P3 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – Medical
... What is the equation for working out potential difference across a transformer? ...
... What is the equation for working out potential difference across a transformer? ...
KINEMATICS PROBLEMS: NEWTON`S LAWS
... 14. A tennis player strikes a tennis ball of mass 56.7 g when it is at the top of the toss, accelerating it to 68.0 m/s in a distance of 0.0250 m. What is the average force the player exerts on the ball? Ignore any other forces acting on the ball. ...
... 14. A tennis player strikes a tennis ball of mass 56.7 g when it is at the top of the toss, accelerating it to 68.0 m/s in a distance of 0.0250 m. What is the average force the player exerts on the ball? Ignore any other forces acting on the ball. ...
Notes in pdf format
... direction) mean there is acceleration. This particular acceleration is called “centripetal acceleration” because is points toward the centre of the circle. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration ac depends on the speed v of the object and the radius r of the circular path. As always, accelera ...
... direction) mean there is acceleration. This particular acceleration is called “centripetal acceleration” because is points toward the centre of the circle. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration ac depends on the speed v of the object and the radius r of the circular path. As always, accelera ...
Newton`s Laws Slides
... massless rope. The boy pulls on the rope with a force of FG and continues to exert the force until they meet. The girl holds on to her end of the rope at all times. a) With what force does the girl pull on the boy? b) What is the acceleration of the girl compared to the boy? c) How far does the boy ...
... massless rope. The boy pulls on the rope with a force of FG and continues to exert the force until they meet. The girl holds on to her end of the rope at all times. a) With what force does the girl pull on the boy? b) What is the acceleration of the girl compared to the boy? c) How far does the boy ...
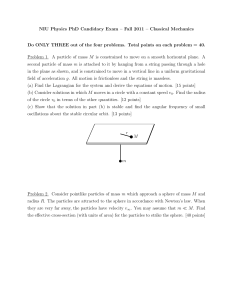
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam – Fall 2011 – Classical
... Problem 1. A particle of mass M is constrained to move on a smooth horizontal plane. A second particle of mass m is attached to it by hanging from a string passing through a hole in the plane as shown, and is constrained to move in a vertical line in a uniform gravitational field of acceleration g. ...
... Problem 1. A particle of mass M is constrained to move on a smooth horizontal plane. A second particle of mass m is attached to it by hanging from a string passing through a hole in the plane as shown, and is constrained to move in a vertical line in a uniform gravitational field of acceleration g. ...
1. Consider the free-body diagram for a person in the “Rotor
... The lines of action of the gravitational and normal forces both pass through the center of the ball (center of mass), and thus exert no torque about its center. The frictional force exerted by the table is much smaller than the collision force of the cue stick, so its effects during the collision ca ...
... The lines of action of the gravitational and normal forces both pass through the center of the ball (center of mass), and thus exert no torque about its center. The frictional force exerted by the table is much smaller than the collision force of the cue stick, so its effects during the collision ca ...
app_A (WP)
... velocity vector is always perpendicular to the position vector R, as shown on Fig. A.4. The change in the velocity vector ∆v is perpendicular to the velocity vector, as can be seen from Fig. A.5. Hence, the acceleration vector, which is proportional to the change in the velocity vector, must lie alo ...
... velocity vector is always perpendicular to the position vector R, as shown on Fig. A.4. The change in the velocity vector ∆v is perpendicular to the velocity vector, as can be seen from Fig. A.5. Hence, the acceleration vector, which is proportional to the change in the velocity vector, must lie alo ...
Unit 2 Study Guide Answer Key
... direction, you find the net force by adding the forces together. If two or more forces are acting on an object in opposite directions, you find the net force by subtracting the forces. The object will move in the direction of the greater force. ...
... direction, you find the net force by adding the forces together. If two or more forces are acting on an object in opposite directions, you find the net force by subtracting the forces. The object will move in the direction of the greater force. ...
Dynamics
... 4. Frictional Force - produced when one surface moves over another; acts in a direction resisting motion. 5. Gravitation Force produced by attraction of any two objects, acts downward on Earth ...
... 4. Frictional Force - produced when one surface moves over another; acts in a direction resisting motion. 5. Gravitation Force produced by attraction of any two objects, acts downward on Earth ...
Review PowerPoint
... The radius of Mars is approximately onehalf the radius of Earth, and the mass of Mars is approximately one-tenth the mass of Earth. Compared to the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth, the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is ...
... The radius of Mars is approximately onehalf the radius of Earth, and the mass of Mars is approximately one-tenth the mass of Earth. Compared to the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth, the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is ...
Line integrals - Binus Repository
... In general, the line integral will depend on the path that is taken There are special physical cases (conservative fields) for which the line integral is independent of path. ...
... In general, the line integral will depend on the path that is taken There are special physical cases (conservative fields) for which the line integral is independent of path. ...
Chapter 4 question 4 - leo physics website
... All objects on the Earth are performing circular motion, i.e. the net forces of all objects are non-zero. The net force (also called centripetal force) is the difference between gravitational pull and the force of support. In the case of a spring balance hanging a mass, the force of support (namely, ...
... All objects on the Earth are performing circular motion, i.e. the net forces of all objects are non-zero. The net force (also called centripetal force) is the difference between gravitational pull and the force of support. In the case of a spring balance hanging a mass, the force of support (namely, ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... net force. If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
... net force. If the net force is zero, an object at rest will stay at rest. If an object is acted upon by unbalanced forces, its motion will change. ...
Acceleration of a Cart
... to which it is raised. The tension on the string at the bottom of the trajectory depends on the mass of the object and velocity of the object. The extra tension beyond the weight of the object is due to the circular motion of the object. ...
... to which it is raised. The tension on the string at the bottom of the trajectory depends on the mass of the object and velocity of the object. The extra tension beyond the weight of the object is due to the circular motion of the object. ...