Std Exam Guide
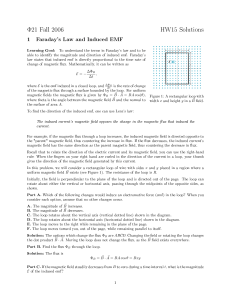
... magnitude is a function of one coordinate, through a rectangular loop perpendicular to the field. b) Students should understand Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law, so they can: (1) Recognize situations in which changing flux through a loop will cause an induced emf or current in the loop. (2) Calculate th ...
... magnitude is a function of one coordinate, through a rectangular loop perpendicular to the field. b) Students should understand Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law, so they can: (1) Recognize situations in which changing flux through a loop will cause an induced emf or current in the loop. (2) Calculate th ...
Electromagnetism G. L. Pollack and D. R. Stump The Exercise
... to the surface. (In the figure I’ve shown them extending to the image charge inside the sphere, just so that we can see how the field of two point charges would look. But of course E = 0 inside a conducting sphere.) Other field lines extend to ∞ because the net charge of the system is q/2. • If the ...
... to the surface. (In the figure I’ve shown them extending to the image charge inside the sphere, just so that we can see how the field of two point charges would look. But of course E = 0 inside a conducting sphere.) Other field lines extend to ∞ because the net charge of the system is q/2. • If the ...
Switching magnetic vortex core by a single nanosecond current
... pulse current can be considered to be the same as in the case of the switching by the resonant excitation. Figure 4 shows the switching probabilities as a function of pulse duration. The switching probability is defined as the ratio of the number of the core switching events to the total trial numbe ...
... pulse current can be considered to be the same as in the case of the switching by the resonant excitation. Figure 4 shows the switching probabilities as a function of pulse duration. The switching probability is defined as the ratio of the number of the core switching events to the total trial numbe ...
For example: an electric iron draws a current of 4A at 250V. What
... There are two main ways of demonstrating the shape and presence of a magnetic field: By sprinkling iron filings: You can place a bar magnet underneath a sheet of white paper and sprinkle the iron filings on top of the paper. Gently tap the paper. The iron flings align themselves with the magnetic fi ...
... There are two main ways of demonstrating the shape and presence of a magnetic field: By sprinkling iron filings: You can place a bar magnet underneath a sheet of white paper and sprinkle the iron filings on top of the paper. Gently tap the paper. The iron flings align themselves with the magnetic fi ...
August 28 /29th th Electric Fields
... does a charge, q1, exert a force on another charge, q2, when the charges don’t touch? ! The charge, q1, sets up an electric field in its surrounding space ! This electric field has both magnitude and direction which determine the magnitude and direction of the force acting on q2 ! How ...
... does a charge, q1, exert a force on another charge, q2, when the charges don’t touch? ! The charge, q1, sets up an electric field in its surrounding space ! This electric field has both magnitude and direction which determine the magnitude and direction of the force acting on q2 ! How ...
Magnetic Field Strength H
... So for an ordinary iron core you might expect a magnification of about 200 compared to the magnetic field produced by the solenoid current with just an air core. This statement has exceptions and limits, since you do reach a saturation magnetization of the iron core quickly, as illustrated in the di ...
... So for an ordinary iron core you might expect a magnification of about 200 compared to the magnetic field produced by the solenoid current with just an air core. This statement has exceptions and limits, since you do reach a saturation magnetization of the iron core quickly, as illustrated in the di ...
Collisionless Shocks
... • If the shock generates a power-law spectrum of accelerated particles, the ions will go farther than the electrons. • The ion cosmic ray precursor of the shock may excite disturbances in the shock upstream, e.g., by current-driven interactions. • In GRB afterglows, the precursor has enough energy t ...
... • If the shock generates a power-law spectrum of accelerated particles, the ions will go farther than the electrons. • The ion cosmic ray precursor of the shock may excite disturbances in the shock upstream, e.g., by current-driven interactions. • In GRB afterglows, the precursor has enough energy t ...
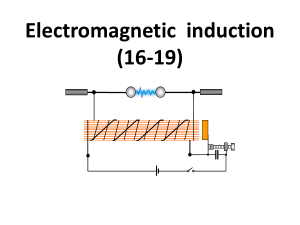
PChapter 18 Electromagnetic Induction
... area vector A (30o above the magnetic field B), the positive direction for ε is clockwise, according to the right-hand rule. The emf in this example is in fact positive and thus is clockwise. If the ends of the wire are connected together, the direction of current in the coil is clockwise. A clockwi ...
... area vector A (30o above the magnetic field B), the positive direction for ε is clockwise, according to the right-hand rule. The emf in this example is in fact positive and thus is clockwise. If the ends of the wire are connected together, the direction of current in the coil is clockwise. A clockwi ...
VCE PHYSICS UNIT 3
... A SOLENOID is, by definition, a series of loops of wire placed side by side to form a coil. In reality, solenoids are produced by winding a single piece of wire around a cylindrical “former”. When a current flows through the wire, a strong, uniform magnetic field is produced down the centre of the c ...
... A SOLENOID is, by definition, a series of loops of wire placed side by side to form a coil. In reality, solenoids are produced by winding a single piece of wire around a cylindrical “former”. When a current flows through the wire, a strong, uniform magnetic field is produced down the centre of the c ...
quadrupole magnet
... An external B-field, created by a current I, creates a B-field in iron by aligning tiny internal dipoles (electron spins) in the material. However, if the current and external field are dropped to zero, the material remains partially magnetized. This gives rise to “hysteresis” and the need for magne ...
... An external B-field, created by a current I, creates a B-field in iron by aligning tiny internal dipoles (electron spins) in the material. However, if the current and external field are dropped to zero, the material remains partially magnetized. This gives rise to “hysteresis” and the need for magne ...
COMPARISON OF NDT METHODS MAGNETIC PARTICLE
... applied to the part while the magnetizing current is flowing, a technique known as the "continuous method.” When the magnetic particles are applied after the current has ceased to flow, depending largely on the magnetization retention (residual magnetism), it is called the "residual method." If resi ...
... applied to the part while the magnetizing current is flowing, a technique known as the "continuous method.” When the magnetic particles are applied after the current has ceased to flow, depending largely on the magnetization retention (residual magnetism), it is called the "residual method." If resi ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.