ppt
... would be approximately that of a single charge of 2q The bulging out of the field lines between the charges indicates the repulsion between the charges The low field lines between the charges indicates a weak field in this region ...
... would be approximately that of a single charge of 2q The bulging out of the field lines between the charges indicates the repulsion between the charges The low field lines between the charges indicates a weak field in this region ...
Atomic Structure
... The n = 3 state has possible l values 0, 1, or 2. Each l value has ml possible values of (0), (-1, 0, 1), or (-2, -1, 0, 1, 2). The total number of states is then 1 + 3 + 5 = 9. We will see later that there is another quantum number s, for electron spin (±½), so there are actually 18 possible states ...
... The n = 3 state has possible l values 0, 1, or 2. Each l value has ml possible values of (0), (-1, 0, 1), or (-2, -1, 0, 1, 2). The total number of states is then 1 + 3 + 5 = 9. We will see later that there is another quantum number s, for electron spin (±½), so there are actually 18 possible states ...
ElectricPotential
... Recall that the valence electrons in a conductor are free to move, but that in electrostatic equilibrium they have no net velocity. Another consequence of this is that: V = 0 across a conductor If not, electrons would move from higher to lower potential, and thus not be in static equilibrium. This ...
... Recall that the valence electrons in a conductor are free to move, but that in electrostatic equilibrium they have no net velocity. Another consequence of this is that: V = 0 across a conductor If not, electrons would move from higher to lower potential, and thus not be in static equilibrium. This ...
SOLID-STATE PHYSICS 3, Winter 2009 O. Entin-Wohlman
... α hα|O|αi/ α , where E where for any operator O, hOi = α are the eigen αe αe energies of the system Hamiltonian, H0 . Inspecting Eq. (8.17), we see that the first term is the average current in the absence of the field. Obviously, this quantity is zero. The second term includes just the density of t ...
... α hα|O|αi/ α , where E where for any operator O, hOi = α are the eigen αe αe energies of the system Hamiltonian, H0 . Inspecting Eq. (8.17), we see that the first term is the average current in the absence of the field. Obviously, this quantity is zero. The second term includes just the density of t ...
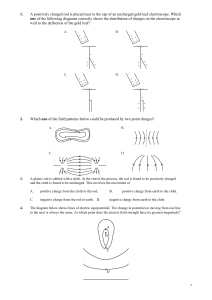
electric field worksheet name
... B) The gravitational force is attractive and the electrostatic force is repulsive. C) The gravitational force is repulsive and the electrostatic force is attractive. D) Both forces are repulsive. 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents two small charged s ...
... B) The gravitational force is attractive and the electrostatic force is repulsive. C) The gravitational force is repulsive and the electrostatic force is attractive. D) Both forces are repulsive. 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents two small charged s ...
tianhu.pdf
... thermoelastic theories. In the context of Lord–Shulman theory, Sherief and Ezzat (1998) investigated a problem of an infinitely long electrically and thermally conducting annular cylinder in generalized magneto-thermoelasticity by Laplace transforms, and the third class thermal boundary condition wa ...
... thermoelastic theories. In the context of Lord–Shulman theory, Sherief and Ezzat (1998) investigated a problem of an infinitely long electrically and thermally conducting annular cylinder in generalized magneto-thermoelasticity by Laplace transforms, and the third class thermal boundary condition wa ...
2_Quantum theory_ techniques and applications
... The use of a barrier to control the flow of electrons from one lead to the other is the basis of transistors. The miniaturization of solid-state devices can’t continue forever. That is, eventually the barriers that are the key to transistor function will be too small to control quantum effects and t ...
... The use of a barrier to control the flow of electrons from one lead to the other is the basis of transistors. The miniaturization of solid-state devices can’t continue forever. That is, eventually the barriers that are the key to transistor function will be too small to control quantum effects and t ...
Electric Potential Work and Potential Energy
... Recall that the valence electrons in a conductor are free to move, but that in electrostatic equilibrium they have no net velocity. Another consequence of this is that: ΔV = 0 across a conductor If not, electrons would move from higher to lower potential, and thus not be in static equilibrium. This ...
... Recall that the valence electrons in a conductor are free to move, but that in electrostatic equilibrium they have no net velocity. Another consequence of this is that: ΔV = 0 across a conductor If not, electrons would move from higher to lower potential, and thus not be in static equilibrium. This ...