TEST I 2-12-09
... Hints about exam I on Thursday 2/12/09-----I will not be able to answer emails till Monday next week. Please bring small blue Scranton that has 50 answers on one side. That way you all are at the same page. Do not bring a big one. May be just bring two of these. Just in case one goes bad or you may ...
... Hints about exam I on Thursday 2/12/09-----I will not be able to answer emails till Monday next week. Please bring small blue Scranton that has 50 answers on one side. That way you all are at the same page. Do not bring a big one. May be just bring two of these. Just in case one goes bad or you may ...
lec30
... field due to the trio, at a point on the positive y axis. The person determines the distance r that each particle is from the point on the y axis in question and kq then calculates the value of E 2 for each of the ...
... field due to the trio, at a point on the positive y axis. The person determines the distance r that each particle is from the point on the y axis in question and kq then calculates the value of E 2 for each of the ...
Chapter 24: Electromagnetic Waves
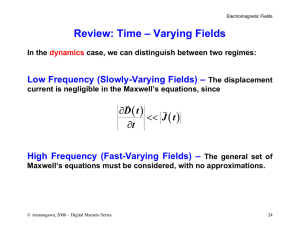
... 1. In an RC circuit, the capacitor begins to discharge. (i) During the discharge, in the region of space between the plates of the capacitor, is there (a) conduction current but no displacement current, (b) displacement current but no conduction current, (c) both conduction and displacement current, ...
... 1. In an RC circuit, the capacitor begins to discharge. (i) During the discharge, in the region of space between the plates of the capacitor, is there (a) conduction current but no displacement current, (b) displacement current but no conduction current, (c) both conduction and displacement current, ...
Polarized sphere
... Two spheres with radii r0 are homogeneously charged with q and −q. The distance between their centers is the vector d~ such that d r0 1. Find the electric field in the whole space. 2. Find the charge distribution on the surface of the sphere ~ 0 . Find the A dielectric sphere (of permittivity ε) i ...
... Two spheres with radii r0 are homogeneously charged with q and −q. The distance between their centers is the vector d~ such that d r0 1. Find the electric field in the whole space. 2. Find the charge distribution on the surface of the sphere ~ 0 . Find the A dielectric sphere (of permittivity ε) i ...
Ampere`s law
... How long would it take an electron to complete one circular orbit around a 1 G magnetic field? ...
... How long would it take an electron to complete one circular orbit around a 1 G magnetic field? ...
[2011 question paper]
... The spins interact via (i) nearest neighbour ferromagnetic interactions with coupling J1 and (ii) next-to-nearest neighbour anti-ferromagnetic interactions (favouring antialigned spins) with coupling J2 . (a) For a one-dimensional system of three spins with a Hamiltonian of the above form, find the ...
... The spins interact via (i) nearest neighbour ferromagnetic interactions with coupling J1 and (ii) next-to-nearest neighbour anti-ferromagnetic interactions (favouring antialigned spins) with coupling J2 . (a) For a one-dimensional system of three spins with a Hamiltonian of the above form, find the ...
Electric Charge
... The purpose of this experiment is to find the thermal capacity CT of the resistor. You need to fill out the following table during the experiment. In the table, Ti is the initial reading of the thermometer for each trial while Tmax is the maximum reading. ΔP is the voltage applied on the capacitor w ...
... The purpose of this experiment is to find the thermal capacity CT of the resistor. You need to fill out the following table during the experiment. In the table, Ti is the initial reading of the thermometer for each trial while Tmax is the maximum reading. ΔP is the voltage applied on the capacitor w ...
Past Year Paper Solution AY11/12 Semester 2 PH1102/PAP112
... The second region is the place where the filtered ions will move with a half-circular path before hitting the photographic plate. Since the radius of the movement depends on the mass of the ion, the ion mass will determine the point where the ions will hit the plate, which is given by: ...
... The second region is the place where the filtered ions will move with a half-circular path before hitting the photographic plate. Since the radius of the movement depends on the mass of the ion, the ion mass will determine the point where the ions will hit the plate, which is given by: ...
COURSE TITLE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY I COURSE CODE
... Electrostatic fields due to distribution of charge, Magnetic fields in and around current carrying conductors. Review of electromagnetic laws in integral form; Gauss’s law Ampere’s and Laplace’s equations and methods of solution. Boundary values problems. Electrostatic fields due to distribution cha ...
