Unit 3Question Booklet Student
... Questions 40 to 43 refer to the following information: A car collides with a low brick wall and comes to rest. A poorly secured parcel becomes detached from the roof of the car. It initially is travelling horizontally and it strikes the ground a distance of 12 m from the point where it left the car. ...
... Questions 40 to 43 refer to the following information: A car collides with a low brick wall and comes to rest. A poorly secured parcel becomes detached from the roof of the car. It initially is travelling horizontally and it strikes the ground a distance of 12 m from the point where it left the car. ...
OBJECTIVE 5 - Motion, Forces, and Energy
... on moon (mass remains constant) > Earth’s gravitational acceleration = 9.8 m/s Weight: measures the force of gravity on an object; measured in Newtons. Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity *Mass vs. weight: http://www.cstephenmurray.com/onlinequizes/physics/forces/MassVsWeight.htm Inertia: th ...
... on moon (mass remains constant) > Earth’s gravitational acceleration = 9.8 m/s Weight: measures the force of gravity on an object; measured in Newtons. Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity *Mass vs. weight: http://www.cstephenmurray.com/onlinequizes/physics/forces/MassVsWeight.htm Inertia: th ...
Lecture 1. Newton`s Laws
... A mass m at rest is dropped from a height H above the ground at time t = 0; what happens to the mass as a function of time? 1. You must select a coordinate system to use to describe what happens. 2. You must write Newton’s Second Law in the coordinate system for all masses, being sure to include all ...
... A mass m at rest is dropped from a height H above the ground at time t = 0; what happens to the mass as a function of time? 1. You must select a coordinate system to use to describe what happens. 2. You must write Newton’s Second Law in the coordinate system for all masses, being sure to include all ...
Companion Classroom Activities for
... part of Explore is the “debriefing” of students or student teams, discussing what results they all obtained in a particular activity. The Explore phase is not the time to explain concepts or provide background material. That might be what one does in more traditional teaching, but not in the learnin ...
... part of Explore is the “debriefing” of students or student teams, discussing what results they all obtained in a particular activity. The Explore phase is not the time to explain concepts or provide background material. That might be what one does in more traditional teaching, but not in the learnin ...
Momentum Conservation
... the freight car on the left is shared with the freight car on the right. ...
... the freight car on the left is shared with the freight car on the right. ...
Ch 14 slides
... object subject to a force that is proportional to the object's displacement. One example of SHM is the motion of a mass attached to a spring. In this case, the relationship between the spring force and the displacement is given by Hooke's Law, F = -kx, where k is the spring constant, x is the displa ...
... object subject to a force that is proportional to the object's displacement. One example of SHM is the motion of a mass attached to a spring. In this case, the relationship between the spring force and the displacement is given by Hooke's Law, F = -kx, where k is the spring constant, x is the displa ...
Forces - U of M Physics
... string. The picture below is similar to the situation with which you will work. The objects A and C, which have the same mass (m), allow you to determine the force exerted on the central object by the string. You do need to make some assumptions about what you can neglect. For this investigation, yo ...
... string. The picture below is similar to the situation with which you will work. The objects A and C, which have the same mass (m), allow you to determine the force exerted on the central object by the string. You do need to make some assumptions about what you can neglect. For this investigation, yo ...
Halliday 9th chapter 9
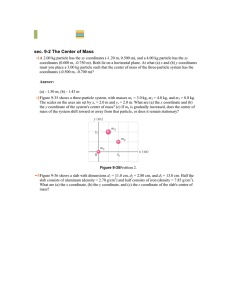
... 0.500 m, 0 m); the block has mass m2 = 0.400 kg, and its center is initially at xy coordinates (0, 0.100 m). The mass of the cord and pulley are negligible. The cart is released from rest, and both cart and block move until the cart hits the pulley. The friction between the cart and the air track a ...
... 0.500 m, 0 m); the block has mass m2 = 0.400 kg, and its center is initially at xy coordinates (0, 0.100 m). The mass of the cord and pulley are negligible. The cart is released from rest, and both cart and block move until the cart hits the pulley. The friction between the cart and the air track a ...