Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
... Magnetic field and number of turns of coil: Magnitude of magnetic field gets summed up with increase in the number of turns of coil. If there are ‘n’ turns of coil, magnitude of magnetic field will be ‘n’ times of magnetic field in case of a single turn of coil. Magnetic Field due to a current in a ...
... Magnetic field and number of turns of coil: Magnitude of magnetic field gets summed up with increase in the number of turns of coil. If there are ‘n’ turns of coil, magnitude of magnetic field will be ‘n’ times of magnetic field in case of a single turn of coil. Magnetic Field due to a current in a ...
Charges, currents & reference frames
... Moving Charges in reference frames O For observer at rest with respect to the external ...
... Moving Charges in reference frames O For observer at rest with respect to the external ...
Physics - WordPress.com
... Electrons have spin and can be crudely pictured as rotating charge, forming a current that produces a magnetic field with a north pole and a south pole. Neither the planetary model nor the image of a spinning electron is completely consistent with modern physics. However, they do provide a useful wa ...
... Electrons have spin and can be crudely pictured as rotating charge, forming a current that produces a magnetic field with a north pole and a south pole. Neither the planetary model nor the image of a spinning electron is completely consistent with modern physics. However, they do provide a useful wa ...
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction 1 Induction Experiments
... 7. When the magnet is turned off, there is a momentary current in the direction opposite to the current when it was turned on. 8. The faster we carry out any of these changes, the greater the current. 9. If all these experiments are repeated with a coil that has the same shape but different material ...
... 7. When the magnet is turned off, there is a momentary current in the direction opposite to the current when it was turned on. 8. The faster we carry out any of these changes, the greater the current. 9. If all these experiments are repeated with a coil that has the same shape but different material ...
Electromagnetism - University of Miami Physics Department
... • Voltage Difference and Power: When an electric charge q moves in an electric field, the field does work on the charge. We say that the charge has moved across a voltage difference V , where the work W = qV . For example, a 3 Coulomb charge that moves across 1.5 Volts, has had 4.5 Joules of work do ...
... • Voltage Difference and Power: When an electric charge q moves in an electric field, the field does work on the charge. We say that the charge has moved across a voltage difference V , where the work W = qV . For example, a 3 Coulomb charge that moves across 1.5 Volts, has had 4.5 Joules of work do ...
Electromagnet

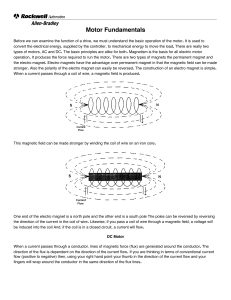
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.