Chapter 3 Fluid dynamics
... If an object moves at constant velocity in viscous fluid, there is a layer of fluid on the surface of the object. There is internal friction between fluid-layer of object and other fluid layers. If the object is a sphere (ball), its resistant force is given by F = 6 v r0 ...
... If an object moves at constant velocity in viscous fluid, there is a layer of fluid on the surface of the object. There is internal friction between fluid-layer of object and other fluid layers. If the object is a sphere (ball), its resistant force is given by F = 6 v r0 ...
Halliday 9th chapter 9
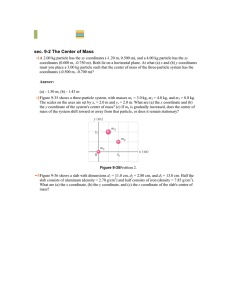
... 0.500 m, 0 m); the block has mass m2 = 0.400 kg, and its center is initially at xy coordinates (0, 0.100 m). The mass of the cord and pulley are negligible. The cart is released from rest, and both cart and block move until the cart hits the pulley. The friction between the cart and the air track a ...
... 0.500 m, 0 m); the block has mass m2 = 0.400 kg, and its center is initially at xy coordinates (0, 0.100 m). The mass of the cord and pulley are negligible. The cart is released from rest, and both cart and block move until the cart hits the pulley. The friction between the cart and the air track a ...
Preview Sample 2
... 20) A package falls off a truck that is moving at 30 m/s. Neglecting air resistance, the horizontal speed of the package just before it hits the ground is A) zero. B) less than 30 m/s but more than zero. C) about 30 m/s. D) more than 30 m/s. Answer: C Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's First Law 21) If your a ...
... 20) A package falls off a truck that is moving at 30 m/s. Neglecting air resistance, the horizontal speed of the package just before it hits the ground is A) zero. B) less than 30 m/s but more than zero. C) about 30 m/s. D) more than 30 m/s. Answer: C Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's First Law 21) If your a ...
Exam 1
... d. L is negative and M is positive e. L is positive and M is negative 7. Two small charged objects attract each other with a force F when separated by a distance d. If the charge on each object is reduced to one-fourth of its original value and the distance between them is reduced to d/2 the force b ...
... d. L is negative and M is positive e. L is positive and M is negative 7. Two small charged objects attract each other with a force F when separated by a distance d. If the charge on each object is reduced to one-fourth of its original value and the distance between them is reduced to d/2 the force b ...
Force - Montville.net
... Objects can speed up, slow down, and change direction while they move. In short, they accelerate. A famous scientist, Sir Isaac Newton, wondered how and why this occurs. Theories about acceleration existed, but Newton did not find them very convincing. His skepticism led him to some of the most impo ...
... Objects can speed up, slow down, and change direction while they move. In short, they accelerate. A famous scientist, Sir Isaac Newton, wondered how and why this occurs. Theories about acceleration existed, but Newton did not find them very convincing. His skepticism led him to some of the most impo ...
Advanced Classical Mechanics Lecture Notes
... sign ambiguity is a nuisance. But in passing to polar coordinates x = ρ cos ϕ, y = ρ sin ϕ, we see that the constraint is simply ρ = R, and ϕ gives a perfectly natural and unambiguous description of the particle’s location. Thus in this situation it would be nice to use ϕ and ϕ̇ as coordinate and ve ...
... sign ambiguity is a nuisance. But in passing to polar coordinates x = ρ cos ϕ, y = ρ sin ϕ, we see that the constraint is simply ρ = R, and ϕ gives a perfectly natural and unambiguous description of the particle’s location. Thus in this situation it would be nice to use ϕ and ϕ̇ as coordinate and ve ...
Chapter 18 Practice
... 18.5.3. Two objects, A with charge +Q and B with charge +4Q, are separated by a distance r. The magnitude of the force exerted on the second object by the first is F. If the first object is moved to a distance 2r from the second object, what is the magnitude of the electric force on the second objec ...
... 18.5.3. Two objects, A with charge +Q and B with charge +4Q, are separated by a distance r. The magnitude of the force exerted on the second object by the first is F. If the first object is moved to a distance 2r from the second object, what is the magnitude of the electric force on the second objec ...
Homework Problems
... textbook. The newspapers continue to compare our system unfavorably to Japanese and European education, where depth is emphasized over breadth, but we can’t seem to create a physics textbook that covers a manageable number of topics for a one-year course and gives honest explanations of everything i ...
... textbook. The newspapers continue to compare our system unfavorably to Japanese and European education, where depth is emphasized over breadth, but we can’t seem to create a physics textbook that covers a manageable number of topics for a one-year course and gives honest explanations of everything i ...
here.
... reproduces Newton’s equation. We denote coordinates by q rather than x to emphasize they need not be Cartesian coordinates. Let us briefly describe how Lagrange’s equations arise. • We consider the problem of determining the classical trajectory that a particle must take if it was at qi at ti and q ...
... reproduces Newton’s equation. We denote coordinates by q rather than x to emphasize they need not be Cartesian coordinates. Let us briefly describe how Lagrange’s equations arise. • We consider the problem of determining the classical trajectory that a particle must take if it was at qi at ti and q ...
Simple Machines
... as the sails of a ship. Pulleys can be fixed to an immovable object or they can be freely floating. Simple machines work with forces. The input force is the force applied to the machine. The input force is the same as the effort force. The output force is the force the machine applies to the load li ...
... as the sails of a ship. Pulleys can be fixed to an immovable object or they can be freely floating. Simple machines work with forces. The input force is the force applied to the machine. The input force is the same as the effort force. The output force is the force the machine applies to the load li ...
Chapter 6: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 3. In question 2, what is your displacement? 4. Why is turning a form of acceleration? 5. Think Critically When you ride in a train that passes a train moving in the opposite direction, the other train appears to rush past you at a speed greater than if you were watching from a parked car at a cross ...
... 3. In question 2, what is your displacement? 4. Why is turning a form of acceleration? 5. Think Critically When you ride in a train that passes a train moving in the opposite direction, the other train appears to rush past you at a speed greater than if you were watching from a parked car at a cross ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... For motion with period = T and angular frequency = w = 2p/T: ...
... For motion with period = T and angular frequency = w = 2p/T: ...
magnetostatic (cont`d)
... • The line integral of H around the path is termed the circulation of H. • To solve for H in given symmetrical current distribution, it is important to make a careful selection of an Amperian Path (analogous to ...
... • The line integral of H around the path is termed the circulation of H. • To solve for H in given symmetrical current distribution, it is important to make a careful selection of an Amperian Path (analogous to ...
The direction of the magnetic field B at any location
... If a magnetic force is exerted on a single charged particle when the particle moves through a magnetic field, it should not surprise you that a current-carrying wire also experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. the current is a collection of many charged particles in motion; hence, the ...
... If a magnetic force is exerted on a single charged particle when the particle moves through a magnetic field, it should not surprise you that a current-carrying wire also experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. the current is a collection of many charged particles in motion; hence, the ...
classroom curling: exploring Forces and motion
... by an external force. The only way to move something that is still is to apply a force, to push or pull it. Likewise, the only way to stop an object that is in motion is to apply a force, to push or pull in the opposite direction of the motion. At this grade level it is not necessary for students to ...
... by an external force. The only way to move something that is still is to apply a force, to push or pull it. Likewise, the only way to stop an object that is in motion is to apply a force, to push or pull in the opposite direction of the motion. At this grade level it is not necessary for students to ...