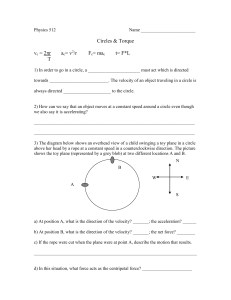
Day 1 Notes: Dealing with projectiles in two dimensions. There are
... B. Every object has its own gravitational pull. This is the reason planets orbit the sun. The law of ilypsis explains that the orbit of planets around the sun, being the one focus, is ilyptical. The law of equal area says that the distance between the center of the sun and the center of each planet ...
... B. Every object has its own gravitational pull. This is the reason planets orbit the sun. The law of ilypsis explains that the orbit of planets around the sun, being the one focus, is ilyptical. The law of equal area says that the distance between the center of the sun and the center of each planet ...
Relativistic Effects - The Physics of Bruce Harvey
... There are four effects of motion through the background which become significant as we approach the speed of light. They are: • contraction in length • increase in mass • slowing of time dependant processes which affects clocks • problems in synchronising clocks Our unified theory follows the relati ...
... There are four effects of motion through the background which become significant as we approach the speed of light. They are: • contraction in length • increase in mass • slowing of time dependant processes which affects clocks • problems in synchronising clocks Our unified theory follows the relati ...
relativity phys311
... Lorentz’s place in history, besides his 1902 Nobel prize for theory of electrons: setting scene for Poincaré (1904): “According to the principle of relativity, the laws of physical phenomena must be the same for a fixed observer as for an observer who has a uniform motion of translation relative to ...
... Lorentz’s place in history, besides his 1902 Nobel prize for theory of electrons: setting scene for Poincaré (1904): “According to the principle of relativity, the laws of physical phenomena must be the same for a fixed observer as for an observer who has a uniform motion of translation relative to ...
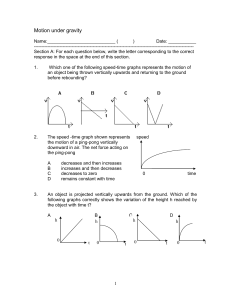
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Section A: For each question below, write the letter corresponding to the correct response in the space at the end of this section. ...
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Section A: For each question below, write the letter corresponding to the correct response in the space at the end of this section. ...
MOTION
... • Instantaneous speed the rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time –Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
... • Instantaneous speed the rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time –Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
Worksheet on W=mgh
... always do negative work on an object. When things move against gravity, gravity is said to do negative work on the object. 1a) Determine the work a hiker must do on a 15.0 kg backpack to carry it up a hill 30⁰ to the horizontal at constant velocity. Assume the height of the hill is 10.0m above the l ...
... always do negative work on an object. When things move against gravity, gravity is said to do negative work on the object. 1a) Determine the work a hiker must do on a 15.0 kg backpack to carry it up a hill 30⁰ to the horizontal at constant velocity. Assume the height of the hill is 10.0m above the l ...
8th grade Energy, Force and Motion Quiz 4 (M) Newton`s Laws of
... 1.________________ This is always equal and opposite to the action force 2. ________________ An object’s tendency to stay at rest or resist a change in motion 3. ______ Any change in a object’s speed or direction 4. ______ A push or a pull that changes an object’s motion ...
... 1.________________ This is always equal and opposite to the action force 2. ________________ An object’s tendency to stay at rest or resist a change in motion 3. ______ Any change in a object’s speed or direction 4. ______ A push or a pull that changes an object’s motion ...