2011 B R = 0.12 m). Therefore,
... DV2 = k 2s This shows that DV1 > DV2 . Since W = qDV, arrangement 1 will require more work to remove the particle at the upper right corner from its present position to a distance a long way away from the arrangement. ...
... DV2 = k 2s This shows that DV1 > DV2 . Since W = qDV, arrangement 1 will require more work to remove the particle at the upper right corner from its present position to a distance a long way away from the arrangement. ...
$doc.title
... 28.7 cm and it is inside a uniform magnetic field of B = 0.303 T, pointing into the plane of the paper. The loop is grasped at points P and Q and stretched until its area is zero. It ...
... 28.7 cm and it is inside a uniform magnetic field of B = 0.303 T, pointing into the plane of the paper. The loop is grasped at points P and Q and stretched until its area is zero. It ...
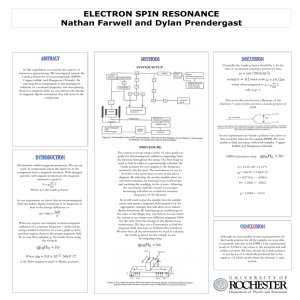
Poster: ESR
... This is not the case however. Because of the electrons ½ spin system, we have a Lande g-factor of ...
... This is not the case however. Because of the electrons ½ spin system, we have a Lande g-factor of ...
Document
... electric field, whereas the magnetic force acts perpendicular to the magnetic field. The electric force acts on a charged particle regardless of whether the particle is moving, whereas the magnetic force acts on a charged particle only when the particle is in motion. The electric force does work in ...
... electric field, whereas the magnetic force acts perpendicular to the magnetic field. The electric force acts on a charged particle regardless of whether the particle is moving, whereas the magnetic force acts on a charged particle only when the particle is in motion. The electric force does work in ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.











![[ ] ò](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003342726_1-ee49ebd06847e97887fd674790b89095-300x300.png)