Level 3 Physics (90521) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... At all points the tension force has to provide the centripetal force required to keep the bag moving in a circle and balance a component of the force of gravity. At the equilibrium point, the tension is greatest because the speed is greatest and the gravity component is the full gravity force. At th ...
... At all points the tension force has to provide the centripetal force required to keep the bag moving in a circle and balance a component of the force of gravity. At the equilibrium point, the tension is greatest because the speed is greatest and the gravity component is the full gravity force. At th ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 2
... Example 4: What is the maximum acceleration for the 2-kg mass in the previous problem? (A = 12 cm, k = 400 N/m) The maximum acceleration occurs when the restoring force is a maximum; i.e., when the stretch or compression of the spring is largest. F = ma = -kx ...
... Example 4: What is the maximum acceleration for the 2-kg mass in the previous problem? (A = 12 cm, k = 400 N/m) The maximum acceleration occurs when the restoring force is a maximum; i.e., when the stretch or compression of the spring is largest. F = ma = -kx ...
First Semester Final Practice
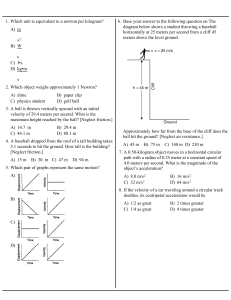
... 3. In the process of delivering mail, a postal worker walks 161 m, due east from his truck. He then turns around and walks 194 m, due west. What is the worker’s displacement relative to his truck? ...
... 3. In the process of delivering mail, a postal worker walks 161 m, due east from his truck. He then turns around and walks 194 m, due west. What is the worker’s displacement relative to his truck? ...
EXAM3
... 13. The block shown is released from rest when the spring is stretched a distance d. If k = 50 N/m, m = 0.50 kg, d = 10 cm, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is equal to 0.25, determine the speed of the block when it first passes through the positi ...
... 13. The block shown is released from rest when the spring is stretched a distance d. If k = 50 N/m, m = 0.50 kg, d = 10 cm, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is equal to 0.25, determine the speed of the block when it first passes through the positi ...
Part V
... Wheel, radius R, mass M, moment of inertia I. A cord is wrapped around it & attached to mass m. System is released & m falls & wheel rotates. Find the tension T in the cord, acceleration a of falling m, angular acceleration α of wheel. ...
... Wheel, radius R, mass M, moment of inertia I. A cord is wrapped around it & attached to mass m. System is released & m falls & wheel rotates. Find the tension T in the cord, acceleration a of falling m, angular acceleration α of wheel. ...
PowerPoint
... • This Law basically says no cause is needed for an object to move. – Uniform (constant) motion is an object’s natural state Translation from original Latin: “Every body perseveres in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right (straight) line, unless it is compelled to change that state by f ...
... • This Law basically says no cause is needed for an object to move. – Uniform (constant) motion is an object’s natural state Translation from original Latin: “Every body perseveres in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right (straight) line, unless it is compelled to change that state by f ...
mass
... Newton’s first law of motion An object moves at constant velocity unless a net force acts to change its speed or direction. Object at rest: Won’t move unless a force acts on it Object moving at constant velocity in straight line: Won’t deflect or change velocity unless a force acts on it ...
... Newton’s first law of motion An object moves at constant velocity unless a net force acts to change its speed or direction. Object at rest: Won’t move unless a force acts on it Object moving at constant velocity in straight line: Won’t deflect or change velocity unless a force acts on it ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Push both of your hand together with the same force. The force is equal in size and opposite in direction, therefore there is no motion. ...
... Push both of your hand together with the same force. The force is equal in size and opposite in direction, therefore there is no motion. ...
Physics 131 Review Translational Kinematics: Position ( ): location relative to an origin
... acceleration in the x-direction, the velocity in that direction is constant. • At any given height, the speed of the ball is the same. Forces Newton's Laws: 1st: An object in motion or an object at rest will remain in motion or at rest if no net force acts on the object. 2nd: Net force is related t ...
... acceleration in the x-direction, the velocity in that direction is constant. • At any given height, the speed of the ball is the same. Forces Newton's Laws: 1st: An object in motion or an object at rest will remain in motion or at rest if no net force acts on the object. 2nd: Net force is related t ...
F=ma Worksheet
... If we know the mass of an object in kilograms, and we know the acceleration that an object experiences then we can calculate the force exerted on that object by multiplying the _______________ x _____________. 1. An unbalanced force of 25 N in an Easterly direction is applied to a 12 kg mass. What w ...
... If we know the mass of an object in kilograms, and we know the acceleration that an object experiences then we can calculate the force exerted on that object by multiplying the _______________ x _____________. 1. An unbalanced force of 25 N in an Easterly direction is applied to a 12 kg mass. What w ...
Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion - Garnet Valley School District
... • We define forces pointing left or down as _____________ • To get Fnet: • Add all parallel forces and subtract off antiparallel forces ...
... • We define forces pointing left or down as _____________ • To get Fnet: • Add all parallel forces and subtract off antiparallel forces ...
Name______________ _________Date____________ General
... 26. Explain the physics behind padded dashboards. Padded dashboards increases contact time thus decrease force. 27. A 500-kg car moves at 5 m/s in 2 seconds. Determine the momentum of the car? ...
... 26. Explain the physics behind padded dashboards. Padded dashboards increases contact time thus decrease force. 27. A 500-kg car moves at 5 m/s in 2 seconds. Determine the momentum of the car? ...
reviewmt1
... through a distance d along the direction of the force, an amount of WORK Fd is done by the first object on the second and an amount of energy Fd is transferred from the first object to the second. Newton’s third law says that when one object exerts a force F on a second object, then the second objec ...
... through a distance d along the direction of the force, an amount of WORK Fd is done by the first object on the second and an amount of energy Fd is transferred from the first object to the second. Newton’s third law says that when one object exerts a force F on a second object, then the second objec ...
KEYPhysics SP09 Inv-7 ExpanIV (WP)
... 5.) The force due to gravity is the same on all objects near the surface of the earth. The FORCE due to gravity is mass times the acceleration due to gravity (g), so objects with different masses have different forces due to gravity. If the statement said that the ACCELERATION due to gravity was abo ...
... 5.) The force due to gravity is the same on all objects near the surface of the earth. The FORCE due to gravity is mass times the acceleration due to gravity (g), so objects with different masses have different forces due to gravity. If the statement said that the ACCELERATION due to gravity was abo ...