Applying Business Ethics
... provided with safe conditions in the workplace. Employees should also feel obligated to bring forward any potential health and safety risks that they notice to ensure the wellbeing of people working in the organisation. When it comes to the difficult issue of employee dismissal, you need to be aware ...
... provided with safe conditions in the workplace. Employees should also feel obligated to bring forward any potential health and safety risks that they notice to ensure the wellbeing of people working in the organisation. When it comes to the difficult issue of employee dismissal, you need to be aware ...
What is Situation Ethics?
... The study above blamed many things on the fact that many people were turning away from the Church’s rules (legalism) and more towards antinomianism (the abandonment of any rules). The world was becoming more secular (non-religious) and people had stopped listening to the Church and their teachings o ...
... The study above blamed many things on the fact that many people were turning away from the Church’s rules (legalism) and more towards antinomianism (the abandonment of any rules). The world was becoming more secular (non-religious) and people had stopped listening to the Church and their teachings o ...
Situation Ethics Revision pp
... The study above blamed many things on the fact that many people were turning away from the Church’s rules (legalism) and more towards antinomianism (the abandonment of any rules). The world was becoming more secular (non-religious) and people had stopped listening to the Church and their teachings o ...
... The study above blamed many things on the fact that many people were turning away from the Church’s rules (legalism) and more towards antinomianism (the abandonment of any rules). The world was becoming more secular (non-religious) and people had stopped listening to the Church and their teachings o ...
12 Substances
... (2a19–20). And the definition of x is the formula that signifies the essence of x (Topics I.5 101b38, VII.5 154a31). We will return to the topic of essence below. For now, it is enough to note that individuals would seem to depend on their species as much as the species do on individuals. But althou ...
... (2a19–20). And the definition of x is the formula that signifies the essence of x (Topics I.5 101b38, VII.5 154a31). We will return to the topic of essence below. For now, it is enough to note that individuals would seem to depend on their species as much as the species do on individuals. But althou ...
The History Of BioMedical Ethics
... decisions and in their interactions with patients. But in giving doctors that freedom society expects them to be able to defend their decisions and actions with reasons...Doctors must be able to show how their decisions and actions relate to the law and to the relevant guidelines.’1 ...
... decisions and in their interactions with patients. But in giving doctors that freedom society expects them to be able to defend their decisions and actions with reasons...Doctors must be able to show how their decisions and actions relate to the law and to the relevant guidelines.’1 ...
Chapter 7
... Explain the conventional approach to business ethics. Differentiate it from the principles approach and ethical tests approach. Analyze economic, legal, and ethical aspects of a decision by using a Venn Model. Identify and explain three models of management ethics. Give examples of each. Describe an ...
... Explain the conventional approach to business ethics. Differentiate it from the principles approach and ethical tests approach. Analyze economic, legal, and ethical aspects of a decision by using a Venn Model. Identify and explain three models of management ethics. Give examples of each. Describe an ...
What is Ethical Humanism Sept. 2015
... Some members associate the word "religion” with creeds and sectarianism. For them, Ethical Culture is a fellowship based upon a philosophy of life, emphasizing education, growth, and social service with the purpose of helping people live better lives. ...
... Some members associate the word "religion” with creeds and sectarianism. For them, Ethical Culture is a fellowship based upon a philosophy of life, emphasizing education, growth, and social service with the purpose of helping people live better lives. ...
FREE Sample Here
... our views or opinions about this, and that when these views are traced to questions of basic values they form the beginnings of an ethical theory. Other questions about whether there is any objective good or right can be deferred to discussions of Chapter 2 on ethical relativism. ...
... our views or opinions about this, and that when these views are traced to questions of basic values they form the beginnings of an ethical theory. Other questions about whether there is any objective good or right can be deferred to discussions of Chapter 2 on ethical relativism. ...
Introduction to Ethics - Department of Computer Science
... • Making ethical decisions is not a science • People do it differently • In ethical decision making the individual must decide what the answer depends on – What the facts are – What harm might be done by each alternative – Which course of action results in the least harm ...
... • Making ethical decisions is not a science • People do it differently • In ethical decision making the individual must decide what the answer depends on – What the facts are – What harm might be done by each alternative – Which course of action results in the least harm ...
Overview of Five Ethical Decision-Making Models
... a. Act on the ethical concerns. (What is my plan of action to follow through on my intent?) Comments: Philosophers, practitioners, and ethicists, and other scholars often commend Rest on the elegant simplicity of his model. However, the model’s parsimonious reduction of a vast array of factors int ...
... a. Act on the ethical concerns. (What is my plan of action to follow through on my intent?) Comments: Philosophers, practitioners, and ethicists, and other scholars often commend Rest on the elegant simplicity of his model. However, the model’s parsimonious reduction of a vast array of factors int ...
FREE Sample Here
... The roots of this system are in the work of Aristotle, who defined virtues as “excellences.” Aristotle believed that we are, by nature, neither good nor evil but become so through training and the acquisition of habits. The principle of the golden mean is that virtue is always the median betwe ...
... The roots of this system are in the work of Aristotle, who defined virtues as “excellences.” Aristotle believed that we are, by nature, neither good nor evil but become so through training and the acquisition of habits. The principle of the golden mean is that virtue is always the median betwe ...
