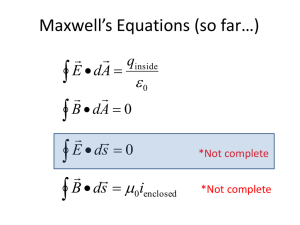A DERIVATION OF NEWTON`S LAW OF GRAVITATION FROM
... Since the forces due to the mesonic charges of Yukawa are very weak when compared to electromagnetic forces for large distances, they seem unlikely to contribute to the gravitational attraction between bodies of matter. The problem is therefore to decide, in the next sections, whether electromagneti ...
... Since the forces due to the mesonic charges of Yukawa are very weak when compared to electromagnetic forces for large distances, they seem unlikely to contribute to the gravitational attraction between bodies of matter. The problem is therefore to decide, in the next sections, whether electromagneti ...
EMF
... We call the curly electric fields Non-Coulomb electric fields ENC They are related to magnetic fields that are changing in time: ...
... We call the curly electric fields Non-Coulomb electric fields ENC They are related to magnetic fields that are changing in time: ...
lecture1423813661
... shown in the Fig. below The force at any point along its path would cause the particle to accelerate and move it out of the region if unconstrained. Since we are dealing with an electrostatic case, a force equal to the negative of that acting on the charge is to be applied while moves from P to Q. T ...
... shown in the Fig. below The force at any point along its path would cause the particle to accelerate and move it out of the region if unconstrained. Since we are dealing with an electrostatic case, a force equal to the negative of that acting on the charge is to be applied while moves from P to Q. T ...
The direction of the magnetic field B at any location
... the magnetic field lines outside the magnet point away from north poles and toward south poles. ...
... the magnetic field lines outside the magnet point away from north poles and toward south poles. ...
Quantum Mechanics Magnetic field
... Biot and Félix Savart discovered the Biot–Savart law in 1820, which correctly predicts the magnetic field around any current-carrying wire. Extending these experiments, Ampère published his own successful model of magnetism in 1825. In it, he showed the equivalence of electrical currents to magnets ...
... Biot and Félix Savart discovered the Biot–Savart law in 1820, which correctly predicts the magnetic field around any current-carrying wire. Extending these experiments, Ampère published his own successful model of magnetism in 1825. In it, he showed the equivalence of electrical currents to magnets ...
SENSORS
... The material between the plates of the capacitor can also be used to sense changes in the environment. • When vacuum (or air) is replaced by another material, the capacitance increases by a factor of , known as the dielectric constant of the material • The increase in C is due to the polarization o ...
... The material between the plates of the capacitor can also be used to sense changes in the environment. • When vacuum (or air) is replaced by another material, the capacitance increases by a factor of , known as the dielectric constant of the material • The increase in C is due to the polarization o ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.