19 electric potential and electric field
... The electron volt (eV) is the most common energy unit for submicroscopic processes. This will be particularly noticeable in the chapters on modern physics. Energy is so important to so many subjects that there is a tendency to define a special energy unit for each major topic. There are, for example ...
... The electron volt (eV) is the most common energy unit for submicroscopic processes. This will be particularly noticeable in the chapters on modern physics. Energy is so important to so many subjects that there is a tendency to define a special energy unit for each major topic. There are, for example ...
Class XII- Physics - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1
... Why in Millikan’s Oil Drop experiment, the charge measured was always found to be of ...
... Why in Millikan’s Oil Drop experiment, the charge measured was always found to be of ...
B.Sc. (H) PHYSICS THREE-YEAR FULL-TIME PROGRAMME (Six-Semester Course)
... Michelson-Morley Experiment and its Outcome. Postulates of Special Theory of Relativity. Lorentz Transformations. Simultaneity and Order of Events. Lorentz Contraction. Time Dilation. Relativistic Transformation of Velocity, Frequency and Wave Number. Relativistic Addition of Velocities. Variation o ...
... Michelson-Morley Experiment and its Outcome. Postulates of Special Theory of Relativity. Lorentz Transformations. Simultaneity and Order of Events. Lorentz Contraction. Time Dilation. Relativistic Transformation of Velocity, Frequency and Wave Number. Relativistic Addition of Velocities. Variation o ...
Symmetry and magnitude of spin-orbit torques in ferromagnetic
... which mediates the transfer of orbital angular momentum from the lattice to the spin system and do away with the need of a polarizer FM. These mechanisms, which include the spin Hall,28 Rashba,29 and Dresselhaus30 effects, exploit the coupling between electron spin and orbital motion to induce noneq ...
... which mediates the transfer of orbital angular momentum from the lattice to the spin system and do away with the need of a polarizer FM. These mechanisms, which include the spin Hall,28 Rashba,29 and Dresselhaus30 effects, exploit the coupling between electron spin and orbital motion to induce noneq ...
Topic 9_2__Gravitational field, potential and energy
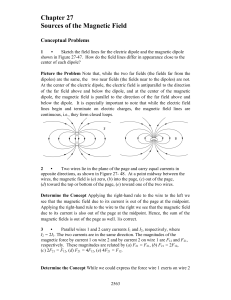
... floor along paths 1 and 2: Clearly the distance along Path 2 is greater than on Path 1 Path 1. The work is different. A Thus its work is not path-independent. Thus it is not conservative. ...
... floor along paths 1 and 2: Clearly the distance along Path 2 is greater than on Path 1 Path 1. The work is different. A Thus its work is not path-independent. Thus it is not conservative. ...
Cassini observations of a Kelvin‐Helmholtz vortex
... comparing the typical magnetic fields measured in the magnetosheath and magnetosphere surrounding the crossings made on each pass. As mentioned in section 1, magnetic tension forces act to stabilize the boundary; thus, the ideal magnetic conditions for the growth of the K‐H instability at Saturn’s m ...
... comparing the typical magnetic fields measured in the magnetosheath and magnetosphere surrounding the crossings made on each pass. As mentioned in section 1, magnetic tension forces act to stabilize the boundary; thus, the ideal magnetic conditions for the growth of the K‐H instability at Saturn’s m ...