Duty Ethics
... Virtue ethics focuses on the person that we would like to become. In virtue ethics, actions are considered right if they support good character traits. The words responsibility, honesty, competence, loyalty are of paramouth importance for virtue ethics. The opposite of virtue is vice (irresponsibili ...
... Virtue ethics focuses on the person that we would like to become. In virtue ethics, actions are considered right if they support good character traits. The words responsibility, honesty, competence, loyalty are of paramouth importance for virtue ethics. The opposite of virtue is vice (irresponsibili ...
Materialy/07/History of Ethics
... that a life detached from the natural events of life will be calmer and less troubled than a life bound up with false desires for worldly things. ...
... that a life detached from the natural events of life will be calmer and less troubled than a life bound up with false desires for worldly things. ...
Business Ethics
... This myth holds that information and computing are neither moral nor immoral, but are amoral, i.e., they are in "gray zone," a questionable area regarding ethics. Information about individuals can be used as “a form of control, power, and manipulation. The point here is to beware of the dark side: ...
... This myth holds that information and computing are neither moral nor immoral, but are amoral, i.e., they are in "gray zone," a questionable area regarding ethics. Information about individuals can be used as “a form of control, power, and manipulation. The point here is to beware of the dark side: ...
Ethical Decision Making in Business
... Pat is being interviewed by Ken as a possible consultant to the City in negotiating a new water contract. Pat asks for a fee of $600 per day for an estimated 10 days of consulting work, for a total fee of $6,000. Ken counters with an offer of a $20,000 fee, for political reasons, and requests Pat t ...
... Pat is being interviewed by Ken as a possible consultant to the City in negotiating a new water contract. Pat asks for a fee of $600 per day for an estimated 10 days of consulting work, for a total fee of $6,000. Ken counters with an offer of a $20,000 fee, for political reasons, and requests Pat t ...
The Study of Ethics
... • 3) Asks the Question: “ What gives people what they deserve? “What rewards or promotes Virtue?” (Aristotle) ...
... • 3) Asks the Question: “ What gives people what they deserve? “What rewards or promotes Virtue?” (Aristotle) ...
Business Ethics Fundamentals
... view that there is no objective truth in morality, right and wrong are only matters of opinion that vary from culture to culture, and possibly, from person to person. ...
... view that there is no objective truth in morality, right and wrong are only matters of opinion that vary from culture to culture, and possibly, from person to person. ...
Slide 1
... Singapore, the UK and other countries have on their websites professional codes of ethics to consider and adopt in the way professionals conduct themselves in and out of the work place. Personal ethics, morality, and integrity will strongly influence a person’s professional ethical conduct. Integrit ...
... Singapore, the UK and other countries have on their websites professional codes of ethics to consider and adopt in the way professionals conduct themselves in and out of the work place. Personal ethics, morality, and integrity will strongly influence a person’s professional ethical conduct. Integrit ...
Ethics & Values
... – Private, personal standards of right and wrong • Laws reflect moral values of society • Nurses have ethical responsibility to be client advocates ...
... – Private, personal standards of right and wrong • Laws reflect moral values of society • Nurses have ethical responsibility to be client advocates ...
lecture
... generally seem less than conclusive. What are the other options? -Morality based on Rules/Principles -Morality based upon Character ...
... generally seem less than conclusive. What are the other options? -Morality based on Rules/Principles -Morality based upon Character ...
ETHICS AT THE PEAK - Naval Postgraduate School
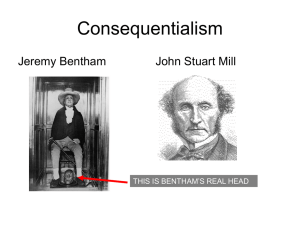
... Will it produce a desired result? Identify/predict goals, results and benefits Teleological: end justifies the means Ethical Theories Consequentialism – balancing good and bad outcomes Utilitarian – maximize benefit for greatest number Egoism – do whatever is best for me and only me Pragmatism – wha ...
... Will it produce a desired result? Identify/predict goals, results and benefits Teleological: end justifies the means Ethical Theories Consequentialism – balancing good and bad outcomes Utilitarian – maximize benefit for greatest number Egoism – do whatever is best for me and only me Pragmatism – wha ...
Ethics - Lagemaat - TOK-eisj
... 1. It is not always clear what the outcome of an action will be, nor is it always possible to determine who will be affected by it. Judging an action by the outcome is therefore hard to do beforehand. 2. It is very difficult to quantify pleasures for cost/benefit analysis (but since this only has to ...
... 1. It is not always clear what the outcome of an action will be, nor is it always possible to determine who will be affected by it. Judging an action by the outcome is therefore hard to do beforehand. 2. It is very difficult to quantify pleasures for cost/benefit analysis (but since this only has to ...
8.1 What are ethics
... What major types of ethical and unethical conduct are likely to occur in negotiation? What factors shape a negotiator’s predisposition to use unethical tactics? How can negotiators deal with the other party’s use of deception? ...
