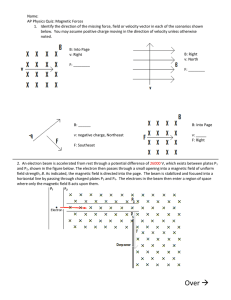
Quiz 19.2–AP–Magnetic Fields
... and P2, shown in the figure below. The electron then passes through a small opening into a magnetic field of uniform field strength, B. As indicated, the magnetic field is directed into the page. The beam is stabilized and focused into a horizontal line by passing through charged plates P3 and P4. T ...
... and P2, shown in the figure below. The electron then passes through a small opening into a magnetic field of uniform field strength, B. As indicated, the magnetic field is directed into the page. The beam is stabilized and focused into a horizontal line by passing through charged plates P3 and P4. T ...
Lecture 13 - UD Physics
... A mass m1 slides in a circular path with speed v on a horizontal frictionless table. It is held at a radius R by a string threaded through a frictionless hole at the center of the table. At the other end of the string hangs a second mass m2. ÍWhat is the tension (T) in the string? ÍWhat is the speed ...
... A mass m1 slides in a circular path with speed v on a horizontal frictionless table. It is held at a radius R by a string threaded through a frictionless hole at the center of the table. At the other end of the string hangs a second mass m2. ÍWhat is the tension (T) in the string? ÍWhat is the speed ...
QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS AND GRAVITATION
... were both equal to 1, and ε0 as if it equaled 1/4π) - neither the charge nor the mass of the electron or any other other charged particle can actually be calculated in QED they have to be assumed. This is because they are seen as the ‘end-products’, as it were, of an infinite series of Feynman diagr ...
... were both equal to 1, and ε0 as if it equaled 1/4π) - neither the charge nor the mass of the electron or any other other charged particle can actually be calculated in QED they have to be assumed. This is because they are seen as the ‘end-products’, as it were, of an infinite series of Feynman diagr ...
Document
... energy/momentum that observers in any inertial frame will measure the as the same – For energy and momentum this invariant says that all observers can agree on mass an object has when it’s at rest! ...
... energy/momentum that observers in any inertial frame will measure the as the same – For energy and momentum this invariant says that all observers can agree on mass an object has when it’s at rest! ...
Semiclassical motion in a perpendicular uniform electric
... The last line is possible since w × H = wH By definition w is perpendicular to H. Thus the equation of motion can be written in a fashion such that it is the equation of motion an electron would have if only the magentic field H is present and if the band structure is given by Ē(k) = E(k) − ~k · w ...
... The last line is possible since w × H = wH By definition w is perpendicular to H. Thus the equation of motion can be written in a fashion such that it is the equation of motion an electron would have if only the magentic field H is present and if the band structure is given by Ē(k) = E(k) − ~k · w ...
The Lorentz Force
... of the velocity does not change. (b) If the electron (or any charged particle) moves at an angle other than 0° or 180° the velocity component parallel to B continues pointing in that direction while the component perpendicular to B rotates in a circle. The combined motion is a helix. ...
... of the velocity does not change. (b) If the electron (or any charged particle) moves at an angle other than 0° or 180° the velocity component parallel to B continues pointing in that direction while the component perpendicular to B rotates in a circle. The combined motion is a helix. ...
Summary Sheet – Waves, Sound, Electricity, Magnetism, Light
... where k = 9.0 × 10 9 N⋅ m 2 C 2 and q1, q2 are the charges separated by distance d. K. Electric charges are surrounded by an electric field equal to the force experienced by a unit positive charge (+1.0 C). E = Felectrical / q. The electrical potential energy of a charged object in an electric field ...
... where k = 9.0 × 10 9 N⋅ m 2 C 2 and q1, q2 are the charges separated by distance d. K. Electric charges are surrounded by an electric field equal to the force experienced by a unit positive charge (+1.0 C). E = Felectrical / q. The electrical potential energy of a charged object in an electric field ...
Chapter 1: Physics Basics (PDF file)
... Electricity consists of the range of physical phenomena which result from the presence of electric charge. Magnetism consists of phenomena which result from the motion of charge. The fields of electricity and magnetism are unified by Maxwell's equations. These equations describe a wave associated wi ...
... Electricity consists of the range of physical phenomena which result from the presence of electric charge. Magnetism consists of phenomena which result from the motion of charge. The fields of electricity and magnetism are unified by Maxwell's equations. These equations describe a wave associated wi ...