6 2,5,7 3,8,12,16,37,45,52,58, J6
... not do work on an object, because if an object is moving in a curved path, by definition the direction towards the center of curvature is always perpendicular to the direction of motion. For a force to do work, the force must have a component in the direction of displacement. So the centripetal forc ...
... not do work on an object, because if an object is moving in a curved path, by definition the direction towards the center of curvature is always perpendicular to the direction of motion. For a force to do work, the force must have a component in the direction of displacement. So the centripetal forc ...
Document
... Both teams pull on the rope with equal strength they each exert the same magnitude of force on it, but in opposite directions. ...
... Both teams pull on the rope with equal strength they each exert the same magnitude of force on it, but in opposite directions. ...
Fall Final Review
... vector force Newton’s 3rd Law displacement vs distance friction free body diagrams velocity vs speed inertia inversely proportional acceleration net force directly proportional free fall mass impulse momentum weight work / energy / power air resistance Newton’s 1st Law action/reaction force pairs Sh ...
... vector force Newton’s 3rd Law displacement vs distance friction free body diagrams velocity vs speed inertia inversely proportional acceleration net force directly proportional free fall mass impulse momentum weight work / energy / power air resistance Newton’s 1st Law action/reaction force pairs Sh ...
File
... ____ 12. A hammer drives a nail into a piece of wood. Identify an action-reaction pair, and compare the forces exerted by each object. a. The nail exerts a force on the hammer; the hammer exerts a force on the wood. b. The hammer exerts a force on the nail; the wood exerts a force on the nail. c. Th ...
... ____ 12. A hammer drives a nail into a piece of wood. Identify an action-reaction pair, and compare the forces exerted by each object. a. The nail exerts a force on the hammer; the hammer exerts a force on the wood. b. The hammer exerts a force on the nail; the wood exerts a force on the nail. c. Th ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... Yes, because net force is now 50 Newtons. A friend helps push with an additional 150 N. By how much does acceleration increase? Net force is now 150+150-100= 200 N. This is FOUR times larger so acceleration increases by a factor of four. ...
... Yes, because net force is now 50 Newtons. A friend helps push with an additional 150 N. By how much does acceleration increase? Net force is now 150+150-100= 200 N. This is FOUR times larger so acceleration increases by a factor of four. ...
Sample Test Questions
... 1. [2] Identical projectiles are fired with the same speed from the same height above flat level ground in two different ways: One is fired horizontally. The other is fired at an angle below horizontal. If air resistance is negligible, how does the speed of impact with the ground compare for the tw ...
... 1. [2] Identical projectiles are fired with the same speed from the same height above flat level ground in two different ways: One is fired horizontally. The other is fired at an angle below horizontal. If air resistance is negligible, how does the speed of impact with the ground compare for the tw ...
Work - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... ball of mass 45.9g if it starts at rest and attains a final velocity of 35m/s? 2. If the golf ball in problem 1 was in contact with the golf club for 0.027s, what force acted on the golf ball? 3. What is the change in momentum of a car as it accelerates from 15m/s to 25m/s if the car as a mass 950kg ...
... ball of mass 45.9g if it starts at rest and attains a final velocity of 35m/s? 2. If the golf ball in problem 1 was in contact with the golf club for 0.027s, what force acted on the golf ball? 3. What is the change in momentum of a car as it accelerates from 15m/s to 25m/s if the car as a mass 950kg ...
Force and Newtons Laws
... • What is the force required to push a 25kg girl in a 100kg wagon with an acceleration of 3m/s2? ...
... • What is the force required to push a 25kg girl in a 100kg wagon with an acceleration of 3m/s2? ...
U3 WKS 4 Name___________________Pd
... C. What is the meaning of the slope of a weight vs. mass graph? What are the units of this slope? D. What is the meaning of the slope of a velocity vs. time graph? What are the units? E. For an object in free fall, how does the acceleration on the way up compare to the acceleration on the way down? ...
