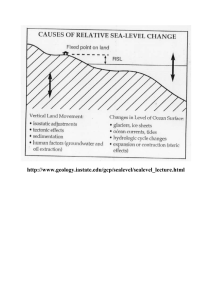
Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms
... Crustal movements may be local or global in scale. For example, tectonic activity along mid-ocean ridges will cause eustatic sea-level changes that are expressed worldwide. The most common tectonic mechanism to impact global sea-level change is the movement of the earth's lithospheric plates. This i ...
... Crustal movements may be local or global in scale. For example, tectonic activity along mid-ocean ridges will cause eustatic sea-level changes that are expressed worldwide. The most common tectonic mechanism to impact global sea-level change is the movement of the earth's lithospheric plates. This i ...
2011 Annual Report
... situ measurements of HMMV emissions in order to determine if they were carbon dioxide or methane. The results, German said, are very encouraging. “The sub-bottom profiler has great potential as a system that can be used in the systematic exploration for further cold seep sites along previously uninv ...
... situ measurements of HMMV emissions in order to determine if they were carbon dioxide or methane. The results, German said, are very encouraging. “The sub-bottom profiler has great potential as a system that can be used in the systematic exploration for further cold seep sites along previously uninv ...
CH 3 - 4
... crop, and the next year a soil enriching crop is planted. Desertification – process by which the loss of plant cover and soil eventually leads to desert ...
... crop, and the next year a soil enriching crop is planted. Desertification – process by which the loss of plant cover and soil eventually leads to desert ...
The Dynamic Earth
... Some heat escapes Some heat is trapped by Greenhouse Gases Ex: water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide ...
... Some heat escapes Some heat is trapped by Greenhouse Gases Ex: water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide ...
Read the article
... over centuries or millennia) which may or may not be irreversible on a human time-scale. If we look on a geological time-scale the earth has experienced ice ages about every 100 000 years for the last million years which would best fit with a change in solar radiation caused by the earth’s orbit aro ...
... over centuries or millennia) which may or may not be irreversible on a human time-scale. If we look on a geological time-scale the earth has experienced ice ages about every 100 000 years for the last million years which would best fit with a change in solar radiation caused by the earth’s orbit aro ...
6TH GRADE EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on climate. 8. How are deep ocean currents formed? 9. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on global wind patterns ...
... transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on climate. 8. How are deep ocean currents formed? 9. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on global wind patterns ...
The Effect of Volcanic Eruption on Climate and Global Warming
... large volcanic eruptions has a direct cause on climate change. In particular, by studying the eruption of Huaynaputina, (a famous volcano in Peru that erupted in 1600 AD) we could have an accurate prediction of how a large volcanic eruption would affect the world today and in the future. ...
... large volcanic eruptions has a direct cause on climate change. In particular, by studying the eruption of Huaynaputina, (a famous volcano in Peru that erupted in 1600 AD) we could have an accurate prediction of how a large volcanic eruption would affect the world today and in the future. ...
200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100
... Place the following in order to describe the creation of earth 1.The earth began to cool. 2.Energy heated the new planet to high temperatures 3.Earth’s molten surface hardened ...
... Place the following in order to describe the creation of earth 1.The earth began to cool. 2.Energy heated the new planet to high temperatures 3.Earth’s molten surface hardened ...
File - geography and history 1eso social studies
... Temperatures decrease as we There is less precipitation as LATITUDE move away from the equator. we move further away from the equator. The temperature falls 0.64oC for Precipitation is more Pressure decreases the ALTITUDE every 100 metre increase in frequent the higher the higher the altitude height ...
... Temperatures decrease as we There is less precipitation as LATITUDE move away from the equator. we move further away from the equator. The temperature falls 0.64oC for Precipitation is more Pressure decreases the ALTITUDE every 100 metre increase in frequent the higher the higher the altitude height ...
