Force Practice Problems Name: Per: ______ Answer the following
... a. Which exerts the larger force; the bug on the car or the car on the bug? How come? b. Which experiences a larger acceleration; the bug or the car? How come? 2. A 450.kg mass is accelerated at 2.50m/s2. a. What is the net force causing this acceleration? b. If the mass of the car is doubled, what ...
... a. Which exerts the larger force; the bug on the car or the car on the bug? How come? b. Which experiences a larger acceleration; the bug or the car? How come? 2. A 450.kg mass is accelerated at 2.50m/s2. a. What is the net force causing this acceleration? b. If the mass of the car is doubled, what ...
Word Format
... Example 1: Calculate the work done by the 5.0 N force as the block is moved 5 m up an inclined plane with 40 degree inclination as shown below: ...
... Example 1: Calculate the work done by the 5.0 N force as the block is moved 5 m up an inclined plane with 40 degree inclination as shown below: ...
Unit 1
... • Mass is described by the amount of matter an object contains. • This is different from weight – weight requires gravity or some other force to exist! • Ex: while swimming, your weight may feel less because the body floats a little. Your mass, however, stays the same! • Inertia is simply the tenden ...
... • Mass is described by the amount of matter an object contains. • This is different from weight – weight requires gravity or some other force to exist! • Ex: while swimming, your weight may feel less because the body floats a little. Your mass, however, stays the same! • Inertia is simply the tenden ...
Sample problems for final exam
... 7. In the previous problem (Problem 6), the time for the object to hit the ground A) depends on v only B) depends on v and h C) depends on v, h and m D) depends on h only E) depends on m only 8. For the same problem (Problem 6), calculate the horizontal distance which the object will travel before h ...
... 7. In the previous problem (Problem 6), the time for the object to hit the ground A) depends on v only B) depends on v and h C) depends on v, h and m D) depends on h only E) depends on m only 8. For the same problem (Problem 6), calculate the horizontal distance which the object will travel before h ...
Physics I - Rose
... 4.10. Solve: (a) This problem calls for an estimate so we are looking for an approximate answer. Table 4.3 gives us no information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of ...
... 4.10. Solve: (a) This problem calls for an estimate so we are looking for an approximate answer. Table 4.3 gives us no information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of ...
Mechanics Aide Memoire
... Potential energy (P.E.) – mass x acceleration x height Kinetic energy (K.E.) - ½ x mass x (velocity) 2 Elastic Potential Energy (E.P.E) - ½ x spring constant x (extension) 2 N.B. spring constant, k = modulus, λ / natural length, l λ measured in N; k measured in Nm-1 ...
... Potential energy (P.E.) – mass x acceleration x height Kinetic energy (K.E.) - ½ x mass x (velocity) 2 Elastic Potential Energy (E.P.E) - ½ x spring constant x (extension) 2 N.B. spring constant, k = modulus, λ / natural length, l λ measured in N; k measured in Nm-1 ...
Newtons laws
... Mass is directly related to inertia. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to resist change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing with out friction. ...
... Mass is directly related to inertia. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to resist change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing with out friction. ...
CTNewtonLaws
... bronze hemispheres together and removed the air from the resulting sphere with a pump. Two eight-horse teams could not pull the spheres apart, even though the hemispheres fell apart when air was re-admitted. Suppose von Güricke had tied both teams of horses to one side and bolted the other side to a ...
... bronze hemispheres together and removed the air from the resulting sphere with a pump. Two eight-horse teams could not pull the spheres apart, even though the hemispheres fell apart when air was re-admitted. Suppose von Güricke had tied both teams of horses to one side and bolted the other side to a ...
Physics Unit Review
... What is a reference point (also called frame of reference)? An object that appears to stay in place A change in position relative to a reference point is known as _motion___________. Write the formula for speed. D/t What is the average speed of a jet plane that flies 7200 km in 9 hours? 800 km/hr Ho ...
... What is a reference point (also called frame of reference)? An object that appears to stay in place A change in position relative to a reference point is known as _motion___________. Write the formula for speed. D/t What is the average speed of a jet plane that flies 7200 km in 9 hours? 800 km/hr Ho ...