... What major types of ethical and unethical conduct are likely to occur in negotiation? What factors shape a negotiator’s predisposition to use unethical tactics? How can negotiators deal with the other party’s use of deception? ...
SEEING THE LIGHT
... What ought I do in the face of this ethical dilemma? What is my duty? What am I morally obligated to do? What ethical guidelines should I follow? ...
... What ought I do in the face of this ethical dilemma? What is my duty? What am I morally obligated to do? What ethical guidelines should I follow? ...
Developing an Effective Ethics Program
... formal structural restraints and guidance on ethical issues ...
... formal structural restraints and guidance on ethical issues ...
The motivation to be ethical
... to behave morally toward their patients. Kant suggested that the ability to reason is the basis of morality and therefore himself reasoned that all persons, being rational beings, have the right to common dignity and respect. These are fundamental tenets in our modern Ethical Code. Kant expressed th ...
... to behave morally toward their patients. Kant suggested that the ability to reason is the basis of morality and therefore himself reasoned that all persons, being rational beings, have the right to common dignity and respect. These are fundamental tenets in our modern Ethical Code. Kant expressed th ...
the discipline of ethics
... evil. • Here the concern is for norms of value: what is good? What is bad? What is the highest good? ...
... evil. • Here the concern is for norms of value: what is good? What is bad? What is the highest good? ...
Ethics
... LO3 Outline a process for making ethical decisions. LO4 Summarize the important issues surrounding corporate social responsibility. LO5 Discuss reasons for businesses’ growing interest in the natural environment. LO6 Identify actions managers can take to manage with the environment in mind. ...
... LO3 Outline a process for making ethical decisions. LO4 Summarize the important issues surrounding corporate social responsibility. LO5 Discuss reasons for businesses’ growing interest in the natural environment. LO6 Identify actions managers can take to manage with the environment in mind. ...
Ethics
... Ethics - Standards of conduct. Ethiko (Greek) – habit. Two dimensions -prudence (right) and virtue (good). ...
... Ethics - Standards of conduct. Ethiko (Greek) – habit. Two dimensions -prudence (right) and virtue (good). ...
Philosophy 323
... identification of the good as happiness. Mill’s TRA is called the Greatest Happiness Principle, and it states, “Actions are right…in proportion to their tendency to promote happiness or the absence of pain, and wrong insofar as the tend to produce pain or displeasure” (19). ...
... identification of the good as happiness. Mill’s TRA is called the Greatest Happiness Principle, and it states, “Actions are right…in proportion to their tendency to promote happiness or the absence of pain, and wrong insofar as the tend to produce pain or displeasure” (19). ...
Day 1 Fundamentals o..
... Any ethical lapse in a company erodes its culture • Society is seeking (2000s) new emphasis on values, morals, ethics ...
... Any ethical lapse in a company erodes its culture • Society is seeking (2000s) new emphasis on values, morals, ethics ...
STEVE SMITH - Society of Corporate Compliance and Ethics
... An action is right, compared to other courses of action, if it results in the greatest good for the greatest number of people (or at least minimum harm). Example: “Utilitarianism” There are no universal principles that can guide action, but rather likely benefits and costs associated with any action ...
... An action is right, compared to other courses of action, if it results in the greatest good for the greatest number of people (or at least minimum harm). Example: “Utilitarianism” There are no universal principles that can guide action, but rather likely benefits and costs associated with any action ...
The moral philosophy of Immanuel Kant (1724
... The moral philosophy of Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) is one of the most influential in the western intellectual tradition. Kant accepted the metaphor / model of „law‟ for understanding the nature of moral obligation. But rather than the moral law being found in a sacred scripture, sacred institutions o ...
... The moral philosophy of Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) is one of the most influential in the western intellectual tradition. Kant accepted the metaphor / model of „law‟ for understanding the nature of moral obligation. But rather than the moral law being found in a sacred scripture, sacred institutions o ...
University Of Phoenix Faculty Material
... systems come from Biblical or other sacred tenets. Some principles of morality are binding, regardless of consequences. This focuses on particular duty instead of results. Moral obligation is more important that what a person wants to do.(Treviño & Nelson, 2007, Ch. 4). ...
... systems come from Biblical or other sacred tenets. Some principles of morality are binding, regardless of consequences. This focuses on particular duty instead of results. Moral obligation is more important that what a person wants to do.(Treviño & Nelson, 2007, Ch. 4). ...
Teaching Ethical Behavior
... Dilemmas are good-good conflicts. That is, there is a choice between two equally acceptable (or good) choices of action. A true moral dilemma requires that one rejects, or turns away from, one moral choice for the sake of another. ...
... Dilemmas are good-good conflicts. That is, there is a choice between two equally acceptable (or good) choices of action. A true moral dilemma requires that one rejects, or turns away from, one moral choice for the sake of another. ...