Earth Science SOL Review Power Point (Oceanography and
... What current affects the climate of the East coast of the United States? _______________ What is an estuary? _________________________________________________________ What local estuary is adjacent to Virginia? _______________________________________ What is the average salinity of seawater? _______ ...
... What current affects the climate of the East coast of the United States? _______________ What is an estuary? _________________________________________________________ What local estuary is adjacent to Virginia? _______________________________________ What is the average salinity of seawater? _______ ...
Notes - Sayre Geography Class
... Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • _______________________. • In other regions that face away from ...
... Why are the days longer in some parts of the year? • The Earth’s axis is at an ___________________. • In about half of the Earth’s orbit, the tilt causes a region to face toward the sun for more hours than it faces away from the sun. • _______________________. • In other regions that face away from ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... which increases the volume of air which reduces its density thus the air raises and causes a circular movement of air called a convection current ...
... which increases the volume of air which reduces its density thus the air raises and causes a circular movement of air called a convection current ...
6TH GRADE EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on climate. 8. How are deep ocean currents formed? 9. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on global wind patterns ...
... transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on climate. 8. How are deep ocean currents formed? 9. What effect does Earth’s rotation have on global wind patterns ...
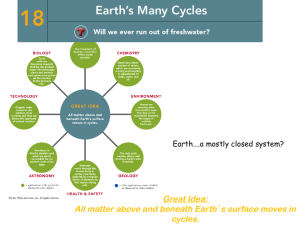
Great Idea: All matter above and beneath Earth`s surface moves in
... When you stop to think about it, our planet does act like a huge organism. If you look at the interrelationship between plants and atmospherics, animals and humans, rocks and water, a complex pattern of symbiotic processes seem to complement each other perfectly. Should one system be pushed out of b ...
... When you stop to think about it, our planet does act like a huge organism. If you look at the interrelationship between plants and atmospherics, animals and humans, rocks and water, a complex pattern of symbiotic processes seem to complement each other perfectly. Should one system be pushed out of b ...
Plate Tectonics and the Changing Earth NO PICS
... However in very cold climates (and higher latitudes) such as the Patagonian Andes, rather than scraping away the surface of the mountain, glaciers protect the mountain top and sides from erosion. As glaciers move, they push about great amounts of debris. When continents are glaciated, they ride Tect ...
... However in very cold climates (and higher latitudes) such as the Patagonian Andes, rather than scraping away the surface of the mountain, glaciers protect the mountain top and sides from erosion. As glaciers move, they push about great amounts of debris. When continents are glaciated, they ride Tect ...
human impact review - Hicksville Public Schools
... 26. The presence of wastes, such as plastic bags and motor oil, in lakes and streams miles away from developed areas suggests that (1) ecosystems are interconnected and human action can alter ecosystem equilibrium (2) recycling programs have failed to conserve biotic resources ...
... 26. The presence of wastes, such as plastic bags and motor oil, in lakes and streams miles away from developed areas suggests that (1) ecosystems are interconnected and human action can alter ecosystem equilibrium (2) recycling programs have failed to conserve biotic resources ...
ESCI 106 – Weather and Climate Lecture 1
... Weather Fact of the Day: August 18 2005: 27 tornadoes were documented in WI, thus establishing its record for the greatest number of tornadoes reported in a calendar day. Most were F0 or F1, but an F3 storm killed 1, and hurt 23 between Fitchburg and ...
... Weather Fact of the Day: August 18 2005: 27 tornadoes were documented in WI, thus establishing its record for the greatest number of tornadoes reported in a calendar day. Most were F0 or F1, but an F3 storm killed 1, and hurt 23 between Fitchburg and ...
Components of the Spheres
... Global Warming causes permafrost to melt which causes the freshwater permafrost supports to sink below the surface ...
... Global Warming causes permafrost to melt which causes the freshwater permafrost supports to sink below the surface ...
How has Earth`s Environment Changed Over Time?
