LAB: Magnetism
... 1. Tape the measuring tape or meter stick to the table, and tape the Magnetic Field Sensor to a convenient location. The sensor should be perpendicular to the stick, with the white spot inside the rod facing along the meter stick in the direction of increasing distance. Carefully measure the locatio ...
... 1. Tape the measuring tape or meter stick to the table, and tape the Magnetic Field Sensor to a convenient location. The sensor should be perpendicular to the stick, with the white spot inside the rod facing along the meter stick in the direction of increasing distance. Carefully measure the locatio ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... the magnetic field is parallel to the loop, no field lines pass through the loop and therefore the flux is zero. • Similarly if the magnetic field is perpendicular to the loop, the most field lines possible can pass through the coil and the flux is a maximum. ...
... the magnetic field is parallel to the loop, no field lines pass through the loop and therefore the flux is zero. • Similarly if the magnetic field is perpendicular to the loop, the most field lines possible can pass through the coil and the flux is a maximum. ...
Chapters 21-29
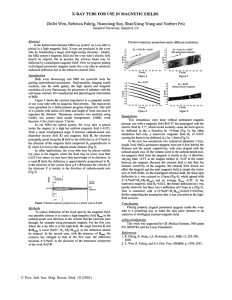
... A beam consisting of five types of ions labeled A, B, C, D, and E enters a region that contains a uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure below. The field is perpendicular to the plane of the paper, but its precise direction is not given. All ions in the beam travel with the same speed.The tab ...
... A beam consisting of five types of ions labeled A, B, C, D, and E enters a region that contains a uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure below. The field is perpendicular to the plane of the paper, but its precise direction is not given. All ions in the beam travel with the same speed.The tab ...
dimensions and kinematics in
... (a) A does not imply B and B does not imply A (b) A implies B but B does not imply A (c) A does not imply B but B implies A (d) A implies B and B implies A 30. Two coils are placed close to each other. The mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends upon: (a) the rates at which currents are chang ...
... (a) A does not imply B and B does not imply A (b) A implies B but B does not imply A (c) A does not imply B but B implies A (d) A implies B and B implies A 30. Two coils are placed close to each other. The mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends upon: (a) the rates at which currents are chang ...
Phet Exploration: Magnets, Transformers, and Generators
... Challenge: Use the field meter, and make a table showing magnetic field strength (“B”, measured in “Gauss”) vs. distance from the end of the magnet. (There are no units given for position, so just use arbitrary units of “one compass away”, “two compasses away”, etc. Alternatively, you can tape a rul ...
... Challenge: Use the field meter, and make a table showing magnetic field strength (“B”, measured in “Gauss”) vs. distance from the end of the magnet. (There are no units given for position, so just use arbitrary units of “one compass away”, “two compasses away”, etc. Alternatively, you can tape a rul ...
Section example:
... The height of ΔE can be modified with an applied voltage ( higher V, lower ΔE, more current flows). If an electron has more energy than ΔE than it will flow from the emitter to collector. Below is a plot of the logarithm of current vs. voltage. ...
... The height of ΔE can be modified with an applied voltage ( higher V, lower ΔE, more current flows). If an electron has more energy than ΔE than it will flow from the emitter to collector. Below is a plot of the logarithm of current vs. voltage. ...
Solutions
... between voltmeter 2 and R R so voltmeter 1 measures the voltage across R and voltmeter 2 measures the voltage across ross R R. Let the current through all resistors be i, using ohm’s law to determine the voltage across R to be iR and that across R R to be 2iR. Therefore V2 reads 2mV. 5. A rod with r ...
... between voltmeter 2 and R R so voltmeter 1 measures the voltage across R and voltmeter 2 measures the voltage across ross R R. Let the current through all resistors be i, using ohm’s law to determine the voltage across R to be iR and that across R R to be 2iR. Therefore V2 reads 2mV. 5. A rod with r ...
$doc.title
... wavelength 429 nm and an index of refraction of 1.610 for red light of wavelength 691 nm. If a beam containing these two colors is incident at an angle of 30.4 degrees on a piece of this ...
... wavelength 429 nm and an index of refraction of 1.610 for red light of wavelength 691 nm. If a beam containing these two colors is incident at an angle of 30.4 degrees on a piece of this ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.