A Boundary Element Method with Surface Conductive Absorbers for 3-D Analysis of Nanophotonics
... Fast surface integral equation (SIE) solvers seem to be ideal approaches for simulating 3-D nanophotonic devices, as these devices generate fields both in an interior channel and in the infinite exterior domain. However, many devices of interest, such as optical couplers, have channels that cannot b ...
... Fast surface integral equation (SIE) solvers seem to be ideal approaches for simulating 3-D nanophotonic devices, as these devices generate fields both in an interior channel and in the infinite exterior domain. However, many devices of interest, such as optical couplers, have channels that cannot b ...
I. Course Title Advanced Placement Physics C: Mechanics and
... covering modern physics and optics. Both courses are strongly calculus-based, and are explicitly aimed at those intending to major in engineering or the physical sciences. There is a significant laboratory component to both courses. Students study a mathematically substantial formulation of Newtonia ...
... covering modern physics and optics. Both courses are strongly calculus-based, and are explicitly aimed at those intending to major in engineering or the physical sciences. There is a significant laboratory component to both courses. Students study a mathematically substantial formulation of Newtonia ...
Second Order QED Processes in an Intense
... with the aid of diagrams [Fey48a, Fey48b, Fey49a, Fey49b]. The equivalence of the Schwinger and Feynman reformulations was proved [Dys49]. It is Feynman’s reformulation of QED that will serve as the basis for the theoretical work in this thesis. The problem of the interaction of an external field wi ...
... with the aid of diagrams [Fey48a, Fey48b, Fey49a, Fey49b]. The equivalence of the Schwinger and Feynman reformulations was proved [Dys49]. It is Feynman’s reformulation of QED that will serve as the basis for the theoretical work in this thesis. The problem of the interaction of an external field wi ...
ørsted, ritter and magnetochemistry
... no such effect, and Ritter’s findings were soon discredited. After the discovery of electromagnetism there arose a new wave of positive reports concerning chemical effects of magnetism, but doubts were again cast on those effects. For several decades there was a disagreement between experimental rep ...
... no such effect, and Ritter’s findings were soon discredited. After the discovery of electromagnetism there arose a new wave of positive reports concerning chemical effects of magnetism, but doubts were again cast on those effects. For several decades there was a disagreement between experimental rep ...
BSc (Hons) Physics - SC340 Optional Minor: Biology/Chemistry
... modules in core areas of physics, we also offer a variety of electives in applied and theoretical areas of physics as well as in other optional scientific disciplines. Overall, our programme combines the study of a fundamental discipline with the opportunity to develop skills in experimental and the ...
... modules in core areas of physics, we also offer a variety of electives in applied and theoretical areas of physics as well as in other optional scientific disciplines. Overall, our programme combines the study of a fundamental discipline with the opportunity to develop skills in experimental and the ...
Theory of Polarization: A Modern Approach
... within each individual anion but vanishes on the cell boundary, while in the latter case the current flows throughout the interior of the crystal. Using the examples of piezoelectricity and of permittivity, we have shown that the induced macroscopic polarization in condensed matter can be defined an ...
... within each individual anion but vanishes on the cell boundary, while in the latter case the current flows throughout the interior of the crystal. Using the examples of piezoelectricity and of permittivity, we have shown that the induced macroscopic polarization in condensed matter can be defined an ...
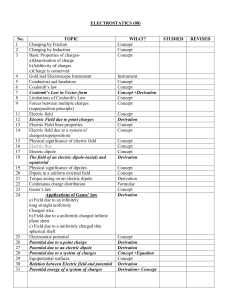
electrostatics (08)
... Coulomb’s Law in Vector form Limitations of Coulomb’s Law Forces between multiple charges (superposition principle) Electric field Electric Field due to point charges Electric Field lines properties Electric field due to a system of charges(superposition) Physical significance of electric field Elec ...
... Coulomb’s Law in Vector form Limitations of Coulomb’s Law Forces between multiple charges (superposition principle) Electric field Electric Field due to point charges Electric Field lines properties Electric field due to a system of charges(superposition) Physical significance of electric field Elec ...
Z - INDIGO @ UIC - University of Illinois at Chicago
... in this thesis. The DRC is not a standard component of any current UEM system other than the UIC system. I developed the concept of the DRC during an attempt to directly measure the duration of the compressed pulses at the temporal focal point. I developed theory which shows that a traveling electro ...
... in this thesis. The DRC is not a standard component of any current UEM system other than the UIC system. I developed the concept of the DRC during an attempt to directly measure the duration of the compressed pulses at the temporal focal point. I developed theory which shows that a traveling electro ...
Hyperfine Structure of Cs2 Molecules in Electronically Excited States
... observed that quantum statistics and tunneling through angular momentum barriers play a crucial role in the reactions of ultracold molecules. When the molecules were prepared in different hyperfine states reaction rates were very high. However, just a tiny modification of the molecular state, namely ...
... observed that quantum statistics and tunneling through angular momentum barriers play a crucial role in the reactions of ultracold molecules. When the molecules were prepared in different hyperfine states reaction rates were very high. However, just a tiny modification of the molecular state, namely ...