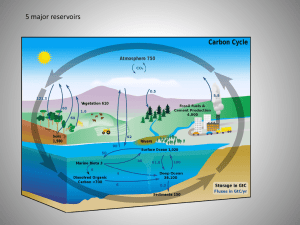
Mass Extinctions
... the impact of an asteroid/comet) may have affected the conditions on Earth and the diversity of its life forms ...
... the impact of an asteroid/comet) may have affected the conditions on Earth and the diversity of its life forms ...
The Royal Meteorological Society
... In a recent survey of the public… • 52% don’t believe climate change will affect them • Only 18% respondents think that climate change will take effect during their children’s lifetime • But 74% said they would make changes to their lifestyle now if they knew climate change was going to affect their ...
... In a recent survey of the public… • 52% don’t believe climate change will affect them • Only 18% respondents think that climate change will take effect during their children’s lifetime • But 74% said they would make changes to their lifestyle now if they knew climate change was going to affect their ...
pdf
... Global mean near near-surface surface temperatures over the 20th century from observations (black) and as obtained from 58 simulations produced by 14 different climate models driven by both natural and humancaused factors that influence climate (yellow). The mean of all these runs is also shown (thi ...
... Global mean near near-surface surface temperatures over the 20th century from observations (black) and as obtained from 58 simulations produced by 14 different climate models driven by both natural and humancaused factors that influence climate (yellow). The mean of all these runs is also shown (thi ...
Introduction and Overview
... (relative to 1980–1999) for the scenarios A2, A1B and B1, shown as continuations of the 20th century simulations. Shading denotes the ±1 standard deviation range of individual model annual averages. The orange line is for the experiment where concentrations were held constant at year 2000 values. Th ...
... (relative to 1980–1999) for the scenarios A2, A1B and B1, shown as continuations of the 20th century simulations. Shading denotes the ±1 standard deviation range of individual model annual averages. The orange line is for the experiment where concentrations were held constant at year 2000 values. Th ...
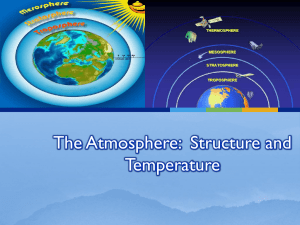
The Atmosphere: Climate and Weather
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
The Gender, Climate Change and Environment Nexus – indicators?
... It is therefore important that environmental management be gender responsive: gender blindness will lead to less effective environmental protection and management in the face of climate change. ...
... It is therefore important that environmental management be gender responsive: gender blindness will lead to less effective environmental protection and management in the face of climate change. ...
Earth System Model (ESM)
... if the warming leads to enhanced rates of decay of organic matter in soils, or a reduction in oceanic carbon uptake, then the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere will rise more rapidly than it would in the absence of such (positive) feedbacks, and the rate of warming will be greater as well. ...
... if the warming leads to enhanced rates of decay of organic matter in soils, or a reduction in oceanic carbon uptake, then the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere will rise more rapidly than it would in the absence of such (positive) feedbacks, and the rate of warming will be greater as well. ...
Week 2: Huerta Climate PPT
... • Sea level – Ice ages cause sea level to rise and fall. – Sea level was ~ 100 m lower during the most recent Ice age – If ice sheets melted, coastal regions would be flooded. ...
... • Sea level – Ice ages cause sea level to rise and fall. – Sea level was ~ 100 m lower during the most recent Ice age – If ice sheets melted, coastal regions would be flooded. ...
Chapter 4
... – Earth’s polar areas annually receive less intense solar energy, and therefore heat, from the sun. – The difference in heat distribution creates three different climate zones: tropical, temperate, and ...
... – Earth’s polar areas annually receive less intense solar energy, and therefore heat, from the sun. – The difference in heat distribution creates three different climate zones: tropical, temperate, and ...
Chapter 4
... – Earth’s polar areas annually receive less intense solar energy, and therefore heat, from the sun. – The difference in heat distribution creates three different climate zones: tropical, temperate, and ...
... – Earth’s polar areas annually receive less intense solar energy, and therefore heat, from the sun. – The difference in heat distribution creates three different climate zones: tropical, temperate, and ...
Honors Earth Science EOC Exam Review
... 47. If Earth’s average temperature increases (global warming), what will be the impact on severe weather events such as hurricanes? Benchmark SC.912.E.7.7: Identify, analyze, and relate the internal (Earth system) and external (astronomical) conditions that contribute to global climate change. 48. W ...
... 47. If Earth’s average temperature increases (global warming), what will be the impact on severe weather events such as hurricanes? Benchmark SC.912.E.7.7: Identify, analyze, and relate the internal (Earth system) and external (astronomical) conditions that contribute to global climate change. 48. W ...
PDF: Printable Version
... summer. The distance between the two research sites, as the arctic tern flies, is 10,289 miles. What the two research teams share is their focus on better understanding how climate change is affecting polar ecosystems. Polar regions are warming faster than anywhere else on Earth, with a rise in aver ...
