Gas Planets
... Gas Planet – a large planet that has a deep, massive atmosphere Planetary Ring – a disk of matter that circles a planet and consists of numerous particles in orbit that range in size from a few millimeters to several hundred meters. ...
... Gas Planet – a large planet that has a deep, massive atmosphere Planetary Ring – a disk of matter that circles a planet and consists of numerous particles in orbit that range in size from a few millimeters to several hundred meters. ...
File
... Other Objects in the Solar System Comets Most comets originate in the Kuiper belt (disc shaped group of millions of objects orbiting the sun. These small objects are left over from the formation of the solar system), and the Oort cloud (at the farthest reach of the sun’s gravitational influence). Ev ...
... Other Objects in the Solar System Comets Most comets originate in the Kuiper belt (disc shaped group of millions of objects orbiting the sun. These small objects are left over from the formation of the solar system), and the Oort cloud (at the farthest reach of the sun’s gravitational influence). Ev ...
Name _________ Science - 7th period Date: The Universe: Objects
... Other objects of the Solar System 1. __________________ planets orbit the sun and are ________________ and have different characteristics than a planet 2. _______________________ is a large chunk of ________________ that orbits the sun. ( the largest is 600 km in diameter) a. Most asteroids orbit in ...
... Other objects of the Solar System 1. __________________ planets orbit the sun and are ________________ and have different characteristics than a planet 2. _______________________ is a large chunk of ________________ that orbits the sun. ( the largest is 600 km in diameter) a. Most asteroids orbit in ...
planets test
... 8. All of the _______________ planets have moons except Mercury. 9. The _________________________ consists of the sun, eight planets and their moons, and several kinds of smaller objects. 10. Mars’s atmosphere is mostly _________________________. 11. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a(n) ________________ ...
... 8. All of the _______________ planets have moons except Mercury. 9. The _________________________ consists of the sun, eight planets and their moons, and several kinds of smaller objects. 10. Mars’s atmosphere is mostly _________________________. 11. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a(n) ________________ ...
Celestial Objects notes
... The Sun is at the center of our solar system and its strong gravitational pull holds 8 planets, asteroids, and other celestial objects in orbital paths around it. Our Sun is a medium sized star yet is the most massive object in our solar system. It is an extremely hot, dense mass of gases which radi ...
... The Sun is at the center of our solar system and its strong gravitational pull holds 8 planets, asteroids, and other celestial objects in orbital paths around it. Our Sun is a medium sized star yet is the most massive object in our solar system. It is an extremely hot, dense mass of gases which radi ...
Outer Solar System
... Orbital eccentricities ranging as high as 0.8 Inclinations as high as 40° Perihelia greater than 30 AU ...
... Orbital eccentricities ranging as high as 0.8 Inclinations as high as 40° Perihelia greater than 30 AU ...
Solar System Study Guide
... * star- an object in space that produces its own heat and light * moon- a natural satellite that orbits a planet * solar system- a sun and all the objects that move around it * orbit- the path that one object in space takes around another object in space * gravity- the force that pulls objects towar ...
... * star- an object in space that produces its own heat and light * moon- a natural satellite that orbits a planet * solar system- a sun and all the objects that move around it * orbit- the path that one object in space takes around another object in space * gravity- the force that pulls objects towar ...
Classroom Activity
... Sit in a rotating office chair and hold a textbook in each hand with your arms outstretched. Have a friend spin you gently. Once you are spinning steadily bring the textbooks in towards your torso. What do you notice about your rotation speed? Does it increase or decrease? This is conservation of an ...
... Sit in a rotating office chair and hold a textbook in each hand with your arms outstretched. Have a friend spin you gently. Once you are spinning steadily bring the textbooks in towards your torso. What do you notice about your rotation speed? Does it increase or decrease? This is conservation of an ...
Flat Earth / Round Earth Activity
... (the line between the object and the sun) sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals (Kepler’s second law of planetary motion). This implies that objects closer to the sun must faster than those farther away. Is this what you found out? ...
... (the line between the object and the sun) sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals (Kepler’s second law of planetary motion). This implies that objects closer to the sun must faster than those farther away. Is this what you found out? ...
Solar System Powerpoint by Katonya Beaubouef
... • A ball of dust and ice that orbits around the sun. ...
... • A ball of dust and ice that orbits around the sun. ...
Comets…
... Small objects in the Solar System Meteors, Comets, : we see them without a telescope Asteroids: small rocky objects mostly between Mars and Jupiter – too faint to see without a telescope Kuiper belt objects: even fainter objects beyond Pluto, debris left over from solar system formation Image of co ...
... Small objects in the Solar System Meteors, Comets, : we see them without a telescope Asteroids: small rocky objects mostly between Mars and Jupiter – too faint to see without a telescope Kuiper belt objects: even fainter objects beyond Pluto, debris left over from solar system formation Image of co ...
