Physics 201 Examples
... a journey to the moon. At what point, as measured from the center of the earth, does the gravitational force exerted on the spacecraft by the earth balance that exerted by the moon? This point lies on a line between the centers of the earth and the moon. The distance between the earth and the moon i ...
... a journey to the moon. At what point, as measured from the center of the earth, does the gravitational force exerted on the spacecraft by the earth balance that exerted by the moon? This point lies on a line between the centers of the earth and the moon. The distance between the earth and the moon i ...
force
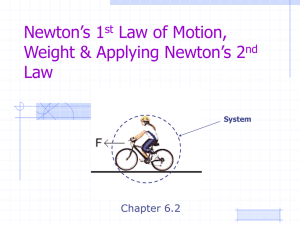
... This object is moving in a circular path at a constant speed. The string is constantly exerting a force on the object At any point in time, there is a net force on the object (no opposite forces) According to Newton’s First Law, the object must be accelerating. How? It is moving at a constant speed. ...
... This object is moving in a circular path at a constant speed. The string is constantly exerting a force on the object At any point in time, there is a net force on the object (no opposite forces) According to Newton’s First Law, the object must be accelerating. How? It is moving at a constant speed. ...
Physics: Forces and Motion
... 2. Gravity is a force of attraction between two objects. The strength of gravitational force depends on the total mass of the two objects and the distance between them. The greater the total mass, the greater the force of gravity. The greater the distance between two objects, the less the force of g ...
... 2. Gravity is a force of attraction between two objects. The strength of gravitational force depends on the total mass of the two objects and the distance between them. The greater the total mass, the greater the force of gravity. The greater the distance between two objects, the less the force of g ...
Third Grade Science
... • Describe our solar system as a collection of nine planets, moons, and numerous other objects (such as asteroids and comets) with the sun at its center • State that the force of gravity keeps the planets in orbit around the sun • Name the planets in our solar system in order starting with the pl ...
... • Describe our solar system as a collection of nine planets, moons, and numerous other objects (such as asteroids and comets) with the sun at its center • State that the force of gravity keeps the planets in orbit around the sun • Name the planets in our solar system in order starting with the pl ...
The Development Of Astronomy
... or what Aristotle referred to as the “earthly realm”, is composed of air, water, fire, and earth, whereas the rest of the universe, or what Aristotle referred to as the “heavenly realm”, is made of fifth element called quintessence (also referred to as aether). 2. The motion (dynamics) of an object ...
... or what Aristotle referred to as the “earthly realm”, is composed of air, water, fire, and earth, whereas the rest of the universe, or what Aristotle referred to as the “heavenly realm”, is made of fifth element called quintessence (also referred to as aether). 2. The motion (dynamics) of an object ...
Gravity Reading - Northwest ISD Moodle
... an invisible force called gravity. Gravity is the force in the universe that attracts all objects to each other. 2 Gravity has existed since the beginning of the universe. It holds everything in the universe in place. We know it is always there. It is hard to understand how it works. First, you nee ...
... an invisible force called gravity. Gravity is the force in the universe that attracts all objects to each other. 2 Gravity has existed since the beginning of the universe. It holds everything in the universe in place. We know it is always there. It is hard to understand how it works. First, you nee ...
Forces
... • For two objects of the same size, the more mass an object has, the more inertia it has. ...
... • For two objects of the same size, the more mass an object has, the more inertia it has. ...
Teacher Resource Pack Unit Planning Resources
... much younger than our sun. Most of them apparently are not an isolated single star as our sun is but are part of systems of two or more stars orbiting around a common center of mass. So too there are other galaxies and clusters of galaxies different from our own in size, shape, and direction of moti ...
... much younger than our sun. Most of them apparently are not an isolated single star as our sun is but are part of systems of two or more stars orbiting around a common center of mass. So too there are other galaxies and clusters of galaxies different from our own in size, shape, and direction of moti ...
the earth in space - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... B. The movements of planets across the nighttime sky is not uniform 1. The reason planets have non-uniform motion is that they really are moving in space - stars only look like they’re moving 2. Planets rotate while they revolve a. we know this because features on the planets surface vary in a predi ...
... B. The movements of planets across the nighttime sky is not uniform 1. The reason planets have non-uniform motion is that they really are moving in space - stars only look like they’re moving 2. Planets rotate while they revolve a. we know this because features on the planets surface vary in a predi ...
Magnetic Fields - Coventry Local Schools
... about finding someone really cute and adorable. It's like the Earth pulling on you and keeping you on the ground. That pull is gravity at work. Every object in the universe that has mass exerts a gravitational pull, or force, on every other mass. The size of the pull depends on the masses of the obj ...
... about finding someone really cute and adorable. It's like the Earth pulling on you and keeping you on the ground. That pull is gravity at work. Every object in the universe that has mass exerts a gravitational pull, or force, on every other mass. The size of the pull depends on the masses of the obj ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... Choose your coordinate system in a clever way: Define one axis along the direction where you expect an object to start moving, the other axis perpendicular to it (these are not necessarily the horizontal and vertical direction. ...
... Choose your coordinate system in a clever way: Define one axis along the direction where you expect an object to start moving, the other axis perpendicular to it (these are not necessarily the horizontal and vertical direction. ...
Universal Law of Gravitation
... Newton based much of his theory on the work of Johannes Kepler, which was based on the astronomical observations of Tycho Brahe. Newton concluded that in order for the planets to proceed in their orbits around the sun there must be a force attracting them towards the sun. Kepler writings could be su ...