Physical Science Worksheet: Force Short Answer 1. The SI unit of
... 1. The SI unit of force, named for the scientist who described the relationship between motion and force, is called the 2. Earth pulls on the moon and holds the moon in its orbit. The moon pulls on Earth with an equal and opposite force. This is an example of 3. What is the unbalanced force that slo ...
... 1. The SI unit of force, named for the scientist who described the relationship between motion and force, is called the 2. Earth pulls on the moon and holds the moon in its orbit. The moon pulls on Earth with an equal and opposite force. This is an example of 3. What is the unbalanced force that slo ...
PHY820 Homework Set 5
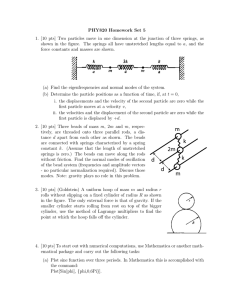
... 2. [10 pts] Three beads of mass m, 2m and m, respectively, are threaded onto three parallel rods, a distance d apart from each other as shown. The beads are connected with springs characterized by a spring constant k. (Assume that the length of unstretched springs is zero.) The beads can move along ...
... 2. [10 pts] Three beads of mass m, 2m and m, respectively, are threaded onto three parallel rods, a distance d apart from each other as shown. The beads are connected with springs characterized by a spring constant k. (Assume that the length of unstretched springs is zero.) The beads can move along ...
NOTE
... compressed by 5.00 cm and has a force constant of 8.00 N/rn. When the cannon is fired, the ball moves 15.0 cm through the horizontal barrel of the cannon and the barrel exerts a constant force of 0.0320 N on the ball. a) With what speed does the ball leave the barrel of the cannon b) At what point a ...
... compressed by 5.00 cm and has a force constant of 8.00 N/rn. When the cannon is fired, the ball moves 15.0 cm through the horizontal barrel of the cannon and the barrel exerts a constant force of 0.0320 N on the ball. a) With what speed does the ball leave the barrel of the cannon b) At what point a ...
Newton`s First Law
... • Definition: An object in motion stays in motion, or an object at rest stays at rest until an unbalanced net force acts on it. • Under these conditions the first law says that if an object is not pushed or pulled upon, its velocity will naturally remain constant. This means that if an object is mov ...
... • Definition: An object in motion stays in motion, or an object at rest stays at rest until an unbalanced net force acts on it. • Under these conditions the first law says that if an object is not pushed or pulled upon, its velocity will naturally remain constant. This means that if an object is mov ...
Force - VCC Library
... Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform velocity in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by the application of some resultant external force. In other words, there can be no acceleration (speed up, slow down, change directions) without a force. Second Law The a ...
... Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform velocity in a straight line unless it is compelled to change that state by the application of some resultant external force. In other words, there can be no acceleration (speed up, slow down, change directions) without a force. Second Law The a ...
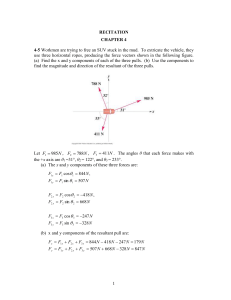
Recitation Ch 4-1
... horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction force between the floor and the bottom crate and a different friction force between the ...
... horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction force between the floor and the bottom crate and a different friction force between the ...
AP-C Physics
... (A) 2Wcos (B) ½Wcos (C) Wcos (D) W/(2cos) (E) W/cos 12. A 2.0–kg cart is given a shove up a long, smooth 30° incline. If the cart is traveling 8.0 m/s after the shove, how much time elapses until the cart returns to its initial position? A. 1.6 s B. 3.2 s C. 4.0 s D. 6.0 s E. 8.0 s 13. A car sl ...
... (A) 2Wcos (B) ½Wcos (C) Wcos (D) W/(2cos) (E) W/cos 12. A 2.0–kg cart is given a shove up a long, smooth 30° incline. If the cart is traveling 8.0 m/s after the shove, how much time elapses until the cart returns to its initial position? A. 1.6 s B. 3.2 s C. 4.0 s D. 6.0 s E. 8.0 s 13. A car sl ...