Physics 227: Lecture 15 Magnetic Fields from wires
... +x direction, generates a magnetic field in the +z direction at the position of the upper + charge. The magnetic force on the upper charge is FM = qvB in the +y direction. There is also an electric field from the lower charge at the position of the upper charge, leading to an electric force FE = qE ...
... +x direction, generates a magnetic field in the +z direction at the position of the upper + charge. The magnetic force on the upper charge is FM = qvB in the +y direction. There is also an electric field from the lower charge at the position of the upper charge, leading to an electric force FE = qE ...
Electric Forces, Fields, and Voltage
... particle? And (b) what is the common charge? (4) Consider a point charge of 1.50 x 10-8 C. (a) what is the radius of an equipotential surface having a potential of 30.0 V? (b) are equipotential surfaces evenly spaced in radius? (5) An electrostatic field of 1.00 x 10-5 NC-1 is pointing radially towa ...
... particle? And (b) what is the common charge? (4) Consider a point charge of 1.50 x 10-8 C. (a) what is the radius of an equipotential surface having a potential of 30.0 V? (b) are equipotential surfaces evenly spaced in radius? (5) An electrostatic field of 1.00 x 10-5 NC-1 is pointing radially towa ...
PHYS 632 Lecture 8: Magnetic Fields
... • A line drawn tangent to a field line is the direction of the field at that point. • The density of field lines still represent the strength of the field. Differences • The magnetic field lines do not terminate on anything. They form complete loops. There is no magnetic charge on which top end as t ...
... • A line drawn tangent to a field line is the direction of the field at that point. • The density of field lines still represent the strength of the field. Differences • The magnetic field lines do not terminate on anything. They form complete loops. There is no magnetic charge on which top end as t ...
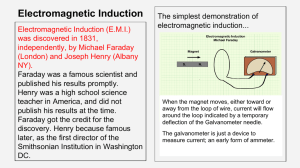
Electromagnetic Induction
... phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
... phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
Chapter 15 - Cloudfront.net
... of tiny particles called atoms which contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons have a certain amount of “electric charge.” ...
... of tiny particles called atoms which contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons have a certain amount of “electric charge.” ...
Wednesday, Mar. 22, 2006 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... Magnetic moment of a hydrogen atom. Determine the magnetic dipole moment of the electron orbiting the proton of a hydrogen atom, assuming (in the Bohr model) it is in its ground state with a circular orbit of radius 0.529x10-10m. What provides the centripetal force? Coulomb force ...
... Magnetic moment of a hydrogen atom. Determine the magnetic dipole moment of the electron orbiting the proton of a hydrogen atom, assuming (in the Bohr model) it is in its ground state with a circular orbit of radius 0.529x10-10m. What provides the centripetal force? Coulomb force ...
Metals that are magnetic
... Check out the *Science Demonstrations link for some neat tricks with magnets. Or check out this video about "LINEMEN" who repair power lines: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7gl-_Liz_0o ...
... Check out the *Science Demonstrations link for some neat tricks with magnets. Or check out this video about "LINEMEN" who repair power lines: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7gl-_Liz_0o ...
Chapter 28
... • To calculate ΦB we integrate over elements of the flux dΦB relating to elements of area dA of our surface. ...
... • To calculate ΦB we integrate over elements of the flux dΦB relating to elements of area dA of our surface. ...
Answers 7
... A Gaussian sphere of radius r > c will enclose no net charge because it contains +Q on the inner conductor and -Q on the outer conductor. So, E(r) = 0 for r > c. (b) ...
... A Gaussian sphere of radius r > c will enclose no net charge because it contains +Q on the inner conductor and -Q on the outer conductor. So, E(r) = 0 for r > c. (b) ...
This starts from Easy derivation of Maxwell’s and Wave Equation.
... of light is c and we define the index of refraction as ratio of ǫµ to its value in free space. Thus nf ree = 1, and the relative index of refraction for materials is dimensionless and small: water- 4/3; good glass- 3/2; diamond- 2.4; GaP3.5 (c.f., page 94 Hecht). Going to equation above and replacin ...
... of light is c and we define the index of refraction as ratio of ǫµ to its value in free space. Thus nf ree = 1, and the relative index of refraction for materials is dimensionless and small: water- 4/3; good glass- 3/2; diamond- 2.4; GaP3.5 (c.f., page 94 Hecht). Going to equation above and replacin ...
Search for effects related to Chiral Magnetic Wave at STAR
... • Is there a smooth transition from 200 GeV to 7.7 GeV? • different magnetic field? ...
... • Is there a smooth transition from 200 GeV to 7.7 GeV? • different magnetic field? ...
Lecture 20
... If one streches his imagination a little, he can then see that the magnetic field forms a circular loop around the axis of the current element. The magnitude of the magnetic field is directly proportional to the current moment and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the s ...
... If one streches his imagination a little, he can then see that the magnetic field forms a circular loop around the axis of the current element. The magnitude of the magnetic field is directly proportional to the current moment and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the s ...
Magnets - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... presence of a magnetic field; however they will usually return to a random arrangement after the field is removed; these are called temporary magnets (like iron) – kind of like induction for charges • Other materials will not easily align the domains, however once aligned they will remain aligned; t ...
... presence of a magnetic field; however they will usually return to a random arrangement after the field is removed; these are called temporary magnets (like iron) – kind of like induction for charges • Other materials will not easily align the domains, however once aligned they will remain aligned; t ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.