Design, Modeling and Simulation of Optoelectronic Devices
... – 1. accelerated charge creates time-varying magnetic field in its neighborhood (through the time-varying conduction current and following Ampere’s law); – 2. time-varying magnetic field excites electric field in its neighborhood (through Faraday’s law) – 3. time-varying electric field excites magne ...
... – 1. accelerated charge creates time-varying magnetic field in its neighborhood (through the time-varying conduction current and following Ampere’s law); – 2. time-varying magnetic field excites electric field in its neighborhood (through Faraday’s law) – 3. time-varying electric field excites magne ...
L24_A2_2009_10_CoulombsLaw
... Two point charges Q1 is +6.3nC & Q2 is 2.7nC exerts a force of 3.2x10-5N when they are d metres apart a. Find d b. Find the force if d increases to 3d [69mm] [3.6 x 10-6N] e = -1.6 x 10-19 C 0 = 8.85 x 10-12 F/m ...
... Two point charges Q1 is +6.3nC & Q2 is 2.7nC exerts a force of 3.2x10-5N when they are d metres apart a. Find d b. Find the force if d increases to 3d [69mm] [3.6 x 10-6N] e = -1.6 x 10-19 C 0 = 8.85 x 10-12 F/m ...
Electric Field - Sites at Penn State
... towards it. A single static1 charge rarely occurs and is considered to be an ideal case. It is more realistic to look at the interaction of two charges on a same plane. In Figure 1 (a), a positive and a negative charges are present. Therefore, the electric field lines are directed towards the negati ...
... towards it. A single static1 charge rarely occurs and is considered to be an ideal case. It is more realistic to look at the interaction of two charges on a same plane. In Figure 1 (a), a positive and a negative charges are present. Therefore, the electric field lines are directed towards the negati ...
ppt
... the conductor as long as there is motion through the field • If the motion is reversed, the polarity of the potential difference is also reversed ...
... the conductor as long as there is motion through the field • If the motion is reversed, the polarity of the potential difference is also reversed ...
General Physics I - University of Rochester
... Magnetic field of the Earth • Earth has a magnetic field B~5x10-5 T • Compass - a small magnet in a form of an arrow - is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field • South magnetic pole is located close to the north geographic pole, that is why north end of the compass is pole is pointi ...
... Magnetic field of the Earth • Earth has a magnetic field B~5x10-5 T • Compass - a small magnet in a form of an arrow - is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field • South magnetic pole is located close to the north geographic pole, that is why north end of the compass is pole is pointi ...
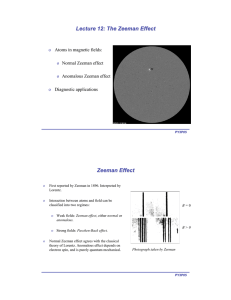
o Atoms in magnetic fields: Normal Zeeman effect Anomalous Zeeman effect
... theory of Lorentz. Anomalous effect depends on electron spin, and is purely quantum mechanical. ...
... theory of Lorentz. Anomalous effect depends on electron spin, and is purely quantum mechanical. ...
Quiz 10 Review – Chapter 24 - Answers
... 7. Name three facts about the magnetic field of the Earth. (1) The magnetic field of the Earth is tilted away from the Earth’s rotational axis by about 10° or 11°. This means that magnetic north/south and true north/south are at different locations. (2) The south pole of Earth’s magnetic field lies ...
... 7. Name three facts about the magnetic field of the Earth. (1) The magnetic field of the Earth is tilted away from the Earth’s rotational axis by about 10° or 11°. This means that magnetic north/south and true north/south are at different locations. (2) The south pole of Earth’s magnetic field lies ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.