8.5
... KEY CONCEPT Translation converts an mRNA message into a polypeptide, or protein. Translation is the process that converts an mRNA message into a polypeptide, or protein. An mRNA message is made up of combinations of four nucleotides, whereas proteins are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The m ...
... KEY CONCEPT Translation converts an mRNA message into a polypeptide, or protein. Translation is the process that converts an mRNA message into a polypeptide, or protein. An mRNA message is made up of combinations of four nucleotides, whereas proteins are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The m ...
Document
... Modelling, comparison, and analysis of proteomes Ram Samudrala University of Washington ...
... Modelling, comparison, and analysis of proteomes Ram Samudrala University of Washington ...
SDS-PAGE_overview
... monomer, the rigidity and pore size of the gel can be controlled. The pore size is chosen according to the size of the molecules to be separated. Separation of proteins. Proteins are variable in their chemical nature because of the variety of R groups in the amino acid residues. The charge of a prot ...
... monomer, the rigidity and pore size of the gel can be controlled. The pore size is chosen according to the size of the molecules to be separated. Separation of proteins. Proteins are variable in their chemical nature because of the variety of R groups in the amino acid residues. The charge of a prot ...
Test 2
... Specific acid-base: H3O+ or OH- is part fo the reaction mechanism General acid-base: Functional groups on the protein act as acids or bases in the catalytic mechanism. Can be in Bronstead -Lowry sense (proton donors or acceptors) or in Lewis sense (electron donors or acceptors) Covalent catalysis: A ...
... Specific acid-base: H3O+ or OH- is part fo the reaction mechanism General acid-base: Functional groups on the protein act as acids or bases in the catalytic mechanism. Can be in Bronstead -Lowry sense (proton donors or acceptors) or in Lewis sense (electron donors or acceptors) Covalent catalysis: A ...
Biochemical Processes
... What is another name for enzymes? What do enzymes do? What happens to enzymes during reactions? Can enzymes be used again? How can you recognize an enzyme in a ...
... What is another name for enzymes? What do enzymes do? What happens to enzymes during reactions? Can enzymes be used again? How can you recognize an enzyme in a ...
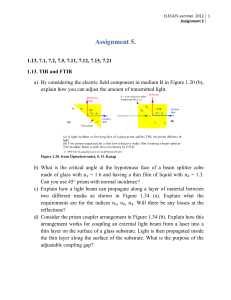
Assignment 5
... we bring prism C close to A, the field in B will reach C and consequently penetrates C. (The tangential field must be continuous from B to C). One cannot just use the field expression for the evanescent wave because this was derived for a light beam incident at an interface between two media only; n ...
... we bring prism C close to A, the field in B will reach C and consequently penetrates C. (The tangential field must be continuous from B to C). One cannot just use the field expression for the evanescent wave because this was derived for a light beam incident at an interface between two media only; n ...
PHYSICS CLASS - XII SAMPLE PAPER BLUE PRINT
... Draw an appropriate ray diagram to show the passage of a ‘white ray’, incident on one of the two refracting faces of a prism. State the relation for the angle of deviation, for a prism of small refracting angle. It is known that the refractive index, , of the material of a prism, depends on the wave ...
... Draw an appropriate ray diagram to show the passage of a ‘white ray’, incident on one of the two refracting faces of a prism. State the relation for the angle of deviation, for a prism of small refracting angle. It is known that the refractive index, , of the material of a prism, depends on the wave ...
Water, Protein, and Nutrients
... Protein chains fold into ___________________________________ Proteins with different shapes ___________________________________ If a protein twists into the wrong shape or has a missing part, ___________________________________. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the code that’s needed to ...
... Protein chains fold into ___________________________________ Proteins with different shapes ___________________________________ If a protein twists into the wrong shape or has a missing part, ___________________________________. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the code that’s needed to ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.