Chemistry 1 HT Warm up - Thomas Tallis Science
... earth’s core release heat... • ...Heat creates a convection current in mantle... • ...which moves the plates ...
... earth’s core release heat... • ...Heat creates a convection current in mantle... • ...which moves the plates ...
Science 7
... be academically achieving a minimum of a 70% overall average in each of his/her classes in order to earn credit in the class. Failure to achieve at least a 70% overall average by the end of each marking period in a class will result in the grade of “N” earned for that class, which equals “No Credit. ...
... be academically achieving a minimum of a 70% overall average in each of his/her classes in order to earn credit in the class. Failure to achieve at least a 70% overall average by the end of each marking period in a class will result in the grade of “N” earned for that class, which equals “No Credit. ...
What is Weather.
... Ions are formed when UV light from the sun knock electrons off of oxygen atoms. These layers reflect radio waves back to earth Each layer can reflect a different frequency. Affected by solar events. Extends toward space. ...
... Ions are formed when UV light from the sun knock electrons off of oxygen atoms. These layers reflect radio waves back to earth Each layer can reflect a different frequency. Affected by solar events. Extends toward space. ...
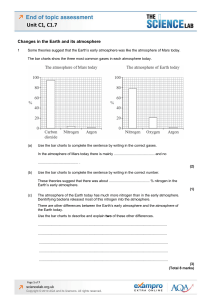
End of topic assessment Unit C1, C1.7
... Life on Earth would not exist without the atmosphere. Billions of years ago the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere was very different from the composition today. ...
... Life on Earth would not exist without the atmosphere. Billions of years ago the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere was very different from the composition today. ...
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY MEDIA ADVISORY AUG. 28, 2009
... places take up carbon dioxide from the air—a basic worldwide process that exerts huge influence on the global carbon cycle, and thus potentially on the course of climate change. In turn, climate change may be alter plant ecology, so it is vital to understand under the rate at which these processes o ...
... places take up carbon dioxide from the air—a basic worldwide process that exerts huge influence on the global carbon cycle, and thus potentially on the course of climate change. In turn, climate change may be alter plant ecology, so it is vital to understand under the rate at which these processes o ...
Climate Connections
... away from the influence of water. Annual temperature range tends to be large and precipitation low. Maritime: Climate type that is strongly influenced by the closeness of an ocean or other large body of water. Annual temperature range tends to be small and precipitation is high. ...
... away from the influence of water. Annual temperature range tends to be large and precipitation low. Maritime: Climate type that is strongly influenced by the closeness of an ocean or other large body of water. Annual temperature range tends to be small and precipitation is high. ...
Layer Depth (km) Rigidity
... •O2 NOT present before life evolved!!! •Photosynthesis can generate O2 •Need carbon- use CO2 from atmos. •Remove the O’s, use the C’s •Build living tissues with C-rich organic matter ...
... •O2 NOT present before life evolved!!! •Photosynthesis can generate O2 •Need carbon- use CO2 from atmos. •Remove the O’s, use the C’s •Build living tissues with C-rich organic matter ...
Venus - Earth`s Evil Twin
... atmosphere traps infrared radiation, powering this process. Long ago the water present early in Venusian history boiled away. Due to the greenhouse effect in its dense atmosphere, Venus' mean surface temperature is about 730 K (900 F). The dense atmosphere insures that the entire surface has about t ...
... atmosphere traps infrared radiation, powering this process. Long ago the water present early in Venusian history boiled away. Due to the greenhouse effect in its dense atmosphere, Venus' mean surface temperature is about 730 K (900 F). The dense atmosphere insures that the entire surface has about t ...
Extreme Earth - Introduction
... Formation of the Earth’s core and crust. The Earth’s atmosphere and the evolution of early life. ...
... Formation of the Earth’s core and crust. The Earth’s atmosphere and the evolution of early life. ...
temperature - MrsFarrell AP Environmental Science
... Land and Water • Land heats and cools quicker and to higher and lower temperatures than water. • Water heats and cools slower than land *Summary- land has greater temperature changes at a faster rate than water! This is why the southern hemisphere (which has more water) has lower temperature range ...