... the gas carbon dioxide, and if you could have looked up at the sky it would have been bright red because scatters red light. Eventually, however, the primitive ocean, still heated from below, began to absorb in huge quantities. A very long time passed before oxygen became a substantial gas in the at ...
... the gas carbon dioxide, and if you could have looked up at the sky it would have been bright red because scatters red light. Eventually, however, the primitive ocean, still heated from below, began to absorb in huge quantities. A very long time passed before oxygen became a substantial gas in the at ...
Name
... do not. 18. Name the different kinds of precipitation. Rain, hail, freezing rain (ice), sleet, snow 19. What is climate? Climate is the average weather in an area over a long period of time. 20. What is the Greenhouse Effect? The greenhouse effect is the rise in temperature that the Earth experience ...
... do not. 18. Name the different kinds of precipitation. Rain, hail, freezing rain (ice), sleet, snow 19. What is climate? Climate is the average weather in an area over a long period of time. 20. What is the Greenhouse Effect? The greenhouse effect is the rise in temperature that the Earth experience ...
GEOG 1101 Physical Geography - Normandale Community College
... their interrelationships, and their global regional distribution. The lab exercises and in-class assignments will help students gain a stronger working knowledge of key concepts and relationships. Furthermore, the course highlights some of the basic interactions between human activity and the natura ...
... their interrelationships, and their global regional distribution. The lab exercises and in-class assignments will help students gain a stronger working knowledge of key concepts and relationships. Furthermore, the course highlights some of the basic interactions between human activity and the natura ...
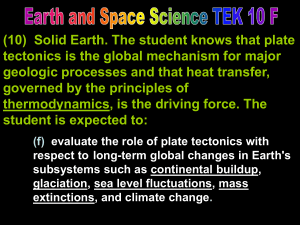
(f) evaluate the role of plate tectonics with respect to long
... However in very cold climates (and higher latitudes) such as the Patagonian Andes, rather than scraping away the surface of the mountain, glaciers protect the mountain top and sides from erosion. As glaciers move, they push about great amounts of debris. When continents are glaciated, they ride Tect ...
... However in very cold climates (and higher latitudes) such as the Patagonian Andes, rather than scraping away the surface of the mountain, glaciers protect the mountain top and sides from erosion. As glaciers move, they push about great amounts of debris. When continents are glaciated, they ride Tect ...
Plate Tectonics and the changing earth ppt
... However in very cold climates (and higher latitudes) such as the Patagonian Andes, rather than scraping away the surface of the mountain, glaciers protect the mountain top and sides from erosion. As glaciers move, they push about great amounts of debris. When continents are glaciated, they ride Tect ...
... However in very cold climates (and higher latitudes) such as the Patagonian Andes, rather than scraping away the surface of the mountain, glaciers protect the mountain top and sides from erosion. As glaciers move, they push about great amounts of debris. When continents are glaciated, they ride Tect ...
History of climate change science

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change the climate. Many other theories of climate change were advanced, involving forces from volcanism to solar variation. In the 1960s, the warming effect of carbon dioxide gas became increasingly convincing, although some scientists also pointed out that human activities, in the form of atmospheric aerosols (e.g., ""pollution""), could have cooling effects as well. During the 1970s, scientific opinion increasingly favored the warming viewpoint. By the 1990s, as a result of improving fidelity of computer models and observational work confirming the Milankovitch theory of the ice ages, a consensus position formed: greenhouse gases were deeply involved in most climate changes, and human emissions were bringing serious global warming.Since the 1990s, scientific research on climate change has included multiple disciplines and has expanded, significantly increasing our understanding of causal relations, links with historic data and ability to numerically model climate change. The most recent work has been summarized in the Assessment Reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions, or in the distribution of weather around the average conditions (i.e., more or fewer extreme weather events). Climate change is caused by factors that include oceanic processes (such as oceanic circulation), biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics and volcanic eruptions, and human-induced alterations of the natural world; these latter effects are currently causing global warming, and ""climate change"" is often used to describe human-specific impacts.