experimentfest 2015 - University of Newcastle
... The cloud chamber, also known as the Wilson chamber, is used for detecting particles of ionising radiation. In its most basic form, a cloud chamber is a sealed environment containing a supercooled, supersaturated alcohol vapour. When an alpha particle or beta particle interacts with the mixture, it ...
... The cloud chamber, also known as the Wilson chamber, is used for detecting particles of ionising radiation. In its most basic form, a cloud chamber is a sealed environment containing a supercooled, supersaturated alcohol vapour. When an alpha particle or beta particle interacts with the mixture, it ...
Poster
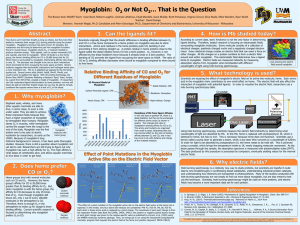
... and understanding how electrons are transported in photosynthesis. Many of the studies conducted with hole burning spectroscopy are not simply to find out more about myoglobin, but are also meant to test out the technique. Someday, hole burning spectroscopy might be used on more proteins, and electr ...
... and understanding how electrons are transported in photosynthesis. Many of the studies conducted with hole burning spectroscopy are not simply to find out more about myoglobin, but are also meant to test out the technique. Someday, hole burning spectroscopy might be used on more proteins, and electr ...
2nd Nutritional Timing Window and BCAA / FFAA
... performance. •SOLs: 11/12.1, 11/12.2, 11/12.3, 11/12.4, 11/12.5 ...
... performance. •SOLs: 11/12.1, 11/12.2, 11/12.3, 11/12.4, 11/12.5 ...
PANEL 3–1 The 20 Amino Acids Found in Proteins THE AMINO
... The α-carbon atom is asymmetric, which allows for two mirror image (or stereo-) isomers, L and D. ...
... The α-carbon atom is asymmetric, which allows for two mirror image (or stereo-) isomers, L and D. ...
PPTX
... • Do we know all participants of the complex? • Do we have (open) sets of participants? • How do we indicate the depth of data available, i.e. compare Reactome import vs. manual curation? ...
... • Do we know all participants of the complex? • Do we have (open) sets of participants? • How do we indicate the depth of data available, i.e. compare Reactome import vs. manual curation? ...
PPT - University of Illinois Urbana
... Depicted graphically by constant magnitude contours or surfaces, and direction lines (or ...
... Depicted graphically by constant magnitude contours or surfaces, and direction lines (or ...
Gennady Jatchevitch, Ph.D
... object with conductive surface. We introduce the concept of the electric field distortion as the deflection of the electric field intensity vector E at each point of the check space due to appearance of the object with conductive surface [1]. We examine four cases: 1. Free space with the uniform ele ...
... object with conductive surface. We introduce the concept of the electric field distortion as the deflection of the electric field intensity vector E at each point of the check space due to appearance of the object with conductive surface [1]. We examine four cases: 1. Free space with the uniform ele ...
Designer materials render objects nearly invisible to
... biological sample, or it can be made sensitive to magnetic fields and function as a field sensor. It is also relatively insensitive to its environment, including temperature and solvent. The displacement of the spring is currently viewed with 2-nm precision by a video camera, but faster and more pre ...
... biological sample, or it can be made sensitive to magnetic fields and function as a field sensor. It is also relatively insensitive to its environment, including temperature and solvent. The displacement of the spring is currently viewed with 2-nm precision by a video camera, but faster and more pre ...
The Electric Field
... this is known as the superpostion principle Question: Given positive charges of charge Q at points r1 = h−1, −1, 0i , r2 = h0, 2, 0i, and r3 = h−2, 0, 0i, and a negative charge of equal magnitude Q at point r4 = h0, 0, 0i, determine the electric field at the point p = h3, 1, 0i. ...
... this is known as the superpostion principle Question: Given positive charges of charge Q at points r1 = h−1, −1, 0i , r2 = h0, 2, 0i, and r3 = h−2, 0, 0i, and a negative charge of equal magnitude Q at point r4 = h0, 0, 0i, determine the electric field at the point p = h3, 1, 0i. ...
Physics 30 Lesson 24 Electromagnetic Waves
... The primary cause of all electromagnetic waves is an accelerating electric charge. As an electric charge oscillates/accelerates, electrical energy will be lost, and an equivalent amount of energy will be radiated outward in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. When the electric ...
... The primary cause of all electromagnetic waves is an accelerating electric charge. As an electric charge oscillates/accelerates, electrical energy will be lost, and an equivalent amount of energy will be radiated outward in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. When the electric ...
PowerPoint
... magnitude but opposite in sign, separated by a fixed distance d. q is the “charge on the dipole.” Earlier, I calculated the electric field along the perpendicular bisector of a dipole (this equation gives the magnitude only). ...
... magnitude but opposite in sign, separated by a fixed distance d. q is the “charge on the dipole.” Earlier, I calculated the electric field along the perpendicular bisector of a dipole (this equation gives the magnitude only). ...
Ion Exchange Chromatography
... molecules based on ionic interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. This type of chromatography is further subdivided into: cation exchange chromatography anion exchange chromatography. Dr Gihan Gawish ...
... molecules based on ionic interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. This type of chromatography is further subdivided into: cation exchange chromatography anion exchange chromatography. Dr Gihan Gawish ...
Lecture 3_Image Theory
... To analyze the performance of an antenna near an infinite plane conductor, virtual sources (images) will be introduced to account for the reflections. As the name implies, these are not real sources but imaginary ones, which when combined with the real sources, form an equivalent system. For analysi ...
... To analyze the performance of an antenna near an infinite plane conductor, virtual sources (images) will be introduced to account for the reflections. As the name implies, these are not real sources but imaginary ones, which when combined with the real sources, form an equivalent system. For analysi ...
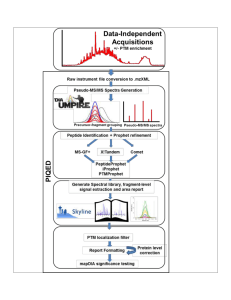
Supplementary Figure 1 Details of PIQED Automated Qualitative
... Examples of high-quality annotated pseudo-MS/MS spectra showing 4/34 phosphorylation sites in Osteopontin identified using PIQED. Osteopontin is overexpressed in a variety of cancers. (A) Annotated spectra for pSer-219 showing the presence of phosphate neutral loss on all y-ions and a prominent fra ...
... Examples of high-quality annotated pseudo-MS/MS spectra showing 4/34 phosphorylation sites in Osteopontin identified using PIQED. Osteopontin is overexpressed in a variety of cancers. (A) Annotated spectra for pSer-219 showing the presence of phosphate neutral loss on all y-ions and a prominent fra ...
Mechanism of Signal Transduction by Rhodopsin as a Model GPCR
... and to determine the critically important sites. These are classified in two categories: ...
... and to determine the critically important sites. These are classified in two categories: ...
Problem 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy : University of
... A solid spherical conductor of radius 15 cm has a charge Q=6.5 nC on it. A second, initially uncharged, spherical conductor of radius 10 cm is moved toward the first until they touch and is then moved far away from it. How much charge is there on the second sphere after the two spheres have been sep ...
... A solid spherical conductor of radius 15 cm has a charge Q=6.5 nC on it. A second, initially uncharged, spherical conductor of radius 10 cm is moved toward the first until they touch and is then moved far away from it. How much charge is there on the second sphere after the two spheres have been sep ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.