... Land and Water • Land heats and cools quicker and to higher and lower temperatures than water. • Water heats and cools slower than land *Summary- land has greater temperature changes at a faster rate than water! This is why the southern hemisphere (which has more water) has lower temperature range ...
View Syllabus
... Define barometric pressure and explain its relationship to daily weather changes, wind, and global circulation patterns. Discuss, diagram, and contrast cyclones and anticyclones. Discuss the possible major natural and human causes of global climate change. Identify by observation, the major cloud ty ...
... Define barometric pressure and explain its relationship to daily weather changes, wind, and global circulation patterns. Discuss, diagram, and contrast cyclones and anticyclones. Discuss the possible major natural and human causes of global climate change. Identify by observation, the major cloud ty ...
draft-draft-draft - 2017 AGU Fall Meeting
... Other aspects of the Paris Agreement suggest that there could be meaningful developments in specific arenas such as ocean protection. Scripps researchers note that marine ecosystems stand to experience profound impacts even under the most ambitious mitigation scenarios, but that they are at least re ...
... Other aspects of the Paris Agreement suggest that there could be meaningful developments in specific arenas such as ocean protection. Scripps researchers note that marine ecosystems stand to experience profound impacts even under the most ambitious mitigation scenarios, but that they are at least re ...
Sea Level Change and Climate - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... Positive values have more 18O and negative values have less 18O than normal seawater When glaciers form, more 16O is stored in glaciers, and more 18O is stored in the ocean, so when we measure the shells of organisms that make their shells from seawater, + values indicate that it is colder and there ...
... Positive values have more 18O and negative values have less 18O than normal seawater When glaciers form, more 16O is stored in glaciers, and more 18O is stored in the ocean, so when we measure the shells of organisms that make their shells from seawater, + values indicate that it is colder and there ...
AP Chapter 5 Study Guide - Bennatti
... Assimilation- absorption of nitrates, ammonia or ammonium and conversion into plant proteins and nucleic acids Ammonification- the conversion of biological nitrogen compounds into ammonia and ammonium ions. Denitrification- the reduction of nitrate to N2 Hydrologic cycle –water cycle Transpiration- ...
... Assimilation- absorption of nitrates, ammonia or ammonium and conversion into plant proteins and nucleic acids Ammonification- the conversion of biological nitrogen compounds into ammonia and ammonium ions. Denitrification- the reduction of nitrate to N2 Hydrologic cycle –water cycle Transpiration- ...
J.T. Reddick Middle School 6th Grade Earth Science Course
... a. Explain the role of the sun as the major source of energy and its relationship to wind and water energy. Objectives (What are OUR goals, and what will YOU learn in this unit?): 1. Describe weather. 2. Identify and describe the four main factors that influence weather. 3. Explain how the sun influ ...
... a. Explain the role of the sun as the major source of energy and its relationship to wind and water energy. Objectives (What are OUR goals, and what will YOU learn in this unit?): 1. Describe weather. 2. Identify and describe the four main factors that influence weather. 3. Explain how the sun influ ...
Theme 3 Natural Hazards pdf
... Global warming – the rise in average world temperature in 1850, this was 14.0°C. In 2000, it was 14.8°C. There are natural and human causes of global warming. Natural- the climate keeps changing: the earth has been warming up for the last 10 000 years, since the ice age. Human- cutting down trees an ...
... Global warming – the rise in average world temperature in 1850, this was 14.0°C. In 2000, it was 14.8°C. There are natural and human causes of global warming. Natural- the climate keeps changing: the earth has been warming up for the last 10 000 years, since the ice age. Human- cutting down trees an ...
Spheres of the Earth
... • Layers of the Atmosphere are: Ionosphere, Mesosphere, Ozone Layer, Stratosphere, Tropopause, and the Troposphere (from top to bottom) • Functions: protects Earth from radiation from space and the sun’s rays • Protects Earth from rapid cooling at night and heating in the day • Reservoir for carbo ...
