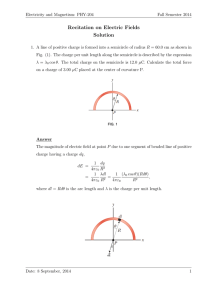
2. Electric field and electric potential (including point charges)
... a. Students should understand the concept of electric charge so they can: 1. Describe the types of charge and the attraction and repulsion of charges. 2. Describe polarization and induced charges. b. Students should understand Coulomb’s Law and the principle of superposition so they can: 1. Calculat ...
... a. Students should understand the concept of electric charge so they can: 1. Describe the types of charge and the attraction and repulsion of charges. 2. Describe polarization and induced charges. b. Students should understand Coulomb’s Law and the principle of superposition so they can: 1. Calculat ...
Some Aspects of Mean Field Dynamo Theory - Indico
... With a judicial choice of α and β (and differential rotation ω) it is possible to reproduce a whole range of observed astrophysical magnetic fields. e.g. butterfly diagrams for dipolar and quadrupolar fields: ...
... With a judicial choice of α and β (and differential rotation ω) it is possible to reproduce a whole range of observed astrophysical magnetic fields. e.g. butterfly diagrams for dipolar and quadrupolar fields: ...
electromagneticinduction1copy
... Dynamic (Motional) EMF Due to Translatory Motion (1) Consider a conducting rod of length l moving with a uniform velocity × ...
... Dynamic (Motional) EMF Due to Translatory Motion (1) Consider a conducting rod of length l moving with a uniform velocity × ...
Psc CH-21 Electric Fields
... field strength when a 25 N force is exerted on a charge of + 5.0 x ...
... field strength when a 25 N force is exerted on a charge of + 5.0 x ...
Assignment 7 Solutions
... We can figure out the forces experienced by each side using the right hand rule, to get a good visualization of what’s causing the torque, and what direction it would be in. However, we can also use the rule: τ = IAB sin θ where θ is the angle between the magnetic field and the area vector of the lo ...
... We can figure out the forces experienced by each side using the right hand rule, to get a good visualization of what’s causing the torque, and what direction it would be in. However, we can also use the rule: τ = IAB sin θ where θ is the angle between the magnetic field and the area vector of the lo ...
Deflection of a Magnetic Needle in a Static Electric Field which Varies
... true. When a charged particle tries to move towards a bar magnet, as shown by path (a) in Fig. 10, the particle gets deflected in downward direction. This is happening because the net spin current constituted by the unpaired electrons, when we look from N pole to S pole of the bar magnet, is in cloc ...
... true. When a charged particle tries to move towards a bar magnet, as shown by path (a) in Fig. 10, the particle gets deflected in downward direction. This is happening because the net spin current constituted by the unpaired electrons, when we look from N pole to S pole of the bar magnet, is in cloc ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.