is called depends on its energy level. At the really high-energy end of the spectrum, you’ve got gamma rays. You’re probably familiar with a close cousin to these: X-rays. They’ ...
energy - Ms. McGuirk`s 6th Grade Science Class
... energy due to random motion of the particles that make up an object. • The hotter something is, the more kinetic energy its particles have. • If something is cold, like ice, its particles are moving very slow, or have little kinetic energy. ...
... energy due to random motion of the particles that make up an object. • The hotter something is, the more kinetic energy its particles have. • If something is cold, like ice, its particles are moving very slow, or have little kinetic energy. ...
ENERGY
... 2. What type of energy is converted into chemical energy by ancient plants and animals at point B? 3. The coal at point C is an example of what type of fuel? Give another example of this type of fuel. 4. How is the stored chemical energy converted into thermal energy at ...
... 2. What type of energy is converted into chemical energy by ancient plants and animals at point B? 3. The coal at point C is an example of what type of fuel? Give another example of this type of fuel. 4. How is the stored chemical energy converted into thermal energy at ...
Review Unit 5 Properties of Energy
... of the bonds between the atoms. This process releases the energy that is stored there. Gasoline is another example. When you start a fire or burn fuel, the bonds between atoms are being broken, and the resulting heat is a sign that energy is being released. When you stretch or compress a spring, you ...
... of the bonds between the atoms. This process releases the energy that is stored there. Gasoline is another example. When you start a fire or burn fuel, the bonds between atoms are being broken, and the resulting heat is a sign that energy is being released. When you stretch or compress a spring, you ...
Energy storage

Energy storage is accomplished by devices or physical media that store energy to perform useful processes at a later time. A device that stores energy is sometimes called an accumulator.Many forms of energy produce useful work, heating or cooling to meet societal needs. These energy forms include chemical energy, gravitational potential energy, electrical potential, electricity, temperature differences, latent heat, and kinetic energy. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store (electricity, kinetic energy, etc.) to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide only short-term energy storage, and others can be very long-term such as power to gas using hydrogen or methane and the storage of heat or cold between opposing seasons in deep aquifers or bedrock. A wind-up clock stores potential energy (in this case mechanical, in the spring tension), a rechargeable battery stores readily convertible chemical energy to operate a mobile phone, and a hydroelectric dam stores energy in a reservoir as gravitational potential energy. Ice storage tanks store ice (thermal energy in the form of latent heat) at night to meet peak demand for cooling. Fossil fuels such as coal and gasoline store ancient energy derived from sunlight by organisms that later died, became buried and over time were then converted into these fuels. Even food (which is made by the same process as fossil fuels) is a form of energy stored in chemical form.