
幻灯片 1
... (1774-1862) and Felix Savart (1791-1841) were the first to provide a precise analysis of the effect. Biot and Savart announced the Biot-Savart Law which can be used to calculate the magnetic field for a segment of current ...
... (1774-1862) and Felix Savart (1791-1841) were the first to provide a precise analysis of the effect. Biot and Savart announced the Biot-Savart Law which can be used to calculate the magnetic field for a segment of current ...
Q - WordPress.com
... is the charge on one electron or one proton: e= 1.602 x 10-19 Coulombs No smaller charge has ever been detected in an ...
... is the charge on one electron or one proton: e= 1.602 x 10-19 Coulombs No smaller charge has ever been detected in an ...
PHYS 196 Class Problem 1
... 6. A spherical shell of radius 25cm has a surface charge density 48nC / m 2 . Find the electric field at a point (a) just outside the surface, (b) in the interior, and (c) at a distance 50cm from the center. 7. A solid sphere of radius 25cm carries a total charge 72nC uniformly distributed over its ...
... 6. A spherical shell of radius 25cm has a surface charge density 48nC / m 2 . Find the electric field at a point (a) just outside the surface, (b) in the interior, and (c) at a distance 50cm from the center. 7. A solid sphere of radius 25cm carries a total charge 72nC uniformly distributed over its ...
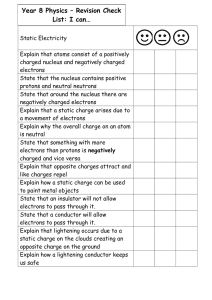
Year 8 Physics Revision Checklist1.02 MB
... heat energy much faster than light ones State that white colours reflect heat energy Explain why air is a good insulator Explain why air will not prevent heat transfer via radiation Calculating the speed of an EM wave: A laser (red light) is shone up to a satellite that is orbiting 35786km above the ...
... heat energy much faster than light ones State that white colours reflect heat energy Explain why air is a good insulator Explain why air will not prevent heat transfer via radiation Calculating the speed of an EM wave: A laser (red light) is shone up to a satellite that is orbiting 35786km above the ...
On the Conservative Nature of Electrostatic Fields
... Similarly, if the charge is distributed on surface S’ with charge density ρs then: ...
... Similarly, if the charge is distributed on surface S’ with charge density ρs then: ...
Historical burdens on physics 57 Instantaneous and average velocity
... equation v = s/t describes the relation between the velocity, the travelled distance and the time that is needed in the case that the velocity is constant. If it is not constant, we proceed in the same way as we do with other physical quantities whose values changes with time. The velocity is measur ...
... equation v = s/t describes the relation between the velocity, the travelled distance and the time that is needed in the case that the velocity is constant. If it is not constant, we proceed in the same way as we do with other physical quantities whose values changes with time. The velocity is measur ...
Slide 1
... ConcepTest #3: A dipole has charges +q and –q separated by some distance. The dipole sits in a uniform electric field that points to the right. What is the direction of the net force acting on the dipole? ...
... ConcepTest #3: A dipole has charges +q and –q separated by some distance. The dipole sits in a uniform electric field that points to the right. What is the direction of the net force acting on the dipole? ...
10.1 Properties of Electric Charges
... 1 Coulomb is the amount of charge, that if placed 1 m apart would result in a force of 9x109 N Charges are quantized – that is they come in discrete values ...
... 1 Coulomb is the amount of charge, that if placed 1 m apart would result in a force of 9x109 N Charges are quantized – that is they come in discrete values ...
Chapter 22: The Electric Field
... NOTE: This is a good example of a special result, which is the answer to an example problem, not a fundamental principle to be memorized. It is the process we are supposed to be learning, not the result! ...
... NOTE: This is a good example of a special result, which is the answer to an example problem, not a fundamental principle to be memorized. It is the process we are supposed to be learning, not the result! ...
Homework#1, Problem 1 - Louisiana State University
... At each point on the surface of the cube shown in Fig. 24-26, the electric field is in the z direction. The length of each edge of the cube is 2.3 m. On the top surface of the cube E = -38 k N/C, and on the bottom face of the cube E = +11 k N/C. Determine the net charge contained within the cube. [- ...
... At each point on the surface of the cube shown in Fig. 24-26, the electric field is in the z direction. The length of each edge of the cube is 2.3 m. On the top surface of the cube E = -38 k N/C, and on the bottom face of the cube E = +11 k N/C. Determine the net charge contained within the cube. [- ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... At each point on the surface of the cube shown in Fig. 24-26, the electric field is in the z direction. The length of each edge of the cube is 2.3 m. On the top surface of the cube E = -38 k N/C, and on the bottom face of the cube E = +11 k N/C. Determine the net charge contained within the cube. [- ...
... At each point on the surface of the cube shown in Fig. 24-26, the electric field is in the z direction. The length of each edge of the cube is 2.3 m. On the top surface of the cube E = -38 k N/C, and on the bottom face of the cube E = +11 k N/C. Determine the net charge contained within the cube. [- ...
If I bring a charged rod to a leaf electrometer: A] nothing will happen
... What vector could represent the electric field at the point shown caused BY THE POSITIVE CHARGE ALONE? B ...
... What vector could represent the electric field at the point shown caused BY THE POSITIVE CHARGE ALONE? B ...
Maxwell`s Equations and the Speed of Light/Electric Motor
... Show that if terms of order a2 /l2 and smaller are ignored, the result of using Baverage to calculate L is to multiply equation 2 by a factor (1 − a/l). Use this to correct your value for c. 4. Equation 1 for the capacitance is also an approximation: It assumes the electric field is uniform right up ...
... Show that if terms of order a2 /l2 and smaller are ignored, the result of using Baverage to calculate L is to multiply equation 2 by a factor (1 − a/l). Use this to correct your value for c. 4. Equation 1 for the capacitance is also an approximation: It assumes the electric field is uniform right up ...
















![If I bring a charged rod to a leaf electrometer: A] nothing will happen](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008769966_2-a075434b174735c9950b41e5a4523a29-300x300.png)