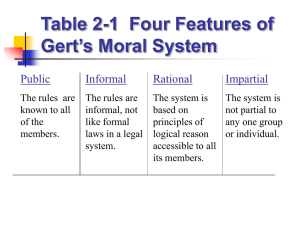
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... The roots of this system are in the work of Aristotle, who defined virtues as “excellences.” Aristotle believed that we are, by nature, neither good nor evil but become so through training and the acquisition of habits. The principle of the golden mean is that virtue is always the median betwe ...
... The roots of this system are in the work of Aristotle, who defined virtues as “excellences.” Aristotle believed that we are, by nature, neither good nor evil but become so through training and the acquisition of habits. The principle of the golden mean is that virtue is always the median betwe ...
VIRTUE IS KNOWLEDGE, MCDOWELL AND ARISTOTLE
... any and all acts of virtue.4 However there is an objection to this Socratic thesis: could not a non-virtuous person perceive a situation in the same way as a virtuous person and nevertheless fail to act virtuously? The answer seems to be yes, yet McDowell argues that this is so not because of some a ...
... any and all acts of virtue.4 However there is an objection to this Socratic thesis: could not a non-virtuous person perceive a situation in the same way as a virtuous person and nevertheless fail to act virtuously? The answer seems to be yes, yet McDowell argues that this is so not because of some a ...
Integrity and Ethics,Mr.Shiva Hari Adhikari
... Ethics refers to well founded standards of right and wrong that prescribe what ought to do, usually in terms of rights, obligations, benefits to society, fairness, or specific virtues. Higher ethical standard and practices is critical in administering work to gain public trust. ...
... Ethics refers to well founded standards of right and wrong that prescribe what ought to do, usually in terms of rights, obligations, benefits to society, fairness, or specific virtues. Higher ethical standard and practices is critical in administering work to gain public trust. ...
I. Ethical Systems: An ethical system is….
... 1. Rather than actions, focuses on what makes a good person 2. In order to be good, one must do good 3. Moral virtue is attained when one displays the median between extremes of character (“principle of the golden mean”) 4. We are neither good nor evil by nature; we become so through our habits 5. “ ...
... 1. Rather than actions, focuses on what makes a good person 2. In order to be good, one must do good 3. Moral virtue is attained when one displays the median between extremes of character (“principle of the golden mean”) 4. We are neither good nor evil by nature; we become so through our habits 5. “ ...
Political ethics
... recommending concepts of right and wrong conduct. • The term comes from the Greek word ethikos from ethos, which means "custom, habit". The superfield within philosophy known as axiology includes both ethics and aesthetics and is unified by each sub-branch's concern with value. • Philosophical ethic ...
... recommending concepts of right and wrong conduct. • The term comes from the Greek word ethikos from ethos, which means "custom, habit". The superfield within philosophy known as axiology includes both ethics and aesthetics and is unified by each sub-branch's concern with value. • Philosophical ethic ...
File - Introduction
... honestly and corporations lack citizenship, social responsibility, and sustainability. But, it starts with ethics. Ethics and Ethical Leadership Many theorists and experts define ethics using words such as “behavior,” “thinking,” and “acting” which are all, by human choice, momentary reactions to su ...
... honestly and corporations lack citizenship, social responsibility, and sustainability. But, it starts with ethics. Ethics and Ethical Leadership Many theorists and experts define ethics using words such as “behavior,” “thinking,” and “acting” which are all, by human choice, momentary reactions to su ...
Lawrence Kohlberg`s Stages of Moral Development from Wikipedia
... theory is overly androcentric.[10] Kohlberg's theory was initially developed based on empirical research using only male participants; Gilligan argued that it did not adequately describe the concerns of women.[21] Kohlberg stated that women tend to get stuck at level 3, focusing on details of how to ...
... theory is overly androcentric.[10] Kohlberg's theory was initially developed based on empirical research using only male participants; Gilligan argued that it did not adequately describe the concerns of women.[21] Kohlberg stated that women tend to get stuck at level 3, focusing on details of how to ...
Developing an Organisational Culture
... Buddhist-Christian view – focus on what is eternally significant, rather than on the ‘self’ Virtues approach – doing the right thing. ...
... Buddhist-Christian view – focus on what is eternally significant, rather than on the ‘self’ Virtues approach – doing the right thing. ...
CSR – FROM ECONOMICS TO LAW AND ETHICS. A CASE AND
... besides, redefine the “profile” of a business person as a benevolent provider for people. The final point will be related to proving that it is CSR that brings about – together with the above-mentioned new type of morality – the turning point in what concerns the relationship between the four social ...
... besides, redefine the “profile” of a business person as a benevolent provider for people. The final point will be related to proving that it is CSR that brings about – together with the above-mentioned new type of morality – the turning point in what concerns the relationship between the four social ...
Chapter 19 PowerPoint Slides
... 6. Explain the differences among the four basic resources for making moral decisions. 7. List the four capacities needed to make moral judgements. 8. Explain how business communication behaviors are related to the study and practice of business ethics. ...
... 6. Explain the differences among the four basic resources for making moral decisions. 7. List the four capacities needed to make moral judgements. 8. Explain how business communication behaviors are related to the study and practice of business ethics. ...