Key Concepts Biot- Savart Law
... The line of earth’s magnetic induction lies in a vertical plane coinciding with the magnetic North – South direction at that ...
... The line of earth’s magnetic induction lies in a vertical plane coinciding with the magnetic North – South direction at that ...
Homework III
... square well of dimension a. At t = 0 the extent of the square well is instantaneously doubled by extending one of the walls by a distance a, without disturbing the wavefunction of the object. (a) What is the ratio of probablities of finding the object in the first excited and ground states of the st ...
... square well of dimension a. At t = 0 the extent of the square well is instantaneously doubled by extending one of the walls by a distance a, without disturbing the wavefunction of the object. (a) What is the ratio of probablities of finding the object in the first excited and ground states of the st ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER PHYSICS (042) CLASS-XII – (2012-13)
... Define the terms (i) mass defect (ii) binding energy for a nucleus and state the relation between the two. For a given nuclear reaction the B.E./nucleon of the product nucleus/nuclei is more than that for the original nucleus/nuclei. Is this nuclear reaction exothermic or endothermic in nature? Just ...
... Define the terms (i) mass defect (ii) binding energy for a nucleus and state the relation between the two. For a given nuclear reaction the B.E./nucleon of the product nucleus/nuclei is more than that for the original nucleus/nuclei. Is this nuclear reaction exothermic or endothermic in nature? Just ...
Does the Everyday World Really Obey Quantum Mechanics?
... PB or C = PB + PC + 2ABAC Suppose AC = ±AB, at random. Then average of PB or C is av. of AB AC PB or C = PB + PC + 2ABAC but ABAC = av. of +A2B and -A2B = 0 so PB or C =PB + PC “COMMON SENSE” RESULT, i.e.“as if” each system chose path B or path C WHEN AB AND AC SIMULTANEOUSLY “EXIST”, NEITHER B N ...
... PB or C = PB + PC + 2ABAC Suppose AC = ±AB, at random. Then average of PB or C is av. of AB AC PB or C = PB + PC + 2ABAC but ABAC = av. of +A2B and -A2B = 0 so PB or C =PB + PC “COMMON SENSE” RESULT, i.e.“as if” each system chose path B or path C WHEN AB AND AC SIMULTANEOUSLY “EXIST”, NEITHER B N ...
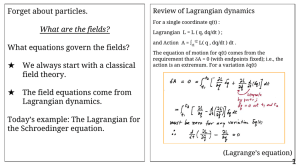
Forget about particles. What equations govern the fields? What are the fields?
... Exercise: Figure out the Lagrangian that would include a 2-body potential. Hint: The Lagrangian must include a term quartic in the field. Exercise: Verify that H is the generator of translation in time, in the quantum theory. ...
... Exercise: Figure out the Lagrangian that would include a 2-body potential. Hint: The Lagrangian must include a term quartic in the field. Exercise: Verify that H is the generator of translation in time, in the quantum theory. ...
Chapter 28
... Gauss’s law for magnetism • Remember, Gauss’s law for electricity showed us that the total electric flux is related to the total enclosed charge. • However, there are no magnetic monopoles, always dipoles. Like in electric dipole case, total flux through a closed surface for a dipole is 0! • For an ...
... Gauss’s law for magnetism • Remember, Gauss’s law for electricity showed us that the total electric flux is related to the total enclosed charge. • However, there are no magnetic monopoles, always dipoles. Like in electric dipole case, total flux through a closed surface for a dipole is 0! • For an ...
AP C Syllabus
... Overview: Mechanics is a calculus-based introduction to the basic principles of the physical description and behavior of macroscopic objects. Topics include but are not limited to: kinematics and dynamics, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, rotational motion, oscillations, and gravita ...
... Overview: Mechanics is a calculus-based introduction to the basic principles of the physical description and behavior of macroscopic objects. Topics include but are not limited to: kinematics and dynamics, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, rotational motion, oscillations, and gravita ...
Magnetism - AP Physics B
... For Every North, There is a South Every magnet has at least one north pole and one south pole. Field lines leave the North end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. No matter ...
... For Every North, There is a South Every magnet has at least one north pole and one south pole. Field lines leave the North end of a magnet and enter the South end of a magnet. If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. No matter ...
Lecture 14 - Purdue Physics
... Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves – Lecture 14 23.1 The Discovery of Electromagnetic Waves 23.2 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 23.3 Electromagnetic Waves Carry Energy and ...
... Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves – Lecture 14 23.1 The Discovery of Electromagnetic Waves 23.2 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 23.3 Electromagnetic Waves Carry Energy and ...
E Field Map
... Repeat the procedure for the 2 dot pattern. This pattern represents positively and negatively charged point charges, an electric dipole. The E field will not be constant between the point charges, so its magnitude is not so easily measured. However it will be constant in a circular pattern around th ...
... Repeat the procedure for the 2 dot pattern. This pattern represents positively and negatively charged point charges, an electric dipole. The E field will not be constant between the point charges, so its magnitude is not so easily measured. However it will be constant in a circular pattern around th ...