... Electrostatic fields due to distribution of charge, Magnetic fields in and around current carrying conductors. Review of electromagnetic laws in integral form; Gauss’s law Ampere’s and Laplace’s equations and methods of solution. Boundary values problems. Electrostatic fields due to distribution cha ...
August 28 /29th th Electric Fields
... does a charge, q1, exert a force on another charge, q2, when the charges don’t touch? ! The charge, q1, sets up an electric field in its surrounding space ! This electric field has both magnitude and direction which determine the magnitude and direction of the force acting on q2 ! How ...
... does a charge, q1, exert a force on another charge, q2, when the charges don’t touch? ! The charge, q1, sets up an electric field in its surrounding space ! This electric field has both magnitude and direction which determine the magnitude and direction of the force acting on q2 ! How ...
Picturing Electric Forces
... Group Question – Predict the net electric force a test charge will experience when placed next to a charge dipole. Draw three vectors for each point – one for each charge and one for the net force. In the next diagram sketch your prediction for the electric field around the dipole. ...
... Group Question – Predict the net electric force a test charge will experience when placed next to a charge dipole. Draw three vectors for each point – one for each charge and one for the net force. In the next diagram sketch your prediction for the electric field around the dipole. ...
Homework: The electric Field
... 1. Electric f______________________________ act over distances meaning there is a force between two objects even if they are ___________________________________. 2. “fields” were developed by __________________________________________ 3. An ________________________________________ goes out from ever ...
... 1. Electric f______________________________ act over distances meaning there is a force between two objects even if they are ___________________________________. 2. “fields” were developed by __________________________________________ 3. An ________________________________________ goes out from ever ...
Example 12. Find electric field a distance h above the center of a (i
... Example 12. Find electric field a distance h above the center of a (i) circular loop of radius R, which carries a uniform line charge λ, (ii) flat circular disc of radius R, which carries a uniform surface charge σ. Explore the limit h → ∞ in both cases and R → ∞ in the case of flat disc. ~ is a spe ...
... Example 12. Find electric field a distance h above the center of a (i) circular loop of radius R, which carries a uniform line charge λ, (ii) flat circular disc of radius R, which carries a uniform surface charge σ. Explore the limit h → ∞ in both cases and R → ∞ in the case of flat disc. ~ is a spe ...
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity that has a value for each point in space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface wind velocity is described by assigning a vector to each point on a map. Each vector represents the speed and direction of the movement of air at that point. As another example, an electric field can be thought of as a ""condition in space"" emanating from an electric charge and extending throughout the whole of space. When a test electric charge is placed in this electric field, the particle accelerates due to a force. Physicists have found the notion of a field to be of such practical utility for the analysis of forces that they have come to think of a force as due to a field.In the modern framework of the quantum theory of fields, even without referring to a test particle, a field occupies space, contains energy, and its presence eliminates a true vacuum. This lead physicists to consider electromagnetic fields to be a physical entity, making the field concept a supporting paradigm of the edifice of modern physics. ""The fact that the electromagnetic field can possess momentum and energy makes it very real... a particle makes a field, and a field acts on another particle, and the field has such familiar properties as energy content and momentum, just as particles can have"". In practice, the strength of most fields has been found to diminish with distance to the point of being undetectable. For instance the strength of many relevant classical fields, such as the gravitational field in Newton's theory of gravity or the electrostatic field in classical electromagnetism, is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source (i.e. they follow the Gauss's law). One consequence is that the Earth's gravitational field quickly becomes undetectable on cosmic scales.A field can be classified as a scalar field, a vector field, a spinor field or a tensor field according to whether the represented physical quantity is a scalar, a vector, a spinor or a tensor, respectively. A field has a unique tensorial character in every point where it is defined: i.e. a field cannot be a scalar field somewhere and a vector field somewhere else. For example, the Newtonian gravitational field is a vector field: specifying its value at a point in spacetime requires three numbers, the components of the gravitational field vector at that point. Moreover, within each category (scalar, vector, tensor), a field can be either a classical field or a quantum field, depending on whether it is characterized by numbers or quantum operators respectively. In fact in this theory an equivalent representation of field is a field particle, namely a boson.






![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881811_1-8ef23f7493d56bc511a2c01dcc81fc96-300x300.png)