... C. What is the meaning of the slope of a weight vs. mass graph? What are the units of this slope? D. What is the meaning of the slope of a velocity vs. time graph? What are the units? E. For an object in free fall, how does the acceleration on the way up compare to the acceleration on the way down? ...
Introduction Worksheet 1
... A 45 kg cart is pushed up a ramp a length of 5.8 m from rest, attaining a speed of 2.6 m/s at the top of the ramp, which is 1.7 m high. The coefficient of friction between the cart and the ramp is 0.13. a) Determine the work done against: 5.8 m i) gravity. ii) inertia. iii) friction. b) What force w ...
... A 45 kg cart is pushed up a ramp a length of 5.8 m from rest, attaining a speed of 2.6 m/s at the top of the ramp, which is 1.7 m high. The coefficient of friction between the cart and the ramp is 0.13. a) Determine the work done against: 5.8 m i) gravity. ii) inertia. iii) friction. b) What force w ...
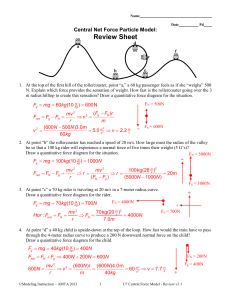
Central Net Force Particle Model:
... 2. At point “b” the rollercoaster has reached a speed of 28 m/s. How large must the radius of the valley be so that a 100 kg rider will experience a normal force of five times their weight (5 G’s)? Draw a quantitative force diagram for the situation. FN = 5000N N Fg mg 100kg(10 kg ) 1000N ...
... 2. At point “b” the rollercoaster has reached a speed of 28 m/s. How large must the radius of the valley be so that a 100 kg rider will experience a normal force of five times their weight (5 G’s)? Draw a quantitative force diagram for the situation. FN = 5000N N Fg mg 100kg(10 kg ) 1000N ...
Document
... magnitude and direction of the displacement (∆ x)? (b) if started to move from X1= 5m toward X2= 1m what is the magnitude and direction of the displacement (∆ x)? Answer of (a) is: The displacement (∆ x) = x2 – x1= 12 - 5= +7m The magnitude is 7 m and +ve result indicates that the motion is in the + ...
... magnitude and direction of the displacement (∆ x)? (b) if started to move from X1= 5m toward X2= 1m what is the magnitude and direction of the displacement (∆ x)? Answer of (a) is: The displacement (∆ x) = x2 – x1= 12 - 5= +7m The magnitude is 7 m and +ve result indicates that the motion is in the + ...
motion - Images
... • Suppose you pull a 10kg sled so that the net force on the sled is 5N. What is the acceleration of the sled? A = 5N ÷ 10kg = 0.5m/s2 • You throw a baseball with a mass of 10kg so it has an acceleration of 40m/s2. How much force did you exert on the baseball? Answer: 400N • Making a connection: Expl ...
... • Suppose you pull a 10kg sled so that the net force on the sled is 5N. What is the acceleration of the sled? A = 5N ÷ 10kg = 0.5m/s2 • You throw a baseball with a mass of 10kg so it has an acceleration of 40m/s2. How much force did you exert on the baseball? Answer: 400N • Making a connection: Expl ...
TEST
... 43. A child’s toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The earth pulls downward on the toy with its weight force of 8 N. If this is the "action force", what is the "reaction force"? A. The string pulling upward on the toy with an 8 N force B. The ceiling pulls upward on the string wit ...
... 43. A child’s toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The earth pulls downward on the toy with its weight force of 8 N. If this is the "action force", what is the "reaction force"? A. The string pulling upward on the toy with an 8 N force B. The ceiling pulls upward on the string wit ...
here - Physics at PMB
... we start measuring these properties. The Cartesian coordinate system may be considered as a frame of reference where its origin is a reference point and the x-, y-, and z-axes are the directions the object may take. In this section we will consider the motion of objects in one direction (i.e. one di ...
... we start measuring these properties. The Cartesian coordinate system may be considered as a frame of reference where its origin is a reference point and the x-, y-, and z-axes are the directions the object may take. In this section we will consider the motion of objects in one direction (i.e. one di ...