Strong-Disorder Fixed Point in the Dissipative Random Transverse-Field Ising Model
... The presence of quenched disorder in a quantum mechanical system may have drastic effects, in particular, close to and at a quantum critical point. The appearance of Griffiths-McCoy singularities [1,2], leading to the divergence of various quantities like the susceptibility at zero temperature even ...
... The presence of quenched disorder in a quantum mechanical system may have drastic effects, in particular, close to and at a quantum critical point. The appearance of Griffiths-McCoy singularities [1,2], leading to the divergence of various quantities like the susceptibility at zero temperature even ...
8-0 8 8
... It is convenient to introduce the area vector A = A nˆ where n̂ is a unit vector in the direction normal to the plane of the loop. The direction of the positive sense of n̂ is set by the conventional right-hand rule. In our case, we have n̂ = +kˆ . The above expression for torque can then be rewritt ...
... It is convenient to introduce the area vector A = A nˆ where n̂ is a unit vector in the direction normal to the plane of the loop. The direction of the positive sense of n̂ is set by the conventional right-hand rule. In our case, we have n̂ = +kˆ . The above expression for torque can then be rewritt ...
PhysChemChemPhys_011..
... versus field curve for BH has in fact a sombrero shape, with minimum at B E ) 0.22 a.u. The field strength defining the energy minimum characterises the transition of the system from closed-shell paramagnetic to closed-shell diamagnetic. This follows from the slope of the energy curve changed by sig ...
... versus field curve for BH has in fact a sombrero shape, with minimum at B E ) 0.22 a.u. The field strength defining the energy minimum characterises the transition of the system from closed-shell paramagnetic to closed-shell diamagnetic. This follows from the slope of the energy curve changed by sig ...
iop-3-2005
... proton annihilation to study gluonic excitations, glueballs and hybrids in the charmonium mass range. The antiproton beam – momentum extending to 15 GeV/c – is incident on a fixed hydrogen target inside a superconducting solenoid, which, together with a forward large acceptance dipole magnet, will f ...
... proton annihilation to study gluonic excitations, glueballs and hybrids in the charmonium mass range. The antiproton beam – momentum extending to 15 GeV/c – is incident on a fixed hydrogen target inside a superconducting solenoid, which, together with a forward large acceptance dipole magnet, will f ...
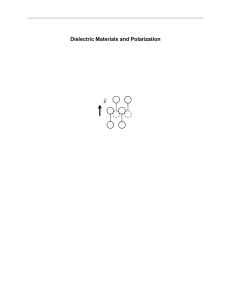
Dielectric Materials and Polarization Chapter 6
... The polarization is defined by the dipole moment per unit volume, so the total dipole moment in the volume d ∆ y ∆ z is: r P D v = d D y D z e o c e E o cos w t e$ x This is equivalent to two charges, each equal to Q = e o c e D y Dz Eo cosw t , separated by distance d . The associated current is: ...
... The polarization is defined by the dipole moment per unit volume, so the total dipole moment in the volume d ∆ y ∆ z is: r P D v = d D y D z e o c e E o cos w t e$ x This is equivalent to two charges, each equal to Q = e o c e D y Dz Eo cosw t , separated by distance d . The associated current is: ...
Electric potential differences across auroral generator interfaces
... magnetic field gradient, the particle will experience the wellknown electric or gradient-B drift parallel to the plane of the TD. While the particle orbits may be much more complicated than helical trajectories around field lines, it is easy to see that the particle will always move in a limited ran ...
... magnetic field gradient, the particle will experience the wellknown electric or gradient-B drift parallel to the plane of the TD. While the particle orbits may be much more complicated than helical trajectories around field lines, it is easy to see that the particle will always move in a limited ran ...
PDF
... the switching time constant, η ≡ (g0M/4ω) and Σ ≡ (i / 2) exp[−i (2ωt + 2φ )] . To lowest order in η, this solution is normalized at all times. Note that if one wants to produce this excitation on an ensemble of atoms using a π /2 pulse and measure the population of the state |1> at a time t=τ so th ...
... the switching time constant, η ≡ (g0M/4ω) and Σ ≡ (i / 2) exp[−i (2ωt + 2φ )] . To lowest order in η, this solution is normalized at all times. Note that if one wants to produce this excitation on an ensemble of atoms using a π /2 pulse and measure the population of the state |1> at a time t=τ so th ...
Field Formulation of Many-Body Quantum Physics {ffmbqp
... As a first step towards developing this powerful theory we shall start from the well-founded Schrödinger theory of nonrelativistic spinless particles. We show that there exists a completely equivalent formulation of this theory in terms of quantum fields. This formulation will serve as a basis for ...
... As a first step towards developing this powerful theory we shall start from the well-founded Schrödinger theory of nonrelativistic spinless particles. We show that there exists a completely equivalent formulation of this theory in terms of quantum fields. This formulation will serve as a basis for ...
________________Table des Matières_______________
... use of this family of compounds in applications has several disadvantages (low Curie temperature, low sensitivity to the applied field, large resistivity..), the importance of manganites is more clear as a model system for several fundamental studies due to the strong coupling between the magnetic, ...
... use of this family of compounds in applications has several disadvantages (low Curie temperature, low sensitivity to the applied field, large resistivity..), the importance of manganites is more clear as a model system for several fundamental studies due to the strong coupling between the magnetic, ...
Physical meaning and derivation of Schrodinger
... Based on first principles we have obtained a transparent and justified dynamical picture. Each eigenfunction of a bound particle is a specific superposition of plane waves that fulfills the averaged energy relation. The Schrodinger and Dirac equations are the conditions that the particle eigenfuncti ...
... Based on first principles we have obtained a transparent and justified dynamical picture. Each eigenfunction of a bound particle is a specific superposition of plane waves that fulfills the averaged energy relation. The Schrodinger and Dirac equations are the conditions that the particle eigenfuncti ...
104 Phys Lecture 1 Dr. M A M El
... This field has an x component dEx = dE Cos along the x axis and a component dE perpendicular to the x axis. As we see in Figure 6-b, however, the resultant field at P must lie along the x axis because the perpendicular components of all the various charge segments sum to zero. That is, the perpen ...
... This field has an x component dEx = dE Cos along the x axis and a component dE perpendicular to the x axis. As we see in Figure 6-b, however, the resultant field at P must lie along the x axis because the perpendicular components of all the various charge segments sum to zero. That is, the perpen ...
Hawking Radiation by Kerr Black Holes and Conformal Symmetry Ivan Agullo,
... existence of an unbounded (exponentially growing) gravitational blueshift that a particle with a given energy at infinity experiences as it approaches the horizon. This blueshift sweeps away any physical scale present in the field theory and makes conformal symmetry arise in a rather natural way. It ...
... existence of an unbounded (exponentially growing) gravitational blueshift that a particle with a given energy at infinity experiences as it approaches the horizon. This blueshift sweeps away any physical scale present in the field theory and makes conformal symmetry arise in a rather natural way. It ...
Atomic processes in antihydrogen experiments: a theoretical and computational perspective TOPICAL REVIEW
... some processes, the magnetic fields enhance the rates while for others the magnetic fields strongly suppress certain processes. The reader will probably note that the majority of the theory and the calculations use classical mechanics to obtain results. Since the positron is light and has low energy ...
... some processes, the magnetic fields enhance the rates while for others the magnetic fields strongly suppress certain processes. The reader will probably note that the majority of the theory and the calculations use classical mechanics to obtain results. Since the positron is light and has low energy ...