HW Solar System Mnemonic
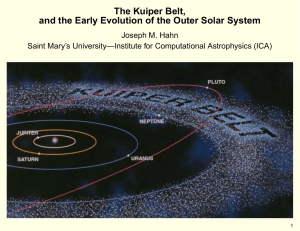
... belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, although it is far larger; 20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of smal ...
... belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, although it is far larger; 20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of smal ...
Solar System Bodies PPT
... Asteroids: originate in the Asteroid belt (large orbital belt in between Mars and Jupiter) Comets: originate either in the Oort cloud (region that surrounds Solar System-full of frozen material) OR in the Kuiper belt (region just beyond Neptune) ...
... Asteroids: originate in the Asteroid belt (large orbital belt in between Mars and Jupiter) Comets: originate either in the Oort cloud (region that surrounds Solar System-full of frozen material) OR in the Kuiper belt (region just beyond Neptune) ...
The Kuiper Belt, and the Early Evolution of the Outer Solar System
... evolve away from each other, ie, Jupiter inwards, Neptune outwards ...
... evolve away from each other, ie, Jupiter inwards, Neptune outwards ...
File - CVHS Chicklas
... The Leftovers (small bodies) • Asteroids: – Made of rock & metal (density 2-3 g/cc) – Sizes: Few 100km to large boulders – Most are found in the Main Belt (2.1-3.2 AU) ...
... The Leftovers (small bodies) • Asteroids: – Made of rock & metal (density 2-3 g/cc) – Sizes: Few 100km to large boulders – Most are found in the Main Belt (2.1-3.2 AU) ...
Chart_set_4
... Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". This is pre-Newton and modern science. But basic idea correct, and the theory evolved as science advanced, as we'l ...
... Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". This is pre-Newton and modern science. But basic idea correct, and the theory evolved as science advanced, as we'l ...
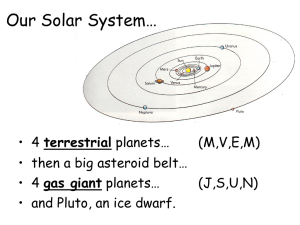
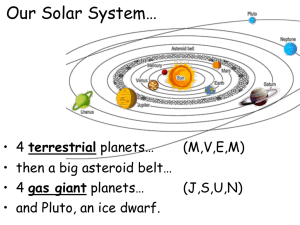
the solar system
... Revolution: is the movement of the planets around the Sun. All of the orbits, excluding Pluto, are approximatedly on the same plane. The time that a planet takes to orbit the Sun is called a year. All the planets move anticlockwise around the Sun. ...
... Revolution: is the movement of the planets around the Sun. All of the orbits, excluding Pluto, are approximatedly on the same plane. The time that a planet takes to orbit the Sun is called a year. All the planets move anticlockwise around the Sun. ...
A Look at Our Solar System: The Sun, the planets and more
... Pluto: Not a planet anymore! Defini&on of a planet: • Orbits a star • Massive enough for its gravity to give it nearly a round shape • Has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit ...
... Pluto: Not a planet anymore! Defini&on of a planet: • Orbits a star • Massive enough for its gravity to give it nearly a round shape • Has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit ...
Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System”
... also blows the gas away forming a long tail (millions of kilometers) ...
... also blows the gas away forming a long tail (millions of kilometers) ...
Scattered disc

The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant region of the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy minor planets, a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc objects (SDOs) have orbital eccentricities ranging as high as 0.8, inclinations as high as 40°, and perihelia greater than 30 astronomical units (4.5×109 km; 2.8×109 mi). These extreme orbits are thought to be the result of gravitational ""scattering"" by the gas giants, and the objects continue to be subject to perturbation by the planet Neptune.Although the closest scattered-disc objects approach the Sun at about 30–35 AU, their orbits can extend well beyond 100 AU. This makes scattered objects among the most distant and coldest objects in the Solar System. The innermost portion of the scattered disc overlaps with a torus-shaped region of orbiting objects traditionally called the Kuiper belt, but its outer limits reach much farther away from the Sun and farther above and below the ecliptic than the Kuiper belt proper.Because of its unstable nature, astronomers now consider the scattered disc to be the place of origin for most periodic comets in the Solar System, with the centaurs, a population of icy bodies between Jupiter and Neptune, being the intermediate stage in an object's migration from the disc to the inner Solar System. Eventually, perturbations from the giant planets send such objects towards the Sun, transforming them into periodic comets. Many Oort cloud objects are also thought to have originated in the scattered disc. Detached objects are not sharply distinct from scattered disc objects, and some such as Sedna have sometimes been considered to be included in this group.






![class16.ppt [Read-Only] - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016866176_1-afb2b342fc43676be8b063b94ba751c2-300x300.png)