... • Layers of the Atmosphere are: Ionosphere, Mesosphere, Ozone Layer, Stratosphere, Tropopause, and the Troposphere (from top to bottom) • Functions: protects Earth from radiation from space and the sun’s rays • Protects Earth from rapid cooling at night and heating in the day • Reservoir for carbo ...
Shrinking mountains (Rocks of the Earth)
... Herman and his team used the thermal ages of rocks – a technique known as thermochronology – to determine past changes in erosion rates. As rocks move away from the heat of the Earth’s core, the minerals begin to cool and change. The scientists used the natural abundance of a mineral’s radioactive i ...
... Herman and his team used the thermal ages of rocks – a technique known as thermochronology – to determine past changes in erosion rates. As rocks move away from the heat of the Earth’s core, the minerals begin to cool and change. The scientists used the natural abundance of a mineral’s radioactive i ...
Global Temperature change Potential compared to Global Warming
... Given that both GWP and GTP are orientated towards providing information for policies, there seems little to be gained and much to be lost by changing from the relatively familiar concept of GWP, which is a specific property of an individual gas and can be used both to rank emissions of individual g ...
... Given that both GWP and GTP are orientated towards providing information for policies, there seems little to be gained and much to be lost by changing from the relatively familiar concept of GWP, which is a specific property of an individual gas and can be used both to rank emissions of individual g ...
Draft 2016 National Research Infrastructure Roadmap
... The vision of Australia’s weather forecasting, atmospheric analysis, earth systems, climate and climate change research communities is to transform the investment-to-date on ACCESS into a national research platform/system that significantly enhances research collaboration, broadens services capabili ...
... The vision of Australia’s weather forecasting, atmospheric analysis, earth systems, climate and climate change research communities is to transform the investment-to-date on ACCESS into a national research platform/system that significantly enhances research collaboration, broadens services capabili ...
Cycle Jeopardy - Western Reserve Public Media
... to the air. These mix with the water vapor in the atmosphere and make it more acidic. True or False ...
... to the air. These mix with the water vapor in the atmosphere and make it more acidic. True or False ...
Tectonic-scale climate change
... superimposed upon, slower changes over longer timescales. Greenhouse gases generated by human activities are expected to affect climate change in the decades and centuries ahead. But the larger-scale tendency towards global cooling and bipolar glaciation that has been driven by plate-tectonic proces ...
... superimposed upon, slower changes over longer timescales. Greenhouse gases generated by human activities are expected to affect climate change in the decades and centuries ahead. But the larger-scale tendency towards global cooling and bipolar glaciation that has been driven by plate-tectonic proces ...
Earth`s Frozen Water
... • As glaciers advance or retreat they affect the environment and leave landmarks. ...
... • As glaciers advance or retreat they affect the environment and leave landmarks. ...
Earth`s Frozen Water
... • As glaciers advance or retreat they affect the environment and leave landmarks. ...
... • As glaciers advance or retreat they affect the environment and leave landmarks. ...
History of climate change science

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change the climate. Many other theories of climate change were advanced, involving forces from volcanism to solar variation. In the 1960s, the warming effect of carbon dioxide gas became increasingly convincing, although some scientists also pointed out that human activities, in the form of atmospheric aerosols (e.g., ""pollution""), could have cooling effects as well. During the 1970s, scientific opinion increasingly favored the warming viewpoint. By the 1990s, as a result of improving fidelity of computer models and observational work confirming the Milankovitch theory of the ice ages, a consensus position formed: greenhouse gases were deeply involved in most climate changes, and human emissions were bringing serious global warming.Since the 1990s, scientific research on climate change has included multiple disciplines and has expanded, significantly increasing our understanding of causal relations, links with historic data and ability to numerically model climate change. The most recent work has been summarized in the Assessment Reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions, or in the distribution of weather around the average conditions (i.e., more or fewer extreme weather events). Climate change is caused by factors that include oceanic processes (such as oceanic circulation), biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics and volcanic eruptions, and human-induced alterations of the natural world; these latter effects are currently causing global warming, and ""climate change"" is often used to describe human-specific impacts.