Psychological Disorders When is behavior likely to be labeled as
... Avoidant Personality disorder Narcissistic Personality disorder Borderline Personality disorder Antisocial Personality disorder Somatoform disorder What role do obsessive thoughts play in anxiety? What role do compulsive behaviors play in anxiety? Why are some people more vulnerable to PTSD? How doe ...
... Avoidant Personality disorder Narcissistic Personality disorder Borderline Personality disorder Antisocial Personality disorder Somatoform disorder What role do obsessive thoughts play in anxiety? What role do compulsive behaviors play in anxiety? Why are some people more vulnerable to PTSD? How doe ...
Music therapy as a treatment for schizophrenia
... People with schizophrenia or any other nonaffective serious mental disorder, diagnosed by any criteria, irrespective of gender, age or nationality. 8 Studies (483 participants) Some studies more specific with diagnosis- based on 3 psychiatric classification systems primarily used in the wester ...
... People with schizophrenia or any other nonaffective serious mental disorder, diagnosed by any criteria, irrespective of gender, age or nationality. 8 Studies (483 participants) Some studies more specific with diagnosis- based on 3 psychiatric classification systems primarily used in the wester ...
Chapter 25 - Stellenbosch University
... problems as physical symptoms. These symptoms are not always intentionally produced – insight is normally dependent on developmental and intelligence level. Severe stressors or “unacceptable” feelings can cause the child to develop unconsciously physical symptoms that give expression to the underlyi ...
... problems as physical symptoms. These symptoms are not always intentionally produced – insight is normally dependent on developmental and intelligence level. Severe stressors or “unacceptable” feelings can cause the child to develop unconsciously physical symptoms that give expression to the underlyi ...
Overview of Mental Illness PowerPoint
... Overview of Mental Illness Mental illnesses include depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, borderline personality disorder and others. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) is the s ...
... Overview of Mental Illness Mental illnesses include depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, borderline personality disorder and others. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) is the s ...
Psychosis - Santa Barbara Therapist
... • Biology produces schizophrenia, environment determines if it is expressed and how • Is Genetic ...
... • Biology produces schizophrenia, environment determines if it is expressed and how • Is Genetic ...
Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic Disorders
... Recent introduction of schizophrenia (1800s) ↑ in urban areas Prenatal exposure to flu ...
... Recent introduction of schizophrenia (1800s) ↑ in urban areas Prenatal exposure to flu ...
Family History of Mental Illness - Emory University Department of
... Mood disorders include major depressive disorder, dysthymia (a milder, but longer-lasting form of depression), and bipolar disorder. Approximately 20.9 million American adults (9.5% of the U.S. adult population) have a mood disorder. The median age of onset for mood disorders is 30 years. • Depressi ...
... Mood disorders include major depressive disorder, dysthymia (a milder, but longer-lasting form of depression), and bipolar disorder. Approximately 20.9 million American adults (9.5% of the U.S. adult population) have a mood disorder. The median age of onset for mood disorders is 30 years. • Depressi ...
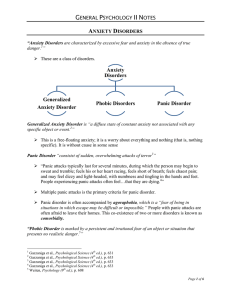
Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... the things that are taken away from one’s life because of the condition), such as aphathy, lack of speech, or social withdrawal. o Some schizophrenic symptoms can be classified as disorganized symptoms (referring erratic/inappropriate thoughts, feelings, and behavior), such as disorganized speech (d ...
... the things that are taken away from one’s life because of the condition), such as aphathy, lack of speech, or social withdrawal. o Some schizophrenic symptoms can be classified as disorganized symptoms (referring erratic/inappropriate thoughts, feelings, and behavior), such as disorganized speech (d ...
2. Personality Disorders
... She plans everything sown to the last detail and becomes very upset if things don’t work out the way she has planned. In the past 9 months Andrew has been fired by three different employers. He was unreliable and often missed work, and each employer finally let him go when they found he had been ste ...
... She plans everything sown to the last detail and becomes very upset if things don’t work out the way she has planned. In the past 9 months Andrew has been fired by three different employers. He was unreliable and often missed work, and each employer finally let him go when they found he had been ste ...
DSM-IV
... Authors highlight the problem of this line of cross-cultural research where Western ethnic groups are seen as homogenous AfA are diagnosed significantly more with Scz than EA and less with depression Satcher (2001) AfAs and Latinos… AfA more likely to receive medication and less likely to be referre ...
... Authors highlight the problem of this line of cross-cultural research where Western ethnic groups are seen as homogenous AfA are diagnosed significantly more with Scz than EA and less with depression Satcher (2001) AfAs and Latinos… AfA more likely to receive medication and less likely to be referre ...
Schizophrenia
... – Schizophrenia. “split mind” – “Breaking of associative threads” – Recognized inability to keep constant stream of thought ...
... – Schizophrenia. “split mind” – “Breaking of associative threads” – Recognized inability to keep constant stream of thought ...
psychology - TeacherWeb
... Dissociative identity disorder (multiple personality) – personal identity – Separate personalities act independently from the others – Rare disorder – Causes: history of very traumatic experiences; childhood abuse – Dominant or stronger personality knows about the weaker, but not the other way aroun ...
