Magnetic Fields
... Experiments on various charged particles moving in a magnetic field give the following results: ...
... Experiments on various charged particles moving in a magnetic field give the following results: ...
these slides
... A magnetic field is caused only by a moving charge. ・ Electric field lines originate at one point in space (a positive charge) and terminate at another point in space (a negative charge). Magnetic field lines form closed loops. ・ An electric field exerts a force on any charge within that field. A ma ...
... A magnetic field is caused only by a moving charge. ・ Electric field lines originate at one point in space (a positive charge) and terminate at another point in space (a negative charge). Magnetic field lines form closed loops. ・ An electric field exerts a force on any charge within that field. A ma ...
Magnetic Fields
... One way to produce a magnetic field is to use moving electric charges to create an electromagnet. This is done in motors, telephones and computer disk drives as well as many other places. Magnetic fields are also produced by some minerals and ores because the molecules and atoms have an intrinsic ma ...
... One way to produce a magnetic field is to use moving electric charges to create an electromagnet. This is done in motors, telephones and computer disk drives as well as many other places. Magnetic fields are also produced by some minerals and ores because the molecules and atoms have an intrinsic ma ...
Magnetism - Cuero ISD
... • The palm points in the direction the magnetic field moves the charge. This is the Fmag, or magnetic force. Fmag MUST BE the direction B moves the charge (or wire) NOT an external force. A current flowing in a wire, due to an external voltage supply is not Fmag; it is the direction of v (moving ch ...
... • The palm points in the direction the magnetic field moves the charge. This is the Fmag, or magnetic force. Fmag MUST BE the direction B moves the charge (or wire) NOT an external force. A current flowing in a wire, due to an external voltage supply is not Fmag; it is the direction of v (moving ch ...
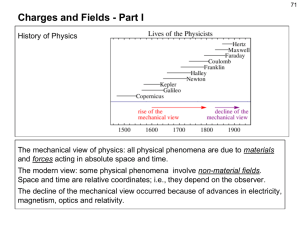
Charges and Fields - Part I
... The mechanical view of physics: all physical phenomena are due to materials and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical vi ...
... The mechanical view of physics: all physical phenomena are due to materials and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical vi ...
• Quantitative rule for computing the magnetic field from any electric
... computing the magnetic field from any electric current • Choose a differential element of wire of length dL and carrying a current i • The field dB from this element µ0 =4πx10-7 T.m/A at a point located by the vector (permeability constant) r is given by the Biot-Savart ...
... computing the magnetic field from any electric current • Choose a differential element of wire of length dL and carrying a current i • The field dB from this element µ0 =4πx10-7 T.m/A at a point located by the vector (permeability constant) r is given by the Biot-Savart ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.