... summer. The distance between the two research sites, as the arctic tern flies, is 10,289 miles. What the two research teams share is their focus on better understanding how climate change is affecting polar ecosystems. Polar regions are warming faster than anywhere else on Earth, with a rise in aver ...
Name: June Proficiency Exam Study Guide 7th Grade Honors
... 25. What causes global winds? Unequal heating of Earth’s atmosphere 26. What is a front? the boundary where two different air masses meet 27. What is the difference between weather and climate? Give an example of each. Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certai ...
... 25. What causes global winds? Unequal heating of Earth’s atmosphere 26. What is a front? the boundary where two different air masses meet 27. What is the difference between weather and climate? Give an example of each. Weather is the atmospheric conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certai ...
GUIDE OF THE EXAM (2 nd BIMONTHLY)
... 7. They are the earthquakes undersea and cause huge waves. a) Erosions b) Hurricanes c) Tsunamis d) Eruptions 8. They are giant slow-moving sheets of ice. a) Ice breaker b) Greenhouse effect c) Erosion d) Glaciers 9. They are the elements that make changes in our climate. a) Temperature, Atmospheri ...
... 7. They are the earthquakes undersea and cause huge waves. a) Erosions b) Hurricanes c) Tsunamis d) Eruptions 8. They are giant slow-moving sheets of ice. a) Ice breaker b) Greenhouse effect c) Erosion d) Glaciers 9. They are the elements that make changes in our climate. a) Temperature, Atmospheri ...
The Changing Environment - Mr. Hamilton`s Classroom
... away of land by weather and water; a natural process where soil is lost, transported, and reformed. ...
... away of land by weather and water; a natural process where soil is lost, transported, and reformed. ...
Sea level impact on Indo-Pacific climate during glacial times
... “we compared the climate of the ice age with our recent warmer climate. We analyzed about 100 proxy records of rainfall and salinity stretching from the tropical western Pacific to the western Indian Ocean and eastern Africa. Rainfall and salinity signals recorded in geological sediments can tell us ...
... “we compared the climate of the ice age with our recent warmer climate. We analyzed about 100 proxy records of rainfall and salinity stretching from the tropical western Pacific to the western Indian Ocean and eastern Africa. Rainfall and salinity signals recorded in geological sediments can tell us ...
ss9_chapter_2_study_guide
... 2. Describe and account for the varying appearance of Canada’s major mountain ranges. (p. 24) 3. How has erosion affected the appearance of the Appalachian Mountains? (p. 26) 4. Explain which of the eight Canadian landform regions you would prefer to live in? Justify your answer with regard to its p ...
... 2. Describe and account for the varying appearance of Canada’s major mountain ranges. (p. 24) 3. How has erosion affected the appearance of the Appalachian Mountains? (p. 26) 4. Explain which of the eight Canadian landform regions you would prefer to live in? Justify your answer with regard to its p ...
KS4 Earth and atmosphere Learning Objectives
... use their skills to explain why scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur ...
... use their skills to explain why scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur ...
Questions Due Thursday
... Continental-Varied Lat. fairly dry with varied temperatures Veg. adapts to climate ...
... Continental-Varied Lat. fairly dry with varied temperatures Veg. adapts to climate ...
Study Guide for 3rd nine week assessment 2017
... 26. Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced in a short period of time. Ex trees, Plants etc. ...
... 26. Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced in a short period of time. Ex trees, Plants etc. ...
Unit 2: Physical Geography Study Guide for Test Learning Targets:
... c. How does the Earth’s tilt cause places in the midlatitudes to have different seasons? ...
... c. How does the Earth’s tilt cause places in the midlatitudes to have different seasons? ...
History of climate change science

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change the climate. Many other theories of climate change were advanced, involving forces from volcanism to solar variation. In the 1960s, the warming effect of carbon dioxide gas became increasingly convincing, although some scientists also pointed out that human activities, in the form of atmospheric aerosols (e.g., ""pollution""), could have cooling effects as well. During the 1970s, scientific opinion increasingly favored the warming viewpoint. By the 1990s, as a result of improving fidelity of computer models and observational work confirming the Milankovitch theory of the ice ages, a consensus position formed: greenhouse gases were deeply involved in most climate changes, and human emissions were bringing serious global warming.Since the 1990s, scientific research on climate change has included multiple disciplines and has expanded, significantly increasing our understanding of causal relations, links with historic data and ability to numerically model climate change. The most recent work has been summarized in the Assessment Reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions, or in the distribution of weather around the average conditions (i.e., more or fewer extreme weather events). Climate change is caused by factors that include oceanic processes (such as oceanic circulation), biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics and volcanic eruptions, and human-induced alterations of the natural world; these latter effects are currently causing global warming, and ""climate change"" is often used to describe human-specific impacts.