... Dissociative identity disorder (multiple personality) – personal identity – Separate personalities act independently from the others – Rare disorder – Causes: history of very traumatic experiences; childhood abuse – Dominant or stronger personality knows about the weaker, but not the other way aroun ...
Chapter 14 Review
... Medical Model- thought that most psychological disorders are biologically based.(like in the nervous system)using the term "sicknesses" is a way to support the medical model of psychological disorders. Biopsychosocial approach- would consider substance abuse as a interactive influence of nature and ...
... Medical Model- thought that most psychological disorders are biologically based.(like in the nervous system)using the term "sicknesses" is a way to support the medical model of psychological disorders. Biopsychosocial approach- would consider substance abuse as a interactive influence of nature and ...
Introduction to Psychology
... the brain that regulate movement; also involved in the experience of pleasure which causes schizophrenics to feel manic or high; malfunctioning dopamine systems are related to the appearance of the movement disorders associated with schizophrenia ...
... the brain that regulate movement; also involved in the experience of pleasure which causes schizophrenics to feel manic or high; malfunctioning dopamine systems are related to the appearance of the movement disorders associated with schizophrenia ...
Question: What is the cause of her psychiatric problems according to
... How do we call the decribed condition? What is the most probable diagnosis? What other diagnoses should we think of? What is the cause of her psychiatric problems according to the patient? • According to you? • The fundamental question of etiology: What causes the disorder? Environmental or genetic ...
... How do we call the decribed condition? What is the most probable diagnosis? What other diagnoses should we think of? What is the cause of her psychiatric problems according to the patient? • According to you? • The fundamental question of etiology: What causes the disorder? Environmental or genetic ...
Part 2 2011
... In the past 9 months Andrew has been fired by three different employers. He was unreliable and often missed work, and each employer finally let him go when they found he had been stealing money and materials. Andrew feels no remorse over his actions, but he has managed to convince each of his former ...
... In the past 9 months Andrew has been fired by three different employers. He was unreliable and often missed work, and each employer finally let him go when they found he had been stealing money and materials. Andrew feels no remorse over his actions, but he has managed to convince each of his former ...
PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS - Eleanor L. Ronquillo MD October 13
... Functional impairment at the time of an episode No decline in social and occupational functioning Schizoaffective Disorder As the term implies, schizoaffective disorder has features of both schizophrenia and affective disorders Delusional Disorder Great variety of false beliefs that can be h ...
... Functional impairment at the time of an episode No decline in social and occupational functioning Schizoaffective Disorder As the term implies, schizoaffective disorder has features of both schizophrenia and affective disorders Delusional Disorder Great variety of false beliefs that can be h ...
disorders and social psych rv sht
... 1. Why are dissociative disorders controversial? Explore the arguments for and against the belief that dissociative disorders are genuine disorders (as opposed to manufactured disorders). 2. How do dissociative disorders relate to the concept of consciousness? Schizophrenia (p. 589-596 in textbook) ...
... 1. Why are dissociative disorders controversial? Explore the arguments for and against the belief that dissociative disorders are genuine disorders (as opposed to manufactured disorders). 2. How do dissociative disorders relate to the concept of consciousness? Schizophrenia (p. 589-596 in textbook) ...
PSC 168 - Psychology
... 4. The concept of "collective unconscious" was developed by: a. Freud b. Jung x c. Sullivan d. Arieti e. Laing 5. The psychiatrist who developed a "social psychiatry" was: a. Freud b. Jung c. Sullivan x d. Arieti e. Laing 6. Which of these individuals most strongly rejected the disease model of ment ...
... 4. The concept of "collective unconscious" was developed by: a. Freud b. Jung x c. Sullivan d. Arieti e. Laing 5. The psychiatrist who developed a "social psychiatry" was: a. Freud b. Jung c. Sullivan x d. Arieti e. Laing 6. Which of these individuals most strongly rejected the disease model of ment ...
Schizophrenia Disorder Diagnostic Tool
... Associated descriptive features and mental disorders: inappropriate affect such as smiling, laughing or a silly facial expression in the absence of an appropriate stimulus anhedonia is common and is manifested by a loss of interest or pleasure dysphoric mood may take the form of depression, anxiety, ...
... Associated descriptive features and mental disorders: inappropriate affect such as smiling, laughing or a silly facial expression in the absence of an appropriate stimulus anhedonia is common and is manifested by a loss of interest or pleasure dysphoric mood may take the form of depression, anxiety, ...
Schizophrenia
... from one's conscious mind, the belief that one's thoughts are being broadcast to other people, hearing hallucinatory voices that comment on one's thoughts ~ see. recent classifications ...
... from one's conscious mind, the belief that one's thoughts are being broadcast to other people, hearing hallucinatory voices that comment on one's thoughts ~ see. recent classifications ...
Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic Disorders
... OTHER SYMPTOMS of insight – lack of awareness that one’s experiences are unusual or abnormal ...
... OTHER SYMPTOMS of insight – lack of awareness that one’s experiences are unusual or abnormal ...
CHS284 Sociocultural Aspects of Mental Health
... • Uses cognitive restructuring: • learning to refute cognitive distortions, such as irrational thinking, • with more accurate and beneficial ones. ...
... • Uses cognitive restructuring: • learning to refute cognitive distortions, such as irrational thinking, • with more accurate and beneficial ones. ...