Physics 169
... A scalar consists of magnitude only (e.g. mass, charge, density) Euclidean vector, a geometric entity endowed with magnitude and direction as well as a positive-definite inner product; an element of a Euclidean vector space! In physics, Euclidean vectors are used to represent physical quantities tha ...
... A scalar consists of magnitude only (e.g. mass, charge, density) Euclidean vector, a geometric entity endowed with magnitude and direction as well as a positive-definite inner product; an element of a Euclidean vector space! In physics, Euclidean vectors are used to represent physical quantities tha ...
Terahertz driven intraband dynamics of excitons in nanorods Fredrik Sy
... electronic properties of quantum dots with the focus being on quantities such as the exciton binding energy, carrier lifetime and band gap of these quantum dots[7]. The exciton Bohr radius is the characteristic length scale of these quantum dots and gives a measure of the average separation of the e ...
... electronic properties of quantum dots with the focus being on quantities such as the exciton binding energy, carrier lifetime and band gap of these quantum dots[7]. The exciton Bohr radius is the characteristic length scale of these quantum dots and gives a measure of the average separation of the e ...
SCANNING TUNNELING SPECTROSCOPY ON ORGANIC MOLECULES A Thesis
... General schematic of the electronics used to control the STM. 1) Communication between the PID feedback program running on the DSP and the control/acquisition program running on an IBM compatible PC. 2,3) Gain and offset signals via the Parallel Port to the Voltage Amplifier. 4) Feedback signals to ...
... General schematic of the electronics used to control the STM. 1) Communication between the PID feedback program running on the DSP and the control/acquisition program running on an IBM compatible PC. 2,3) Gain and offset signals via the Parallel Port to the Voltage Amplifier. 4) Feedback signals to ...
ll ne - Arihant Book
... created equal and opposite charges and total charge is zero, before and after their creation. ...
... created equal and opposite charges and total charge is zero, before and after their creation. ...
Drift velocity and temporal phase fluctuations of sliding charge
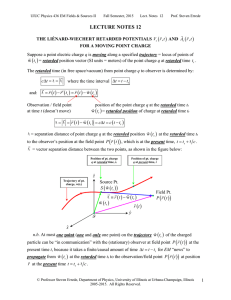
... Applying a constant current through the sample above threshold induces a voltage V (t) fluctuating in time. In NbSe3, in some cases where the CDW current may be homogeneous within the sample V (t ) is nearly periodic and the frequency spectrum V2(v) of the fluctuations of V2(t) consists of a narrow ...
... Applying a constant current through the sample above threshold induces a voltage V (t) fluctuating in time. In NbSe3, in some cases where the CDW current may be homogeneous within the sample V (t ) is nearly periodic and the frequency spectrum V2(v) of the fluctuations of V2(t) consists of a narrow ...
Electric and magnetic fields of a toroidal dipole in
... necessarily an associated axial vector density which should appear on the right-hand side of Eq. (2a). However, this problem may be avoided to a certain extent by assuming that the dipole is observed in a frame where there is only toroidization and it is given by T(x, t) = 7(t) S{x - r(t)}. After an ...
... necessarily an associated axial vector density which should appear on the right-hand side of Eq. (2a). However, this problem may be avoided to a certain extent by assuming that the dipole is observed in a frame where there is only toroidization and it is given by T(x, t) = 7(t) S{x - r(t)}. After an ...
X-ray spectroscopies through damped linear response theory Thomas Fransson
... There are numerous people I would like to acknowledge for making the writing of this thesis possible, or just for making the ride to a Ph.D. much more enjoyable. Let me start by thanking the past and present members of the group of theoretical chemistry (formerly known as computational physics) for ...
... There are numerous people I would like to acknowledge for making the writing of this thesis possible, or just for making the ride to a Ph.D. much more enjoyable. Let me start by thanking the past and present members of the group of theoretical chemistry (formerly known as computational physics) for ...
7p 2P
... The Standard Model (SM) [1–3] is the theoretical framework which provides a consistent description of three of the four known fundamental interactions in nature, namely the electromagnetic, the weak and the strong interactions [4]. The fourth interaction gravity refuses the quantum field theory appr ...
... The Standard Model (SM) [1–3] is the theoretical framework which provides a consistent description of three of the four known fundamental interactions in nature, namely the electromagnetic, the weak and the strong interactions [4]. The fourth interaction gravity refuses the quantum field theory appr ...
Catalysis of Conversion Between the Spin Isomers
... requires that the combined wavefunction of two fermions, such as protons, be antisymmetric. For our purposes here, we are concerned with the spin and rotational components of the wavefunction. Thus a symmetric rotational state requires an antisymmetric spin state, and vice versa. Heisenberg found th ...
... requires that the combined wavefunction of two fermions, such as protons, be antisymmetric. For our purposes here, we are concerned with the spin and rotational components of the wavefunction. Thus a symmetric rotational state requires an antisymmetric spin state, and vice versa. Heisenberg found th ...
Electric Field: Sphere of Uniform Charge
... From these two equation we see that electric forces exerted by two charges on each other are equal in magnitude but are opposite in direction In above equation, we find a positive constant K and experimentally found value of K is K = 8.98755 × 10 9 Nm2/C2 K ≅ 9 × 10 9 Nm2/C2 sometimes K is written a ...
... From these two equation we see that electric forces exerted by two charges on each other are equal in magnitude but are opposite in direction In above equation, we find a positive constant K and experimentally found value of K is K = 8.98755 × 10 9 Nm2/C2 K ≅ 9 × 10 9 Nm2/C2 sometimes K is written a ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.