... Newton based much of his theory on the work of Johannes Kepler, which was based on the astronomical observations of Tycho Brahe. Newton concluded that in order for the planets to proceed in their orbits around the sun there must be a force attracting them towards the sun. Kepler writings could be su ...
Habitats Jr. 04
... Do you ever wonder how the Earth is different from the Moon? For starters there is no liquid water on the Moon, only ice. Another difference between the Earth and the Moon is that there is a lower amount of gravity on the Moon. Also, the wide range of temperatures on the Moon are so extreme that you ...
... Do you ever wonder how the Earth is different from the Moon? For starters there is no liquid water on the Moon, only ice. Another difference between the Earth and the Moon is that there is a lower amount of gravity on the Moon. Also, the wide range of temperatures on the Moon are so extreme that you ...
9.2.3 Gravity in Space
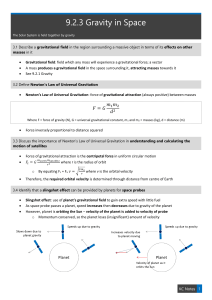
... Various variations in gravitational acceleration is due to: o Altitude: Further away, less gravity (mountains, valleys, satellites) o Local crust density: more dense, more gravity o Oblation/shape: greater radius at equator than poles The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity ...
... Various variations in gravitational acceleration is due to: o Altitude: Further away, less gravity (mountains, valleys, satellites) o Local crust density: more dense, more gravity o Oblation/shape: greater radius at equator than poles The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity ...
Our Universe SPA-4101
... Topics covered include an introduc5on to the history of the subject (da5ng back to ancient greek astronomers), the Sun, Solar System bodies (planets, satellites/ moons, asteroids, comets, Kuiper belt), extrasolar ...
... Topics covered include an introduc5on to the history of the subject (da5ng back to ancient greek astronomers), the Sun, Solar System bodies (planets, satellites/ moons, asteroids, comets, Kuiper belt), extrasolar ...
a force
... Because the gravitational force decreases with (distance)2, the attractive force experienced by one object (e.g., the Earth) due to the gravitational field of a second object (e.g., the Moon) varies with position (closest parts attracted most strongly). ...
... Because the gravitational force decreases with (distance)2, the attractive force experienced by one object (e.g., the Earth) due to the gravitational field of a second object (e.g., the Moon) varies with position (closest parts attracted most strongly). ...
Chapter 12 - AJRomanello
... We all know the earth is round, but why is it round? Universal Gravitation! Since everything is attracted to everything else, the earth “pulled itself together” before it became solid. Any “corners” have been pulled in so that earth (and most other celestial objects) are basically spheres. This also ...
... We all know the earth is round, but why is it round? Universal Gravitation! Since everything is attracted to everything else, the earth “pulled itself together” before it became solid. Any “corners” have been pulled in so that earth (and most other celestial objects) are basically spheres. This also ...
celestial clock - the sun, the moon, and the stars
... ecliptic, it would take 36 years for the Vernal Equinox to transit the moon. Looking at it another way, it takes 72 years for the Vernal Equinox to move 1 degree. If three score and ten are the years of man, it takes about one lifetime or generation of man for the Vernal Equinox to move 1 degree. Th ...
... ecliptic, it would take 36 years for the Vernal Equinox to transit the moon. Looking at it another way, it takes 72 years for the Vernal Equinox to move 1 degree. If three score and ten are the years of man, it takes about one lifetime or generation of man for the Vernal Equinox to move 1 degree. Th ...
Lecture2
... How can the Sun and Moon have the same angular size (30´)? A) The Sun and the Moon are the same size ✪ B)The Sun is much larger than the moon, but is also much farther away ...
... How can the Sun and Moon have the same angular size (30´)? A) The Sun and the Moon are the same size ✪ B)The Sun is much larger than the moon, but is also much farther away ...
Final Exam from 2004 - Onondaga Community College
... A. The force of gravity around a star never vanishes no matter how far away you are. B. The force of gravity is an attractive force between any two objects with mass. C. The force of gravity is usually attractive, but under special conditions and be repulsive as in escape velocity situations. D. The ...
... A. The force of gravity around a star never vanishes no matter how far away you are. B. The force of gravity is an attractive force between any two objects with mass. C. The force of gravity is usually attractive, but under special conditions and be repulsive as in escape velocity situations. D. The ...
HW attached
... more gravity it has. But, when analyzing the effects of gravity, distance also matters. The closer objects are to each other, the greater their gravitational force of attraction. As they get farther apart, the force between them becomes weaker. Even though the Sun is much more massive than Earth, th ...
... more gravity it has. But, when analyzing the effects of gravity, distance also matters. The closer objects are to each other, the greater their gravitational force of attraction. As they get farther apart, the force between them becomes weaker. Even though the Sun is much more massive than Earth, th ...
Basic Observations of the Night Sky
... • The Earth 'wobbles' like a top; this is known as precession. • It takes 26,000 years for the Earth to make one complete cycle – This means that Polaris was not always, nor will it remain, the North Star ...
... • The Earth 'wobbles' like a top; this is known as precession. • It takes 26,000 years for the Earth to make one complete cycle – This means that Polaris was not always, nor will it remain, the North Star ...
Lecture 5
... Earth and it says that your weight is W. What will the same scale say your weight is on the surface of the ...
... Earth and it says that your weight is W. What will the same scale say your weight is on the surface of the ...
History of Astronomy
... • An 8 arc-minute discrepancy (about 13% of one degree) led him eventually to ellipses. • Developed 3 “laws” of orbits ...
... • An 8 arc-minute discrepancy (about 13% of one degree) led him eventually to ellipses. • Developed 3 “laws” of orbits ...