Document
... at different places. Examples to be considered in this unit are electric field, electrostatic potential and magnetic field. An electric field is said to exist at a point in space if a charged particle placed at that point experiences a force that would not be felt by an uncharged particle. We have a ...
... at different places. Examples to be considered in this unit are electric field, electrostatic potential and magnetic field. An electric field is said to exist at a point in space if a charged particle placed at that point experiences a force that would not be felt by an uncharged particle. We have a ...
Electromagnetic Demos
... and note the duration of fall. 2. Repeat the same procedure using the plastic tube. 3. Compare the time taken for the magnet to fall through both tubes? 4. In which tube was the overall velocity of the magnet least? 5. In which direction does the force of gravity act? 6. In which direction is the fo ...
... and note the duration of fall. 2. Repeat the same procedure using the plastic tube. 3. Compare the time taken for the magnet to fall through both tubes? 4. In which tube was the overall velocity of the magnet least? 5. In which direction does the force of gravity act? 6. In which direction is the fo ...
Self-organization into quantized eigenstates of a classical wave
... here is a large variety of physical systems in which localized objects (particles, point-like sources or singularities) are associated with extended waves. These entities have a generic character being observed in, for example, localized soliton-like dissipative structures, defects in extended nonli ...
... here is a large variety of physical systems in which localized objects (particles, point-like sources or singularities) are associated with extended waves. These entities have a generic character being observed in, for example, localized soliton-like dissipative structures, defects in extended nonli ...
Electrostatics Packet
... In mechanics our basic property of matter was MASS. In electricity, our basic property is CHARGE. Who named the two kinds of charge? ___ ___________ (Famous American Scientist) He thought that the positive charges were moving (the structure of the atom wasn’t really know yet), and designated the dir ...
... In mechanics our basic property of matter was MASS. In electricity, our basic property is CHARGE. Who named the two kinds of charge? ___ ___________ (Famous American Scientist) He thought that the positive charges were moving (the structure of the atom wasn’t really know yet), and designated the dir ...
Advances in Electromagnetic Theory
... All illustrations of the TEM Wave on the www are of the sine wave. Even such sine wave illustrations are missing from text books. No text book contains the crucial diagrams in my book, Figures 4 and 5 in http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/1_2.htm . Central to my theories is the negative charge on the bottom ...
... All illustrations of the TEM Wave on the www are of the sine wave. Even such sine wave illustrations are missing from text books. No text book contains the crucial diagrams in my book, Figures 4 and 5 in http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/1_2.htm . Central to my theories is the negative charge on the bottom ...
Magnetic structure and hysteresis in hard magnetic nanocrystalline film: Computer simulation
... Equation 共7兲 is valid under the assumption of a single-phase polycrystal with ‘‘perfect’’ grain boundaries. For the case of imperfect grain boundaries the energy density constants K 1 and K 2 at the boundaries are different from those inside grains, and thus coordinate dependent. ...
... Equation 共7兲 is valid under the assumption of a single-phase polycrystal with ‘‘perfect’’ grain boundaries. For the case of imperfect grain boundaries the energy density constants K 1 and K 2 at the boundaries are different from those inside grains, and thus coordinate dependent. ...
Emag Homework really..
... In spherical coordinates, show that the electric field E of a point charge is conservative. Determine and write the electric potential in rectangular (cartesian) and cylindrical coordinates. Find E using both cartesian and cylindrical coordinates and show that the results are the same as in ...
... In spherical coordinates, show that the electric field E of a point charge is conservative. Determine and write the electric potential in rectangular (cartesian) and cylindrical coordinates. Find E using both cartesian and cylindrical coordinates and show that the results are the same as in ...
Diapositive 1
... moments of a pair of electrons. Order of magnitude ~ μ2/r 3. Normally negligible for electrons, however important for nuclear spins ...
... moments of a pair of electrons. Order of magnitude ~ μ2/r 3. Normally negligible for electrons, however important for nuclear spins ...
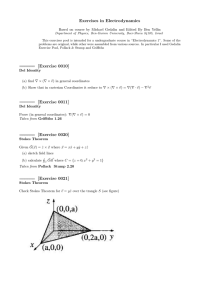
Exercises in Electrodynamics
... A photon of energy E0 ”bounces” off an electron, initially at rest. Find the energy E of the outgoing photon, as a function of the scattering angle θ Taken from Griffiths example 12.9 ...
... A photon of energy E0 ”bounces” off an electron, initially at rest. Find the energy E of the outgoing photon, as a function of the scattering angle θ Taken from Griffiths example 12.9 ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.