المحاضرة الثالثة Circular Motion
... a- V=squar root(2*R*g) where R :radius of the planet g :the gravitational acceleration at its surface b- A car with a mass 2500kg moving with velocity 2ookm/hr ,a break force applied on it to stop after 5 sec find The acceleration The distance traveled before it stopa ...
... a- V=squar root(2*R*g) where R :radius of the planet g :the gravitational acceleration at its surface b- A car with a mass 2500kg moving with velocity 2ookm/hr ,a break force applied on it to stop after 5 sec find The acceleration The distance traveled before it stopa ...
Rotation Lecture Notes B
... example a person swinging a ball on the end of a string. If you have ever done this yourself, you know that you feel a force pulling outward on your hand. This misconception arises when this pull is interpreted as an outward "centrifugal" force pulling on the ball that is transmitted along the strin ...
... example a person swinging a ball on the end of a string. If you have ever done this yourself, you know that you feel a force pulling outward on your hand. This misconception arises when this pull is interpreted as an outward "centrifugal" force pulling on the ball that is transmitted along the strin ...
Amusement Park Ride Project
... angular acceleration of -1.5 rad/s2 until it topples. If the top will topple at an angular speed of 150 rad/s or less, and the top toppled after spinning for 45 seconds, what was the initial angular velocity of the top? ...
... angular acceleration of -1.5 rad/s2 until it topples. If the top will topple at an angular speed of 150 rad/s or less, and the top toppled after spinning for 45 seconds, what was the initial angular velocity of the top? ...
Chapter 18 Test Review
... • Magnetic force: The force that pushes magnets apart or pulls them together. • Motion: object’s change in position relative to a reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
... • Magnetic force: The force that pushes magnets apart or pulls them together. • Motion: object’s change in position relative to a reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
Gravity-centripetal acceleration
... during their travel. This type of motion is called angular motion. A special case of angular motion is circular motion (when things travel around in circles). We know that velocity and acceleration are both vectors. Recall that vectors have both magnitude and direction. Change either one and you hav ...
... during their travel. This type of motion is called angular motion. A special case of angular motion is circular motion (when things travel around in circles). We know that velocity and acceleration are both vectors. Recall that vectors have both magnitude and direction. Change either one and you hav ...
Vector Worksheet: Solutions
... d)The magnitude of the force required to push a pumpkin off an abandoned overpass. Scalar e)The acceleration of said pumpkin. Vector ...
... d)The magnitude of the force required to push a pumpkin off an abandoned overpass. Scalar e)The acceleration of said pumpkin. Vector ...
South Pasadena
... CENTRIPETAL means “center seeking so centripetal acceleration is directed toward the center of a circle in which an object is moving in uniform circular motion. V V0 Let’s see WHY it is directed towards the center. ...
... CENTRIPETAL means “center seeking so centripetal acceleration is directed toward the center of a circle in which an object is moving in uniform circular motion. V V0 Let’s see WHY it is directed towards the center. ...
South Pasadena - cloudfront.net
... CENTRIPETAL means “center seeking so centripetal acceleration is directed toward the center of a circle in which an object is moving in uniform circular motion. V V0 Let’s see WHY it is directed towards the center. ...
... CENTRIPETAL means “center seeking so centripetal acceleration is directed toward the center of a circle in which an object is moving in uniform circular motion. V V0 Let’s see WHY it is directed towards the center. ...
Name - forehandspace
... d. Processes by which the human body makes proteins. e. Figments of your imagination. 5) What is the acceleration due to gravity on earth? ...
... d. Processes by which the human body makes proteins. e. Figments of your imagination. 5) What is the acceleration due to gravity on earth? ...
centripetal acceleration/force
... Gravitational Force Between People •Calculate the gravitational force between you and your neighbor. Assume your masses are 100 kg and the distance between you is 50 cm. Compare this to the gravitational force between you and the Earth. ...
... Gravitational Force Between People •Calculate the gravitational force between you and your neighbor. Assume your masses are 100 kg and the distance between you is 50 cm. Compare this to the gravitational force between you and the Earth. ...
Circular Motion
... Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3→A4 and using back to back on the photocopier. We know that angles can be measured in degrees. They can also be measured in something called Radians*, where ...
... Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3→A4 and using back to back on the photocopier. We know that angles can be measured in degrees. They can also be measured in something called Radians*, where ...
Document
... Ex: Two blocks are connected over a frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the system given no friction. m1=2kg ...
... Ex: Two blocks are connected over a frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the system given no friction. m1=2kg ...
Lecture powerpoint
... going in a circular path (or part of one) the ideas in this chapter will apply. ...
... going in a circular path (or part of one) the ideas in this chapter will apply. ...
Quiz 1 Force and Vectors Static Equilibrium Problem Solving
... become models for thinking about new problems. ...
... become models for thinking about new problems. ...
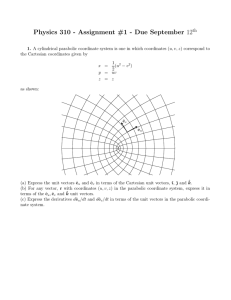
Physics 310 - Assignment #1 - Due September 12
... 2. Find a solution for the motion of an object of mass m with initial velocity v0 , moving through a fluid that produces both linear and quadratic fiscous drag, that is, find x(t) when the only forces acting on the object are Fdrag = −c1 v − c2 v|v|. Consider separately the two cases when the initi ...
... 2. Find a solution for the motion of an object of mass m with initial velocity v0 , moving through a fluid that produces both linear and quadratic fiscous drag, that is, find x(t) when the only forces acting on the object are Fdrag = −c1 v − c2 v|v|. Consider separately the